As AI technology advances, how confident are consumers in distinguishing between real and AI images, and does their confidence match their performance? Building on previous studies from 2023 and 2024, Conjointly examines these questions alongside evolving consumer attitudes towards AI-generated marketing content.
Have you noticed that brands have been using fewer AI-generated images lately? Or has AI image quality advanced to the point where you can’t tell if an image is AI-generated or not?
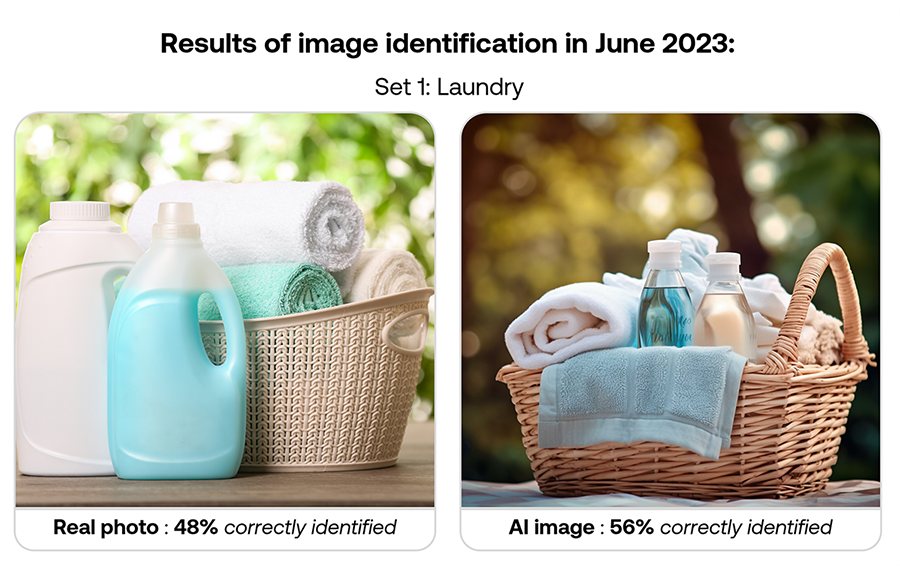
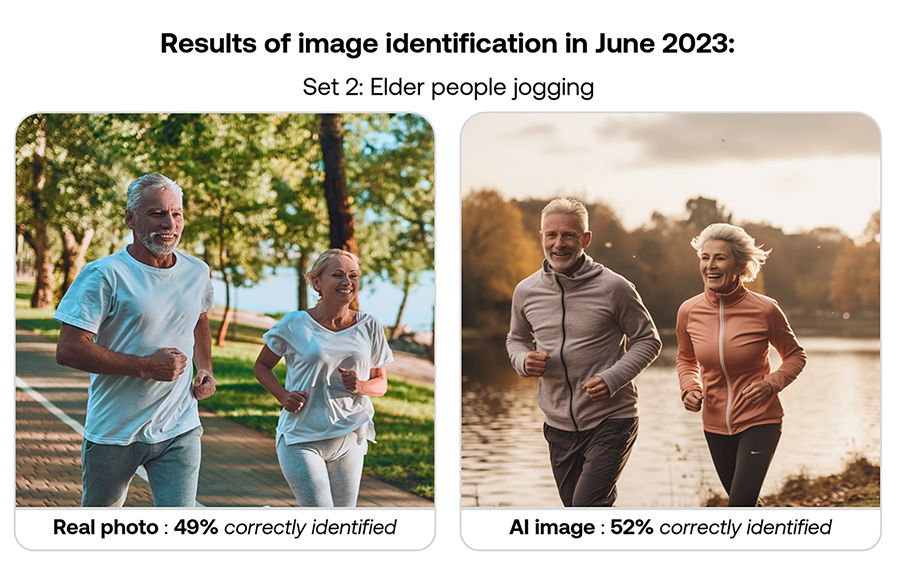
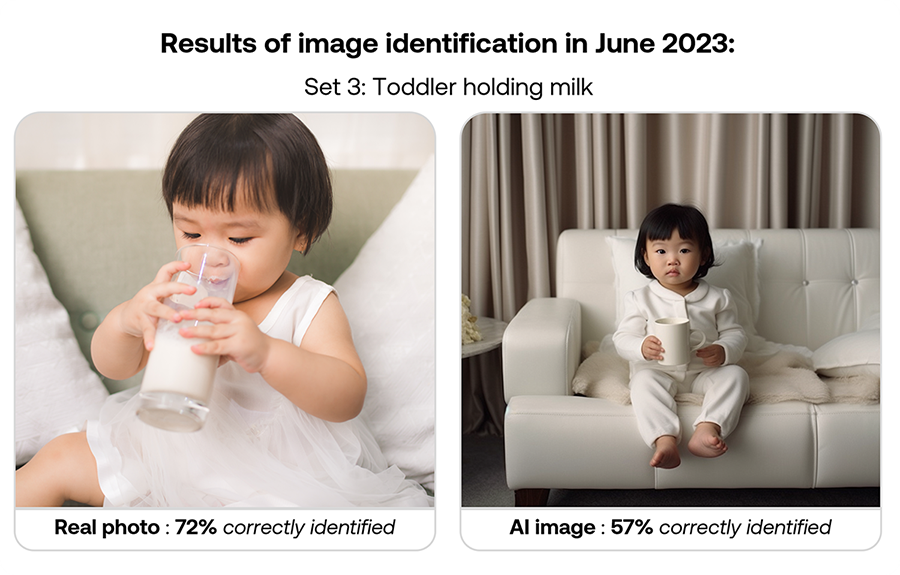
When Conjointly first explored this topic in June 2023, AI image generation produced decent images that some consumers struggled to distinguish from real. The technology has since continued to evolve, with AI image generators now creating images of far higher quality.
Google’s latest Gemini 2.5 Flash Image (Nano Banana) model has particularly impressed the AI community, with users describing it as a significant leap forward in image quality and realism.
Announcing Gemini 2.5 Flash Image! (Nano Banana) from @GoogleDeepMind. This model brings you state of the art image generation! Here's 7m of demos.
— Addy Osmani (@addyosmani) August 26, 2025
Today marks a leap forward in AI-powered image creativity with the launch of stronger native image generation and editing in Gemini… pic.twitter.com/mySnJdVwue
This advancement prompted Conjointly to build on its June 2023 and October 2024 studies in early September 2025, presenting 301 US adults with six real images and six AI-generated images created using Google’s Gemini 2.5 Flash model, where participants were asked to identify each image as real or AI-generated. Participants were also asked a variety of questions about AI tool awareness, usage patterns, and attitudes towards AI-generated content.

Consumer confidence remained high while detection accuracy stayed low
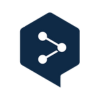
The findings revealed that 42% of respondents reported feeling confident or extremely confident in distinguishing between AI and real images, similar to the results reported in October 2024 survey but significantly higher than the 31% recorded in the June 2023 study.
However, only 9% of consumers correctly identified at least 70% of images, similar to the 10% recorded in the October 2024 study but significantly lower than the 25% achieved in the June 2023 study.
Consumers performed at chance levels for image identification
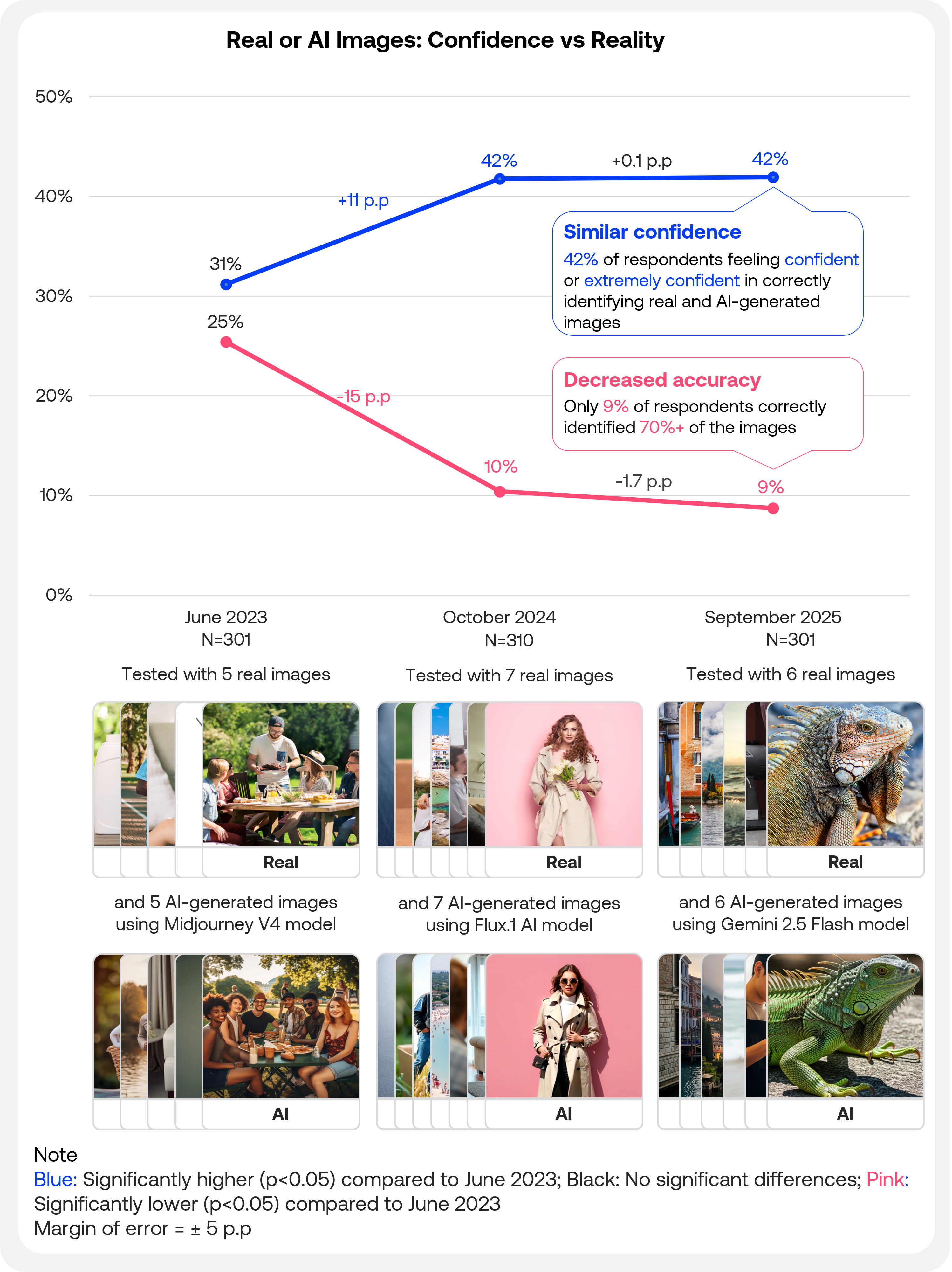
Breaking down by image type, real images were correctly identified 49% of the time, similar to the 51% in the October 2024 survey but significantly lower than the 57% recorded in the June 2023 study.
AI images were correctly identified 52% of the time, compared to 48% in October 2024 and 56% in June 2023.
Both results hover around chance levels (50%), indicating consumers performed no better than random guessing when identifying real versus AI images.
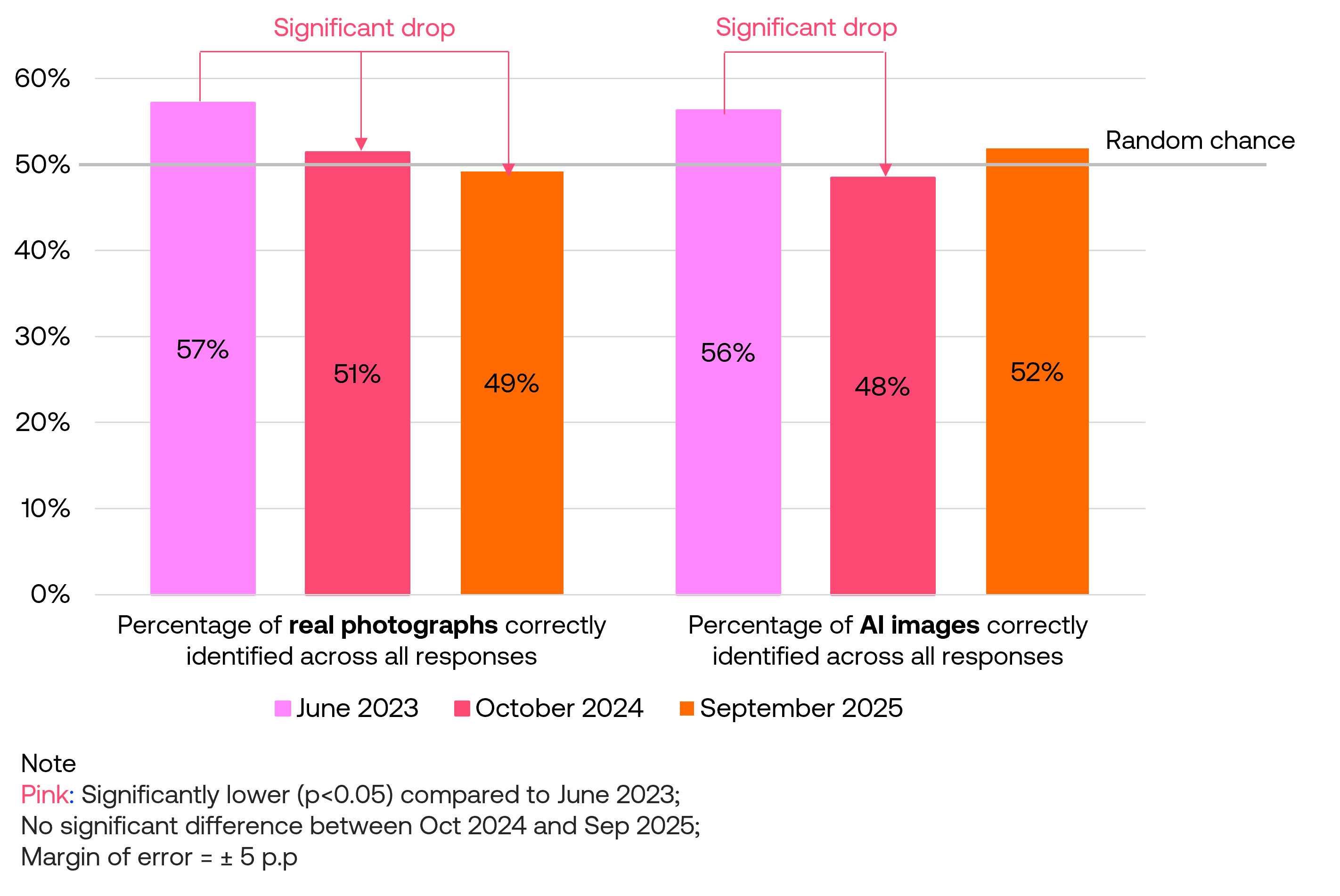
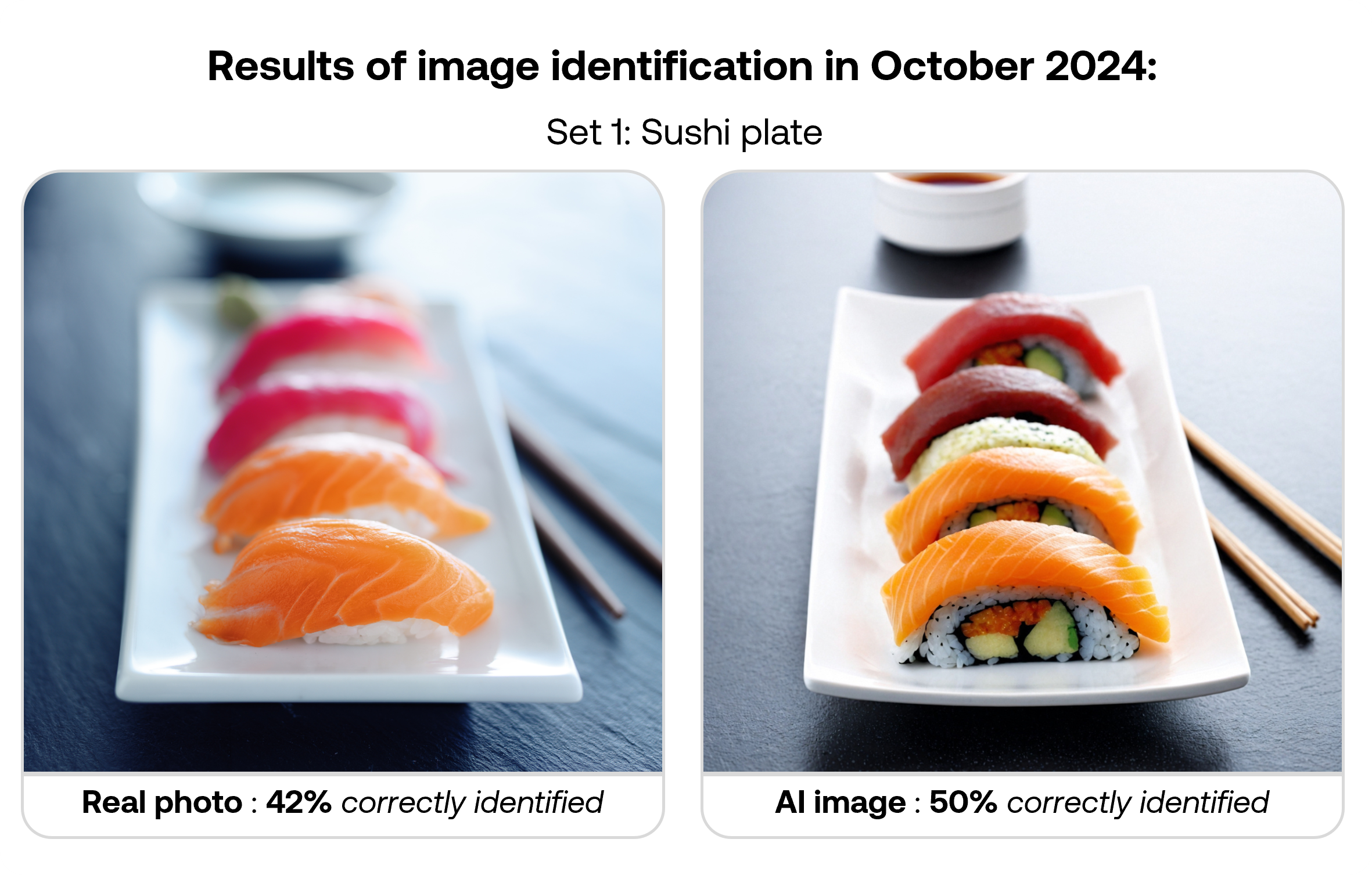
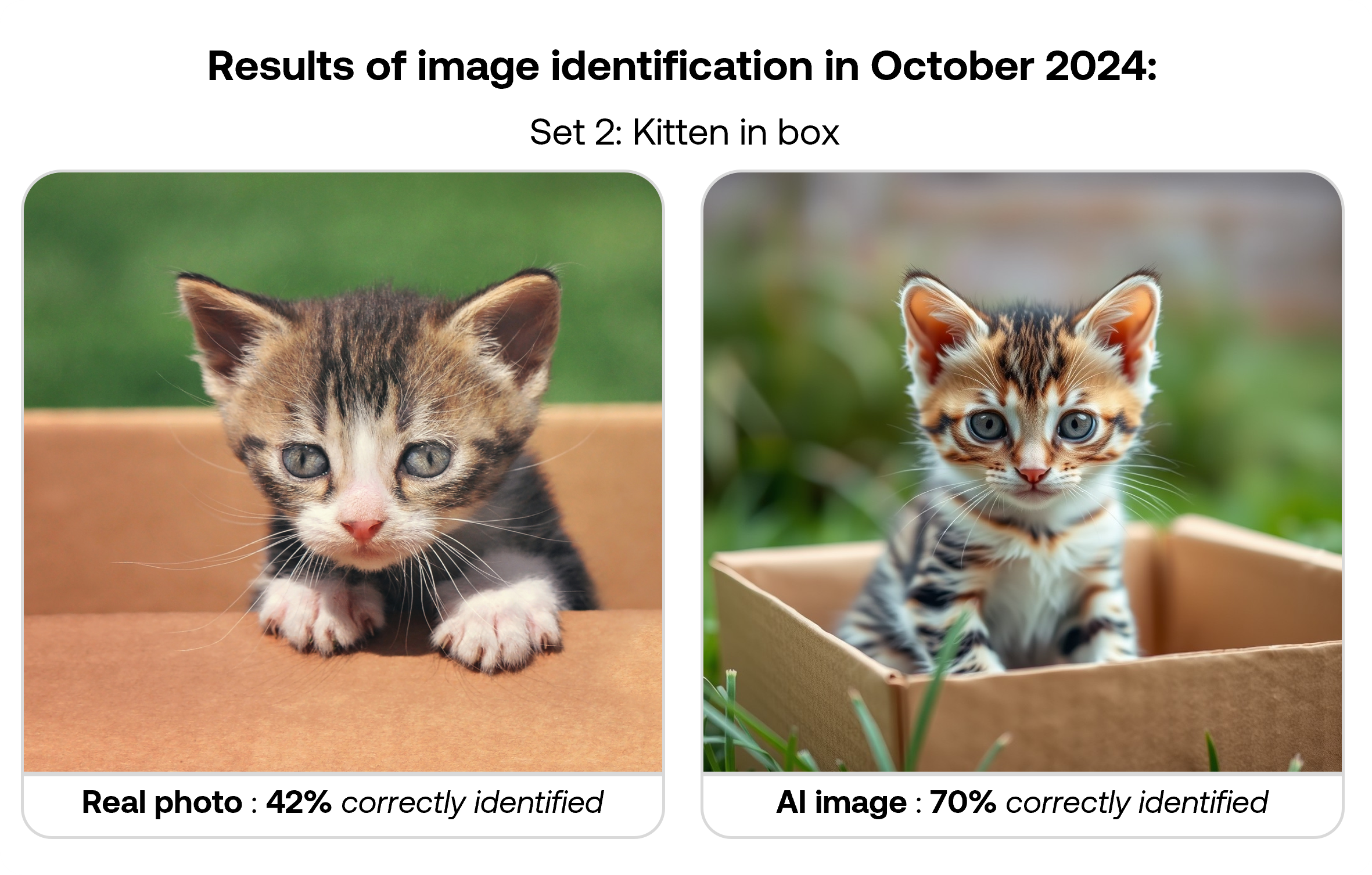
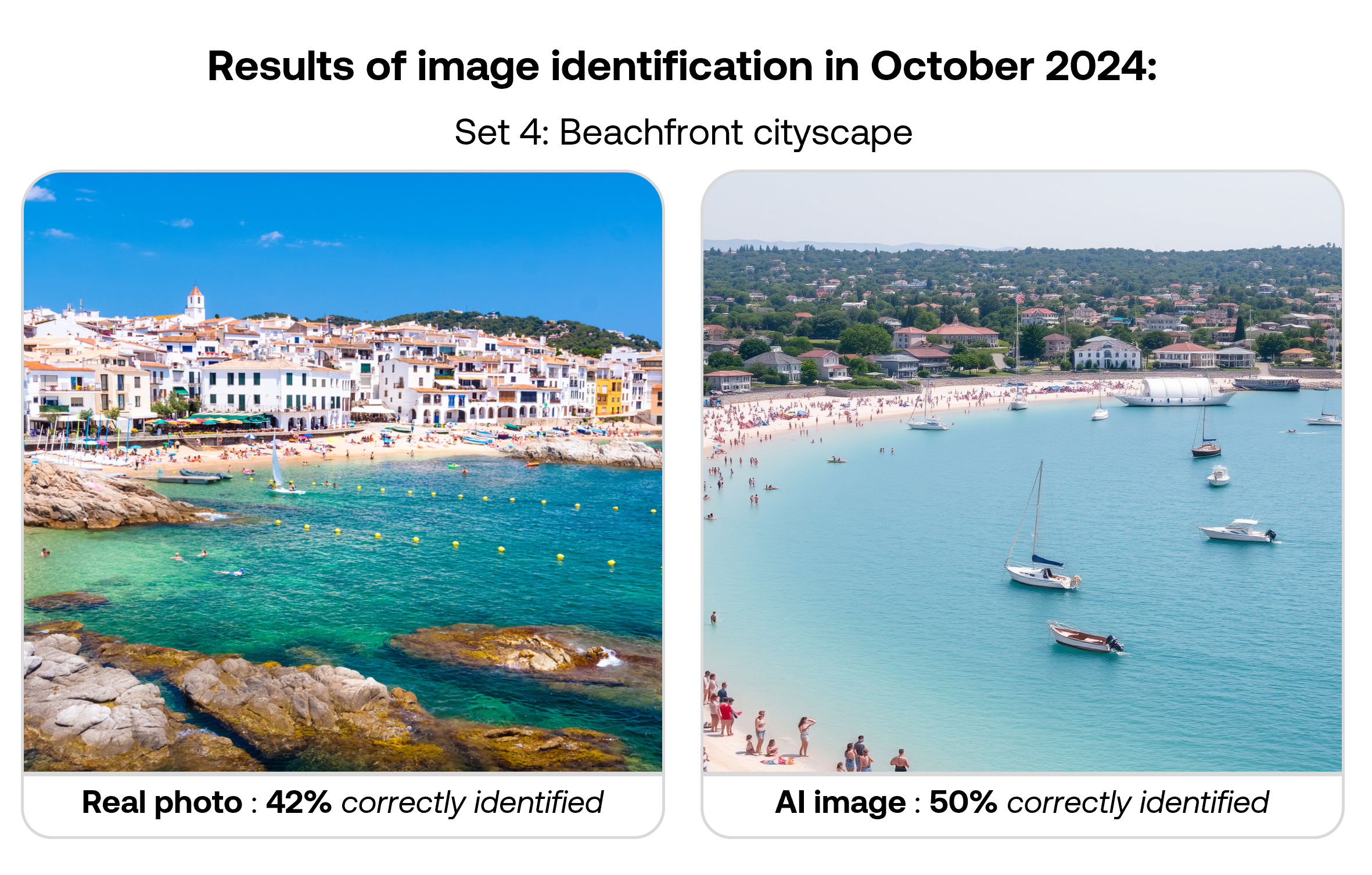
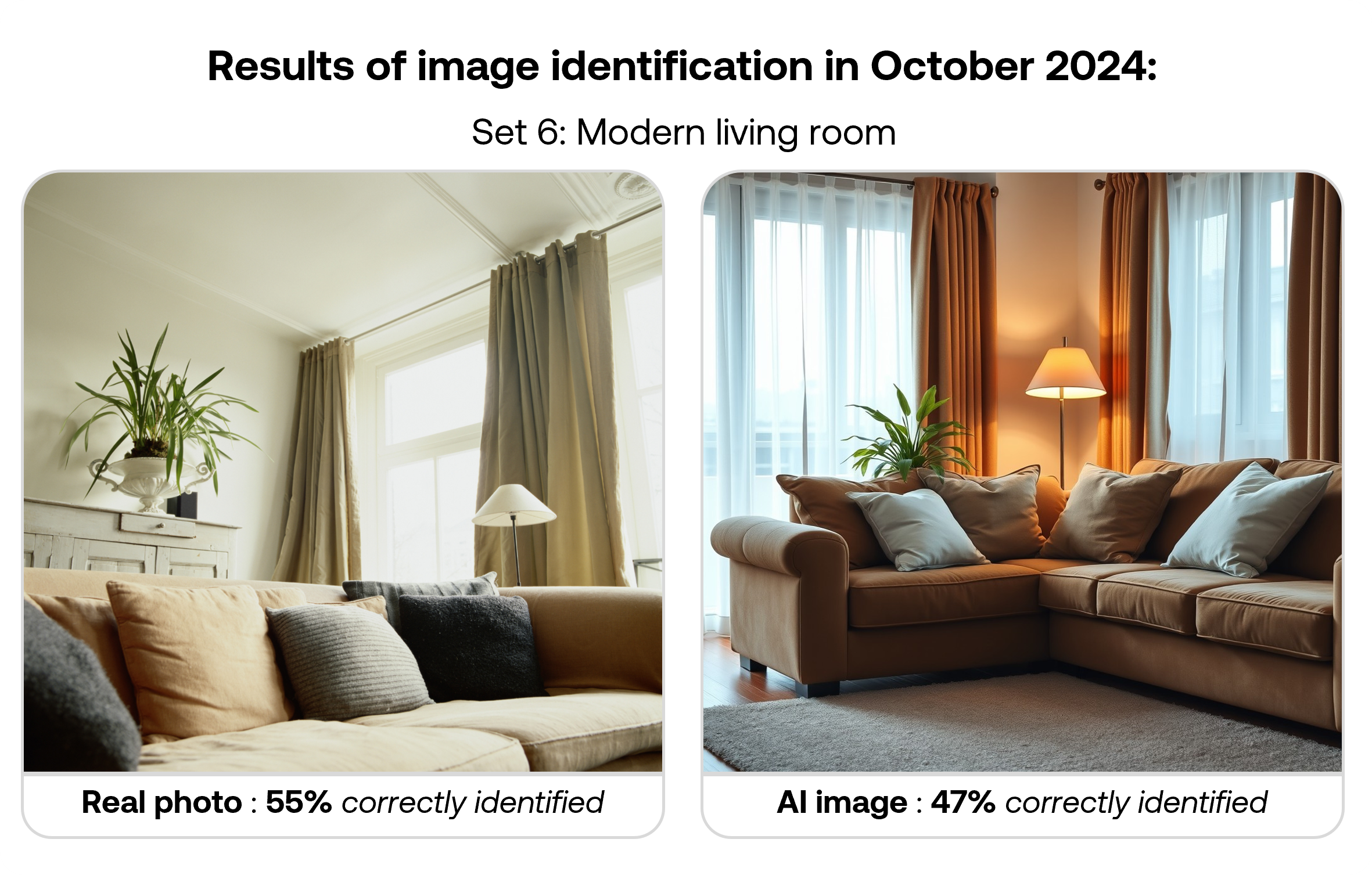
The table below shows correct identification rates for each image type in the September 2025 survey. While images were shown randomly to participants, results are organised by matched pairs of real and AI-generated images covering similar subjects.
| Real images | AI-generated images |
|---|---|
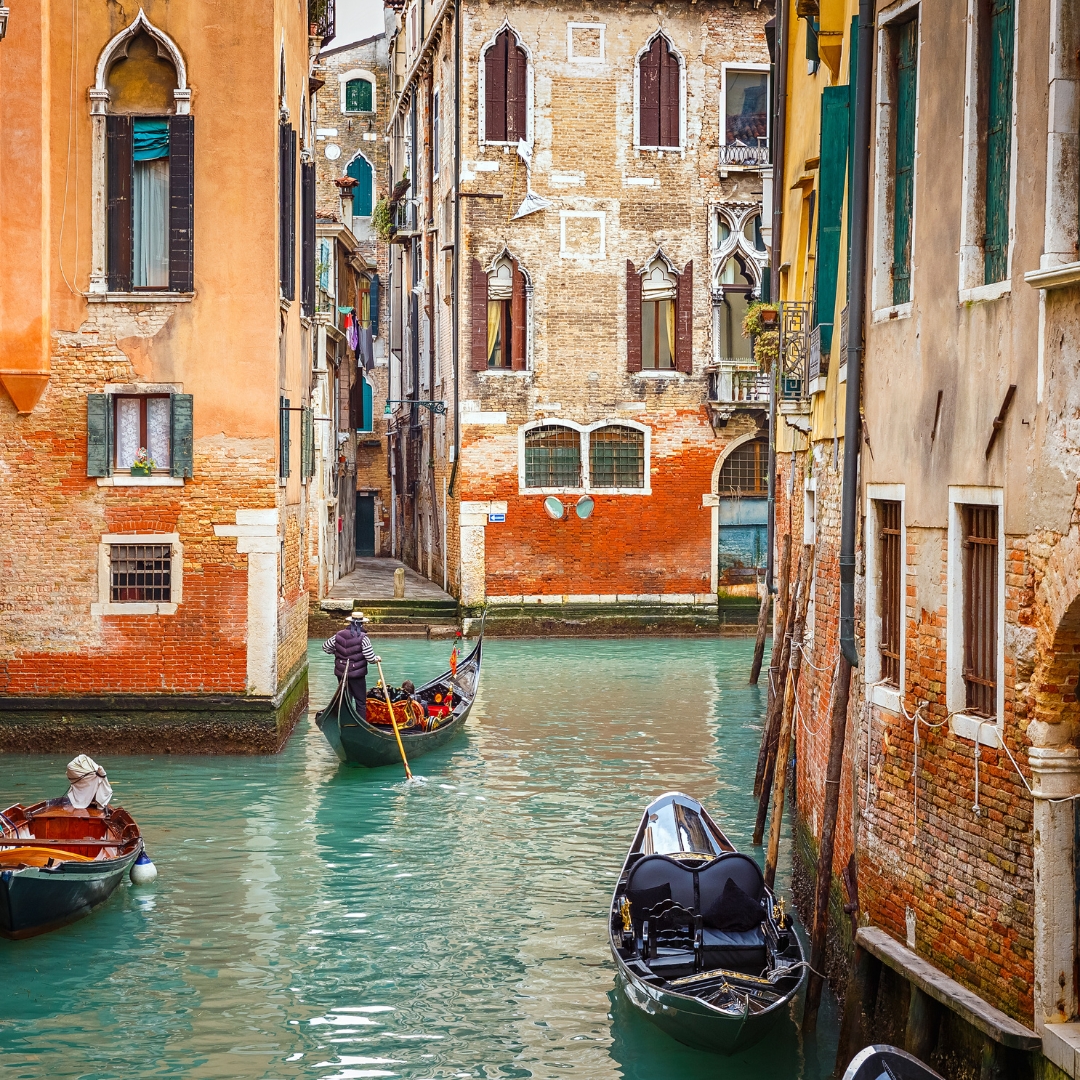
| Set 1: Venice canal crew | |
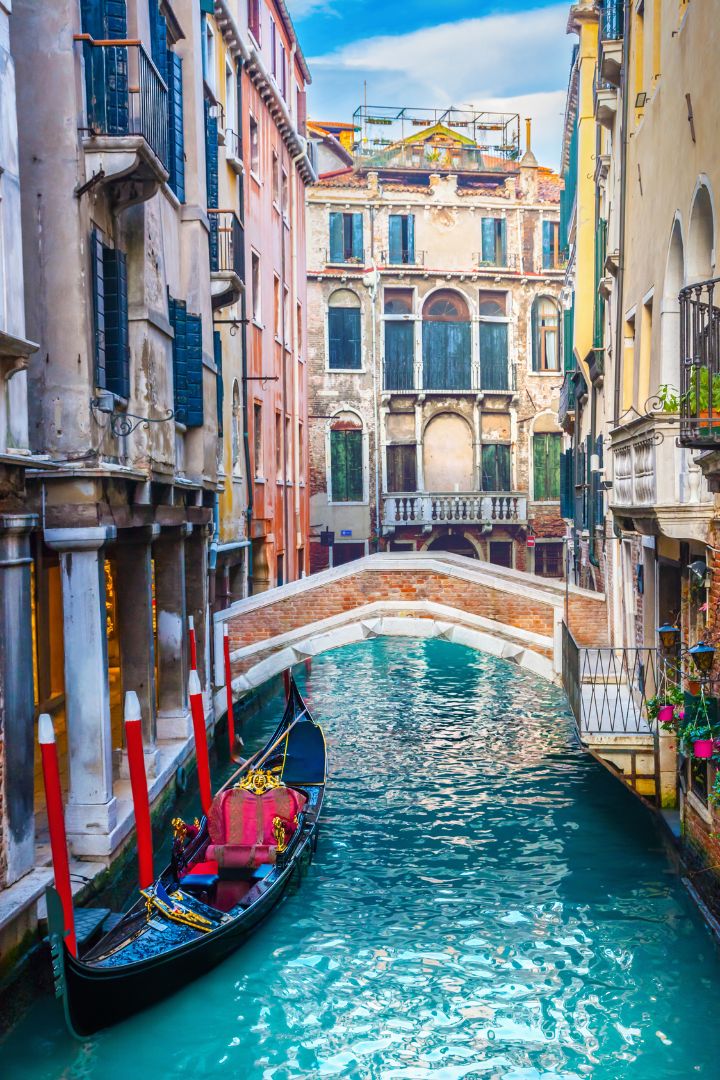 Real image : 31% correctly identified |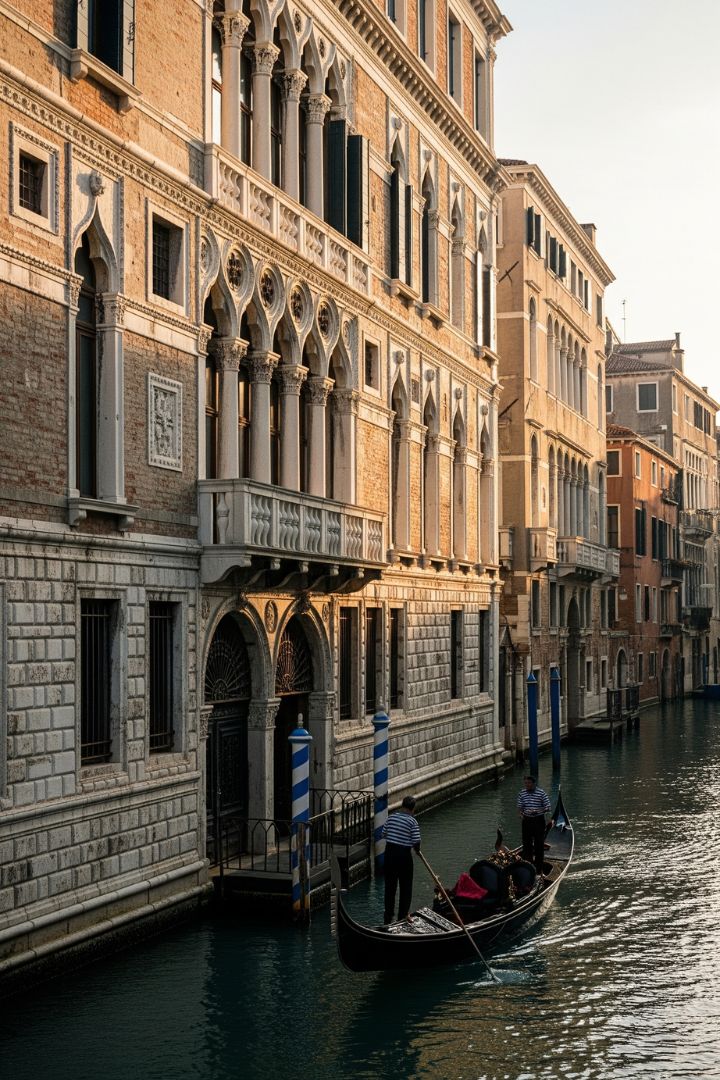  AI-generated image : 35% correctly identified |
| Set 2: Venice morning view | |
 Real image : 43% correctly identified |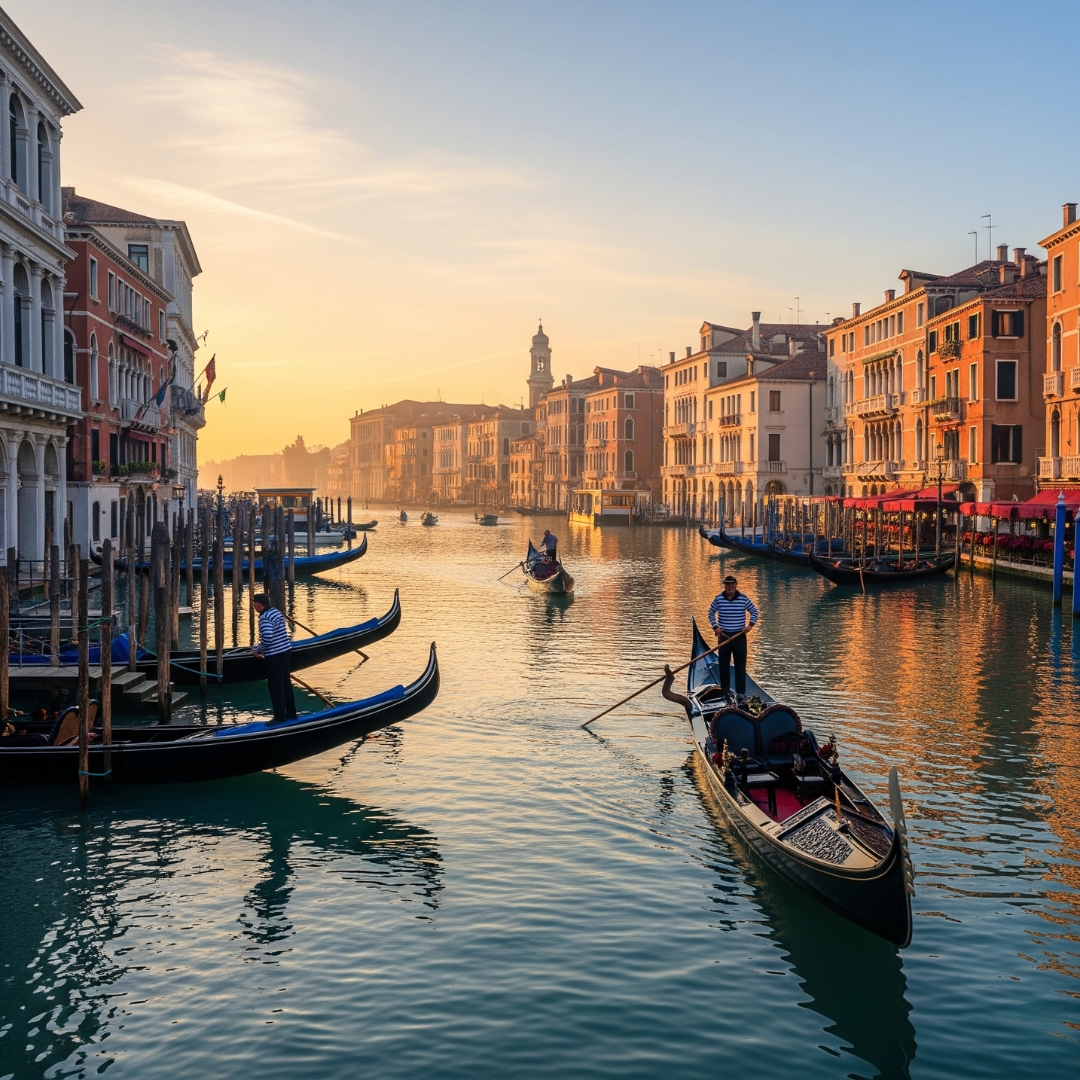  AI-generated image : 62% correctly identified |
| Set 3: Varenna lakeside town | |
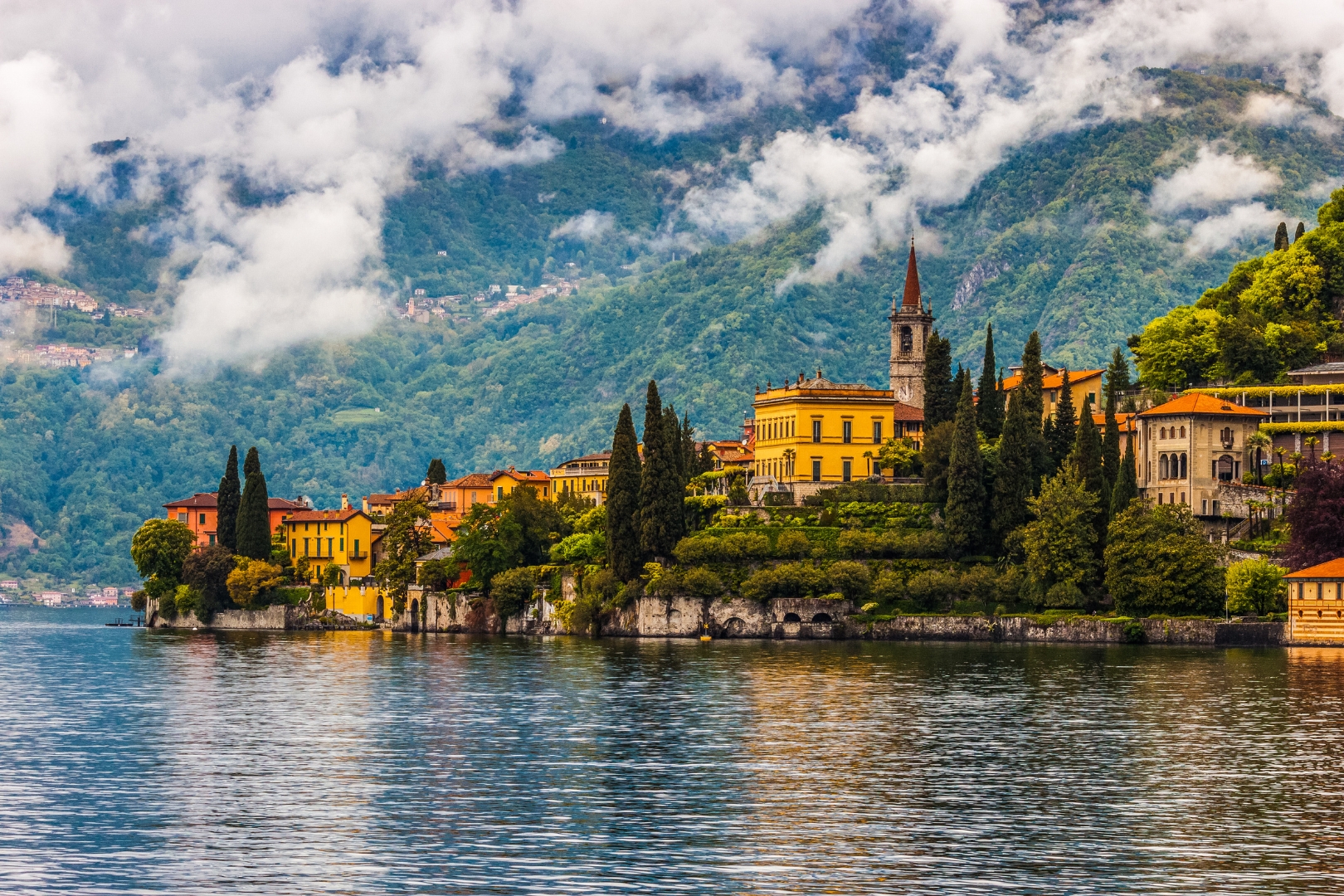 Real image : 33% correctly identified |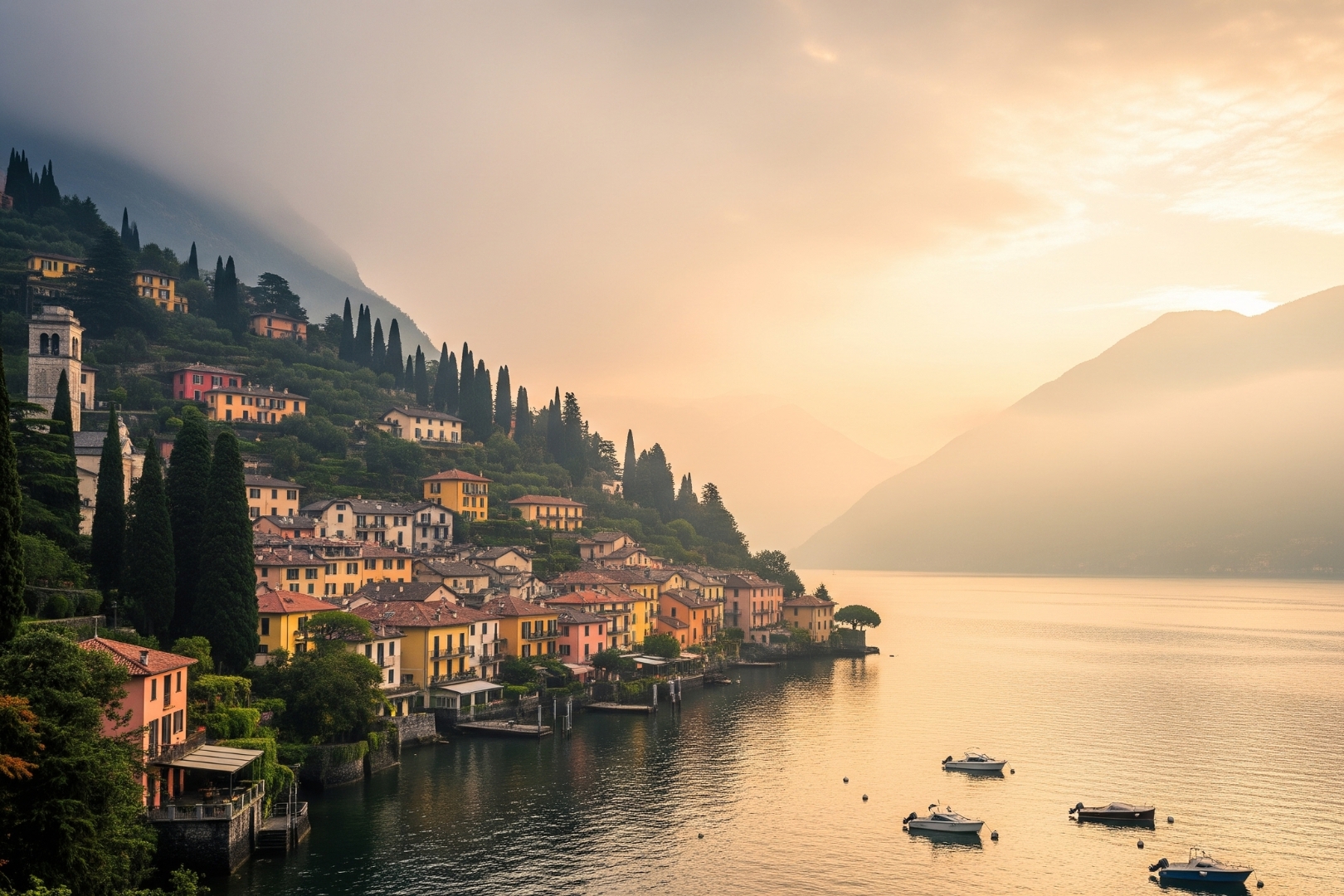  AI-generated image : 74% correctly identified |
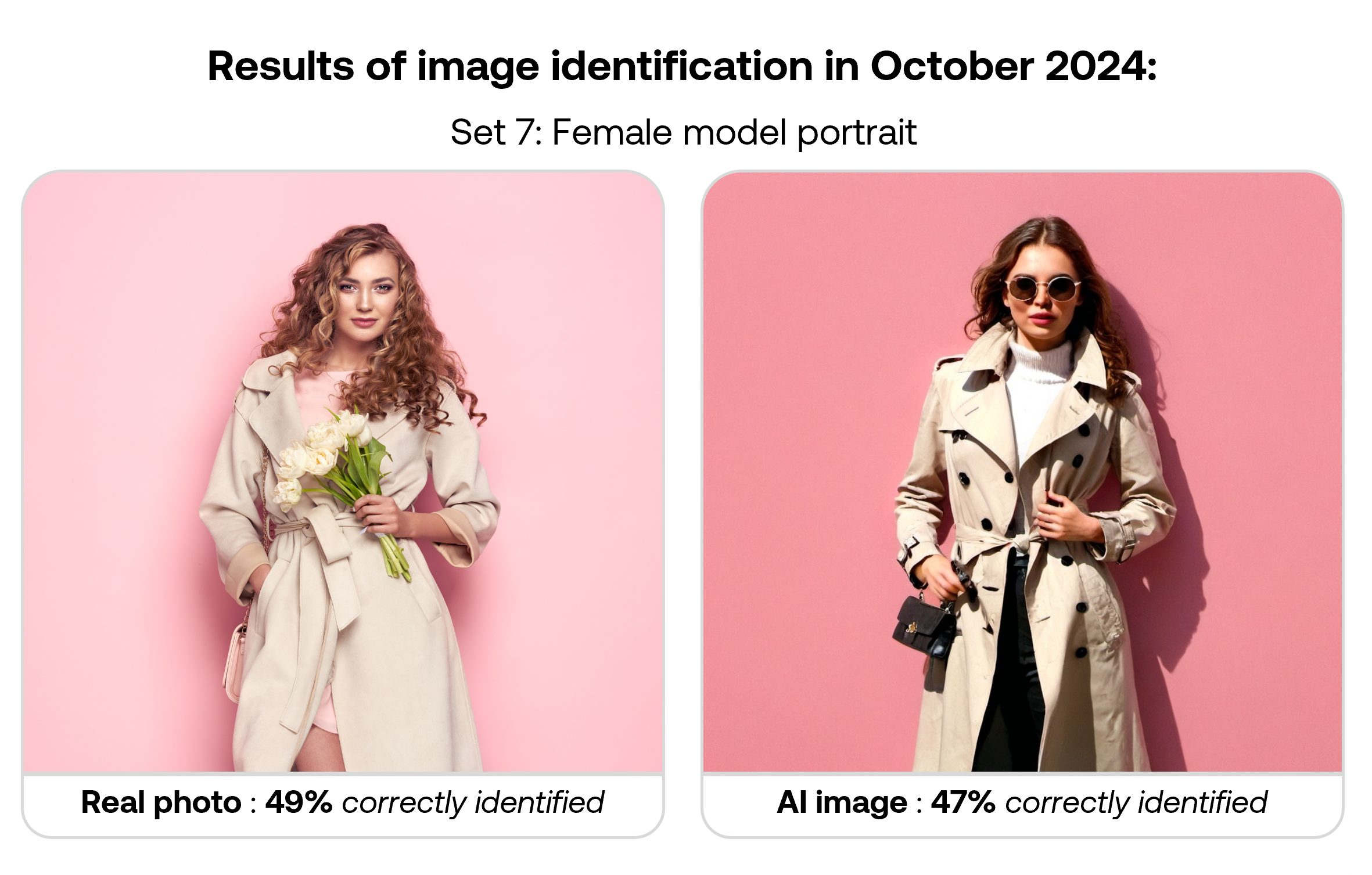
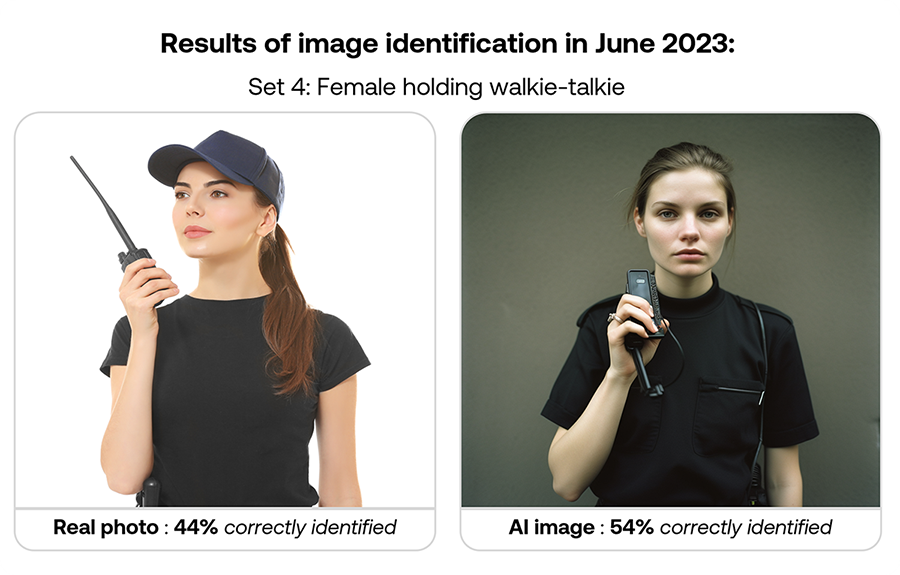
| Set 4: Beachfront model portrait | |
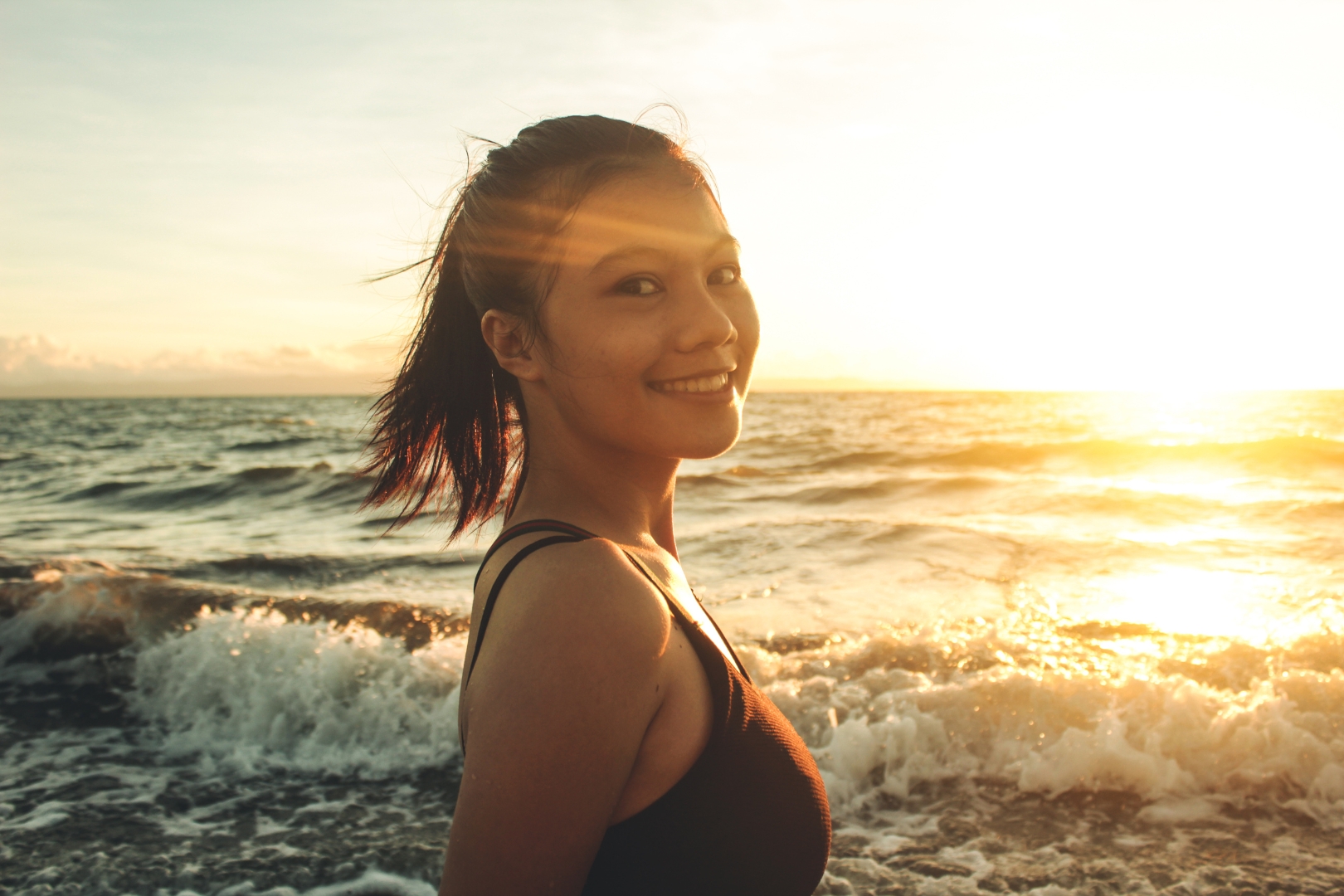 Real image : 65% correctly identified |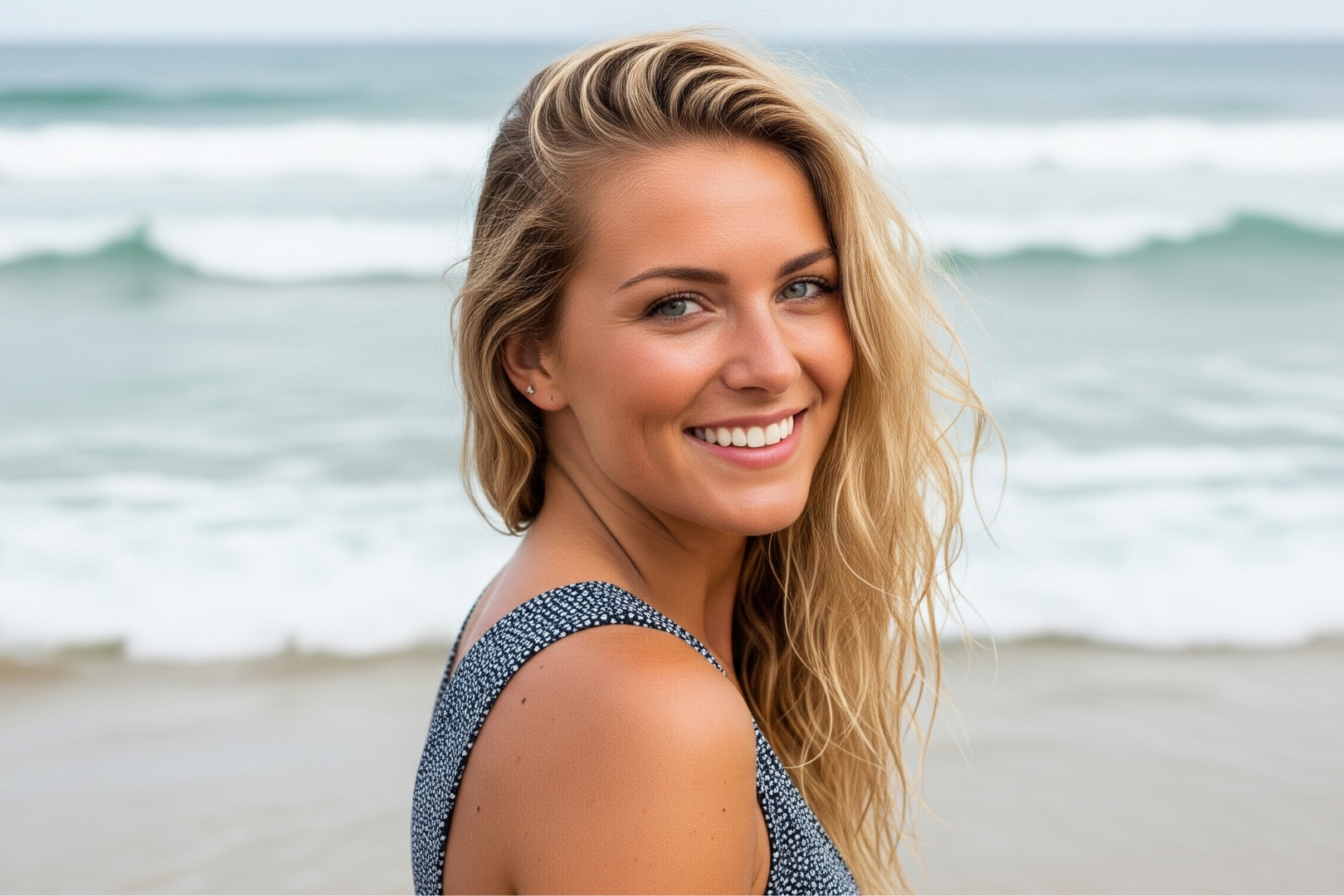  AI-generated image : 51% correctly identified |
| Set 5: Coffee barista working | |
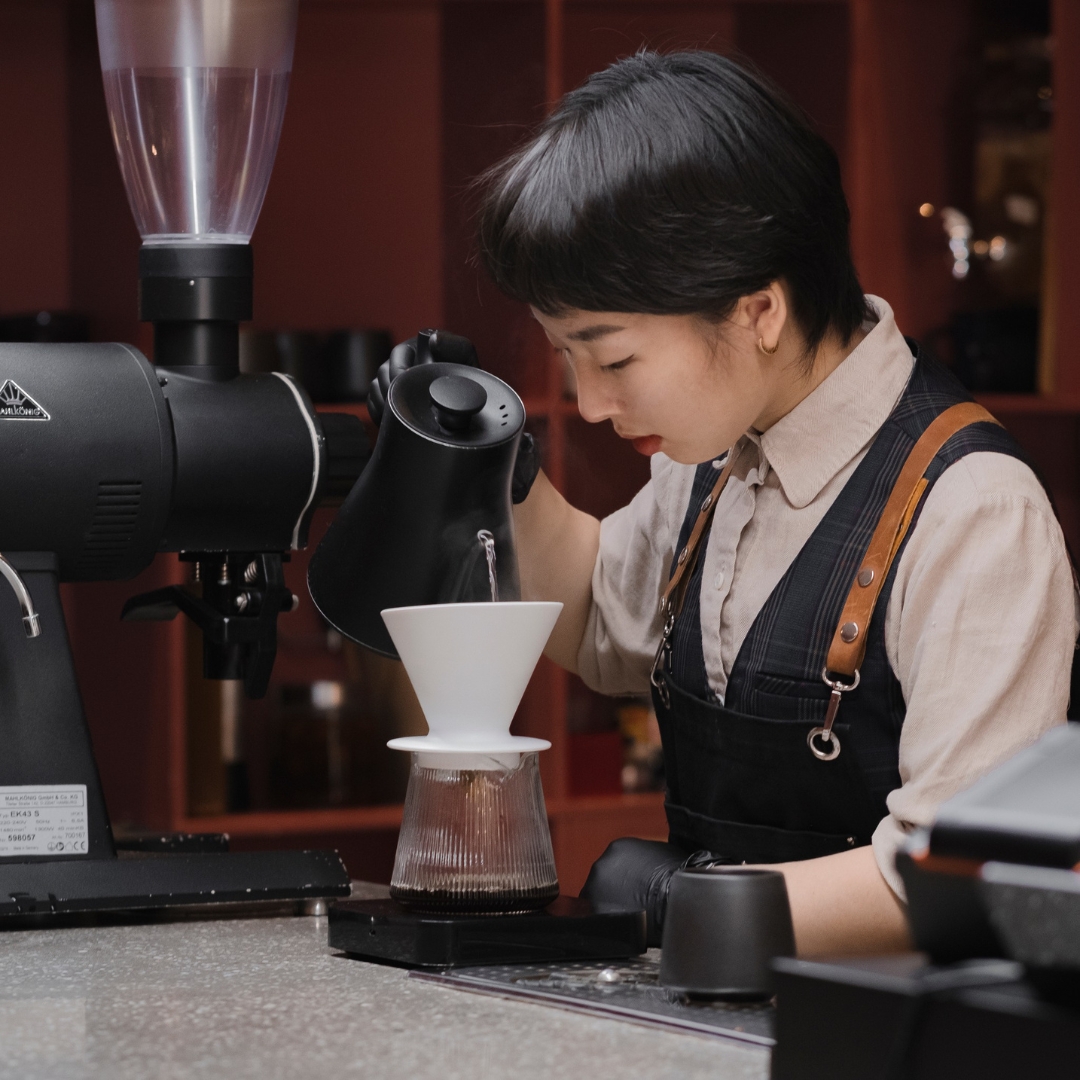 Real image : 54% correctly identified |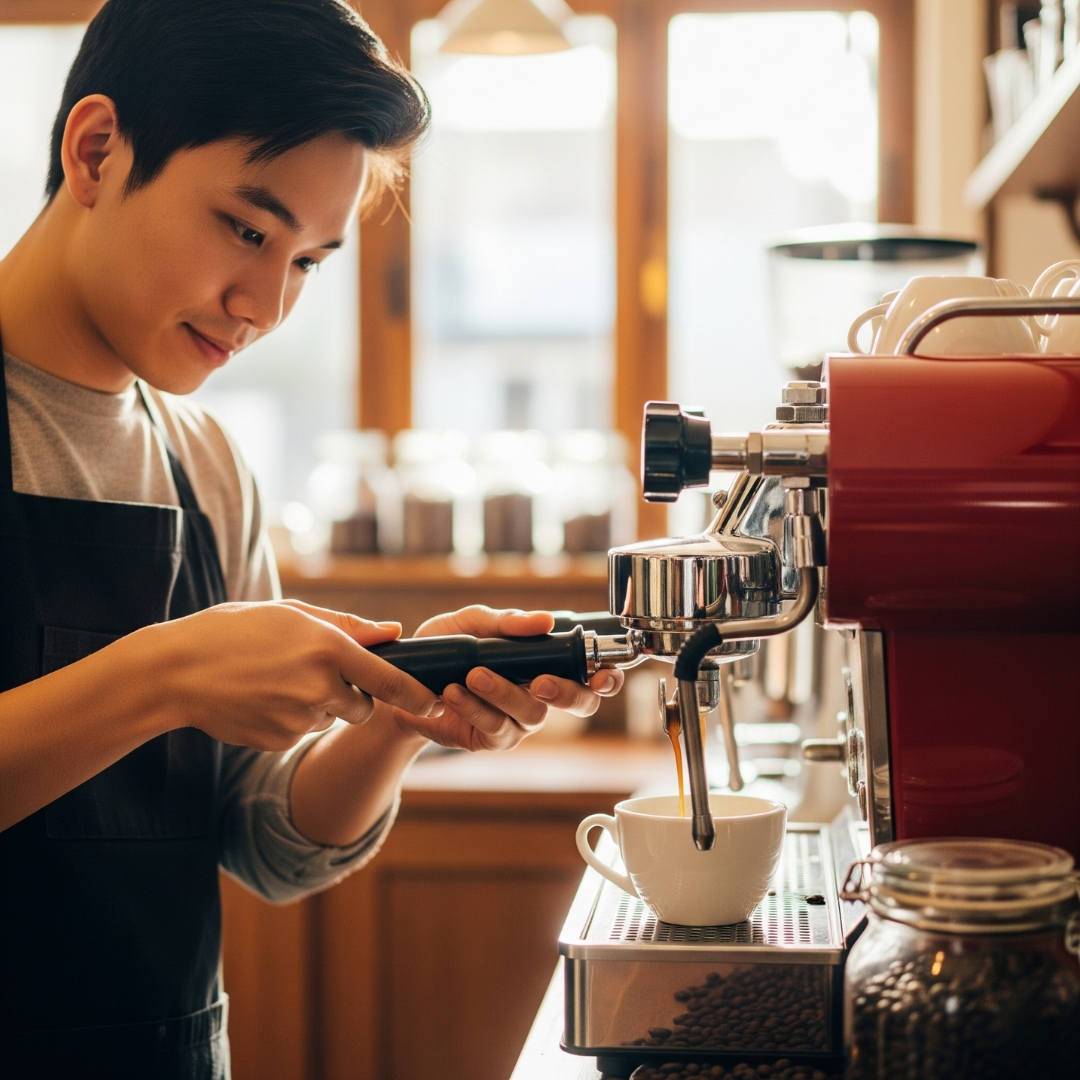  AI-generated image : 47% correctly identified |
| Set 6: Iguana close-up shot | |
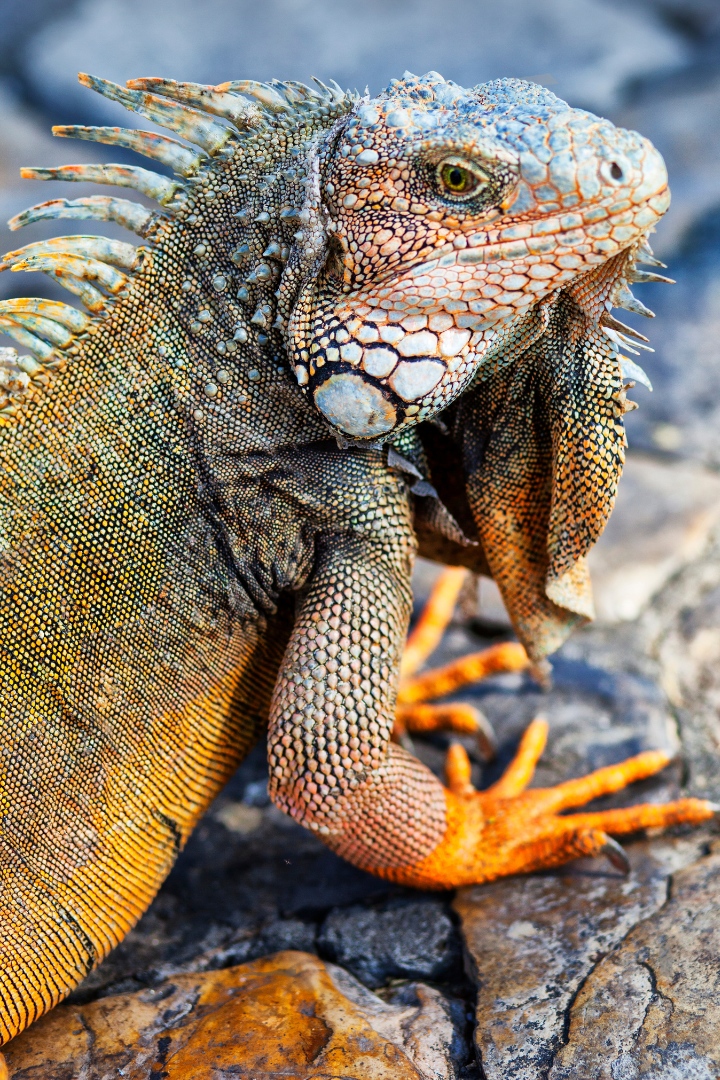 Real image : 69% correctly identified |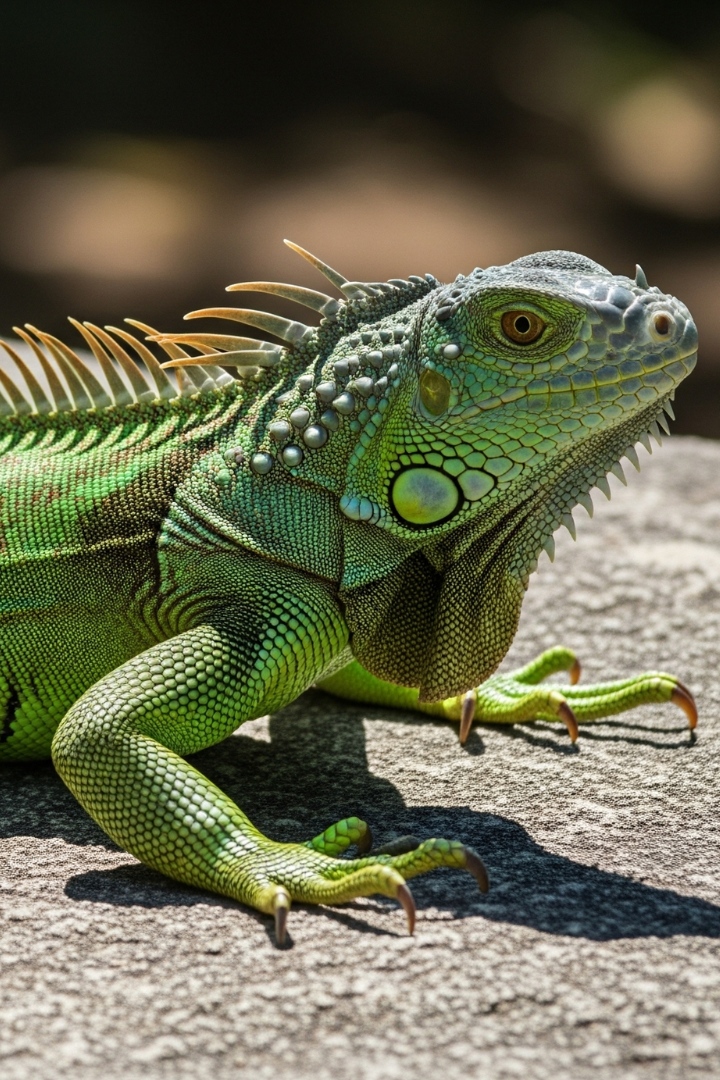  AI-generated image : 43% correctly identified |
| Average : 49% correctly identified real images | Average : 52% correctly identified AI-generated images |
Here’s how participants performed in October 2024 and June 2023:
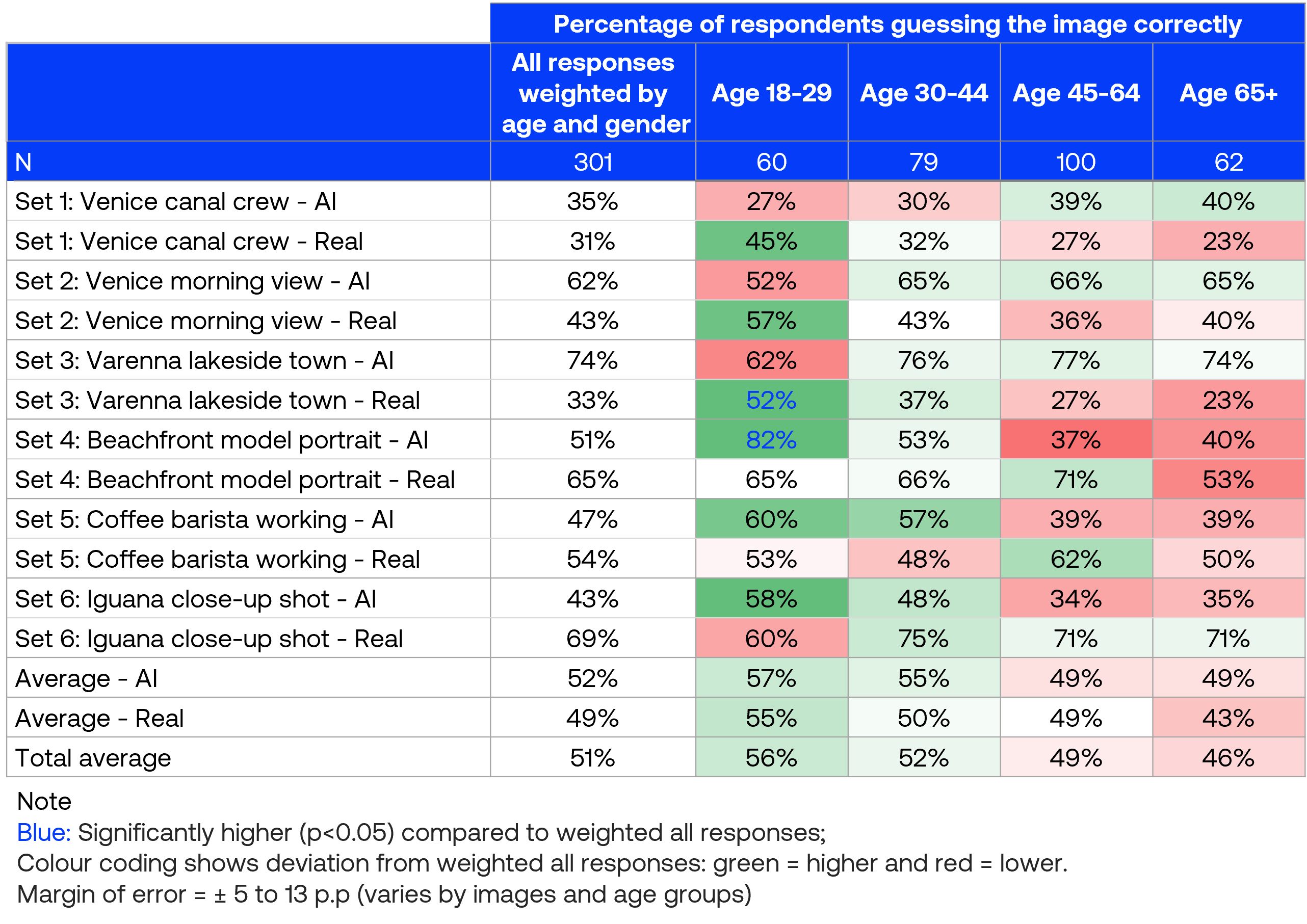
Age shows limited differences in image identification
Consumers aged 18-29 achieved 57% accuracy for correctly identifying AI images and 55% for real images, while those aged 65+ scored 49% and 43% respectively. These overall differences were not statistically significant, falling within the margin of error.
Looking at individual images, the 18-29 age group performed significantly better than the overall average on only 2 specific images out of the 12 tested.
These findings suggest age has minimal impact on consumers’ ability to distinguish between real and AI-generated images.
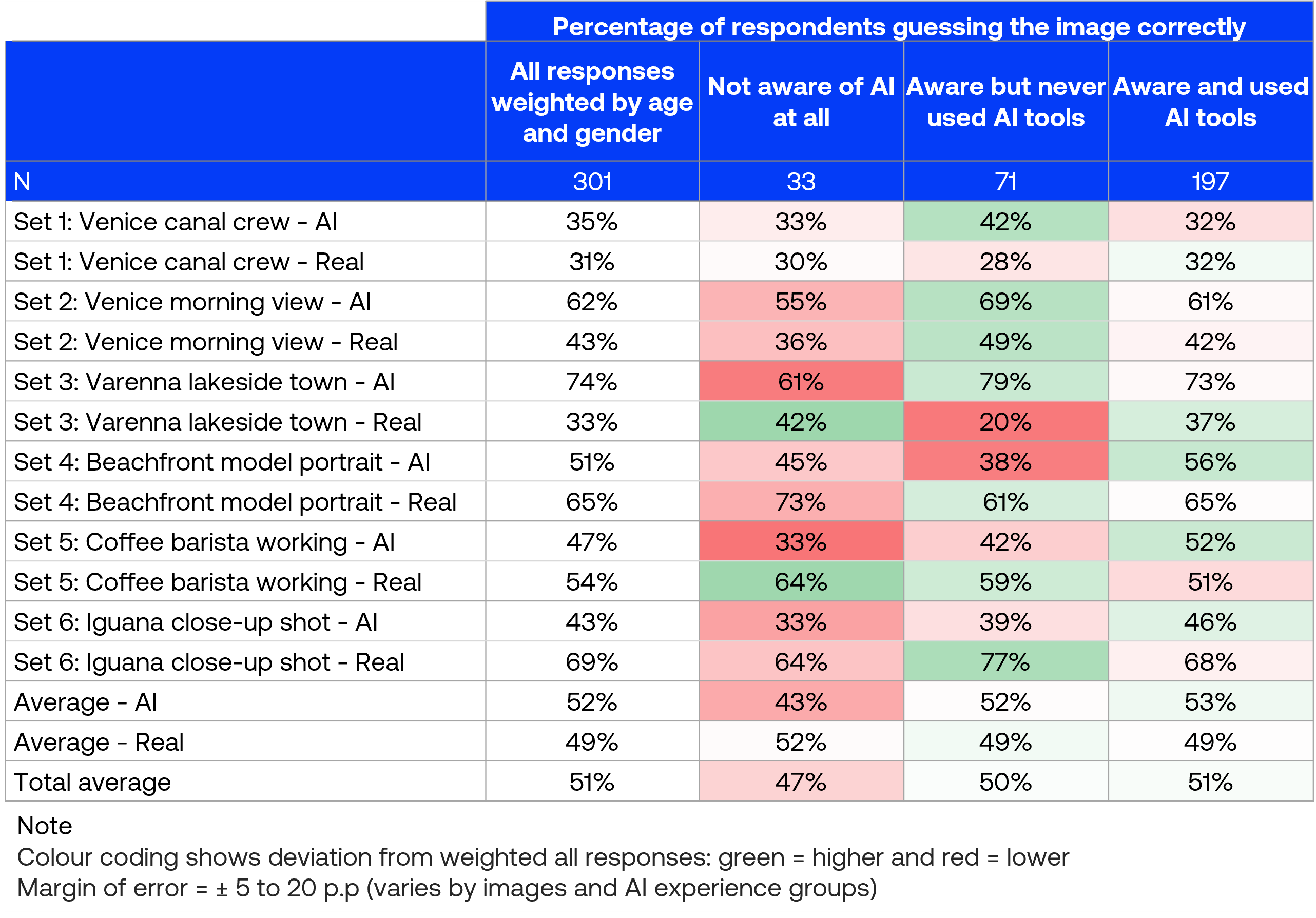
Experience with AI tools does not significantly improve image identification
Those who have used AI tools achieved 53% accuracy for correctly identifying AI images, while those aware but never used scored 52%, and those unaware of AI technology correctly identified only 43% of AI images. For real images, performance differences among experience groups (49% to 52%) were not significantly different.
However, these observed differences between groups fell within the margin of error, indicating that familiarity with AI tools does not meaningfully improve consumers’ ability to distinguish between real and AI-generated images.
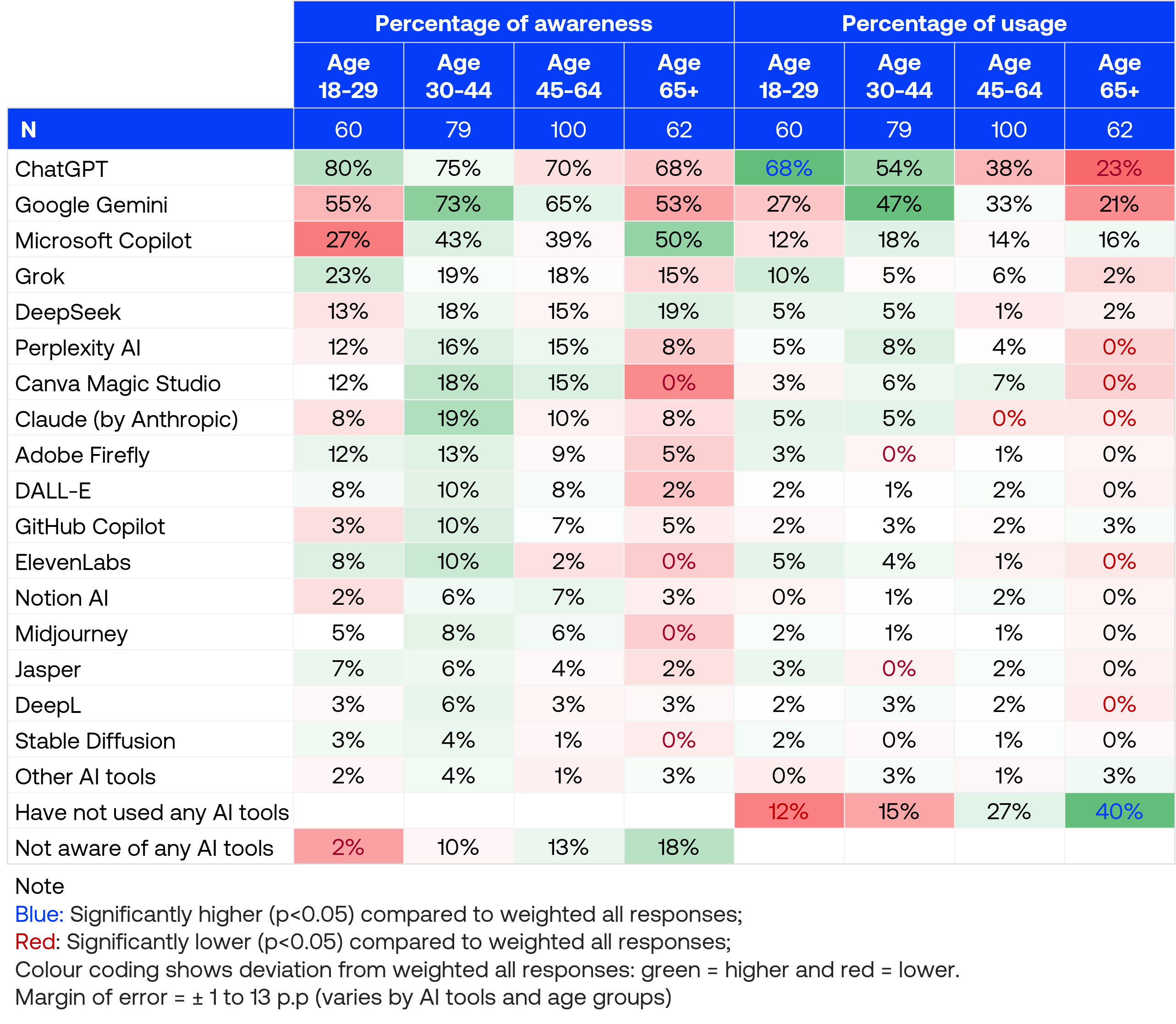
ChatGPT leads AI tool awareness and adoption
To assess the competitive landscape among generative AI tools and identify market leaders in awareness and adoption, respondents were asked two questions:
- Which of the following generative AI tools are you aware of?
- Which of the following generative AI tools have you used in the past three months?
Unsurprisingly, ChatGPT dominates both awareness and usage among consumers, with 73% aware of the tool and 45% having used it in the past three months. Google Gemini follows with 62% awareness and 32% reporting recent usage, while Microsoft Copilot rounds out the top three with 40% awareness and 15% usage.
Notably, 11% of respondents reported being completely unaware of any AI tools, while 24% are aware of AI tools but have not used any in the past three months, with older age groups accounting for the majority of these segments.
Age-related differences emerge in AI tools engagement
Among 18-29 year-olds, 80% were aware of ChatGPT while Gemini ranked second at 55%, with remaining tools falling below 30%. Meanwhile, 30-44 and 45-64 year-olds distributed their awareness more broadly across tools.
Compared to overall averages, consumers aged 65+ showed significantly lower awareness of AI tools including DALL-E, Midjourney, ElevenLabs, and Canva Magic Studio. Only 2% of 18-29 year-olds reported no awareness of any AI tools.
In terms of usage, 18-29 year-olds demonstrated strong ChatGPT focus with 68% having used it in the past three months. Significantly fewer young adults aged 18-29 reported being aware but not using any AI tools (12%), while older adults aged 65+ were significantly more likely to report non-usage (40%).
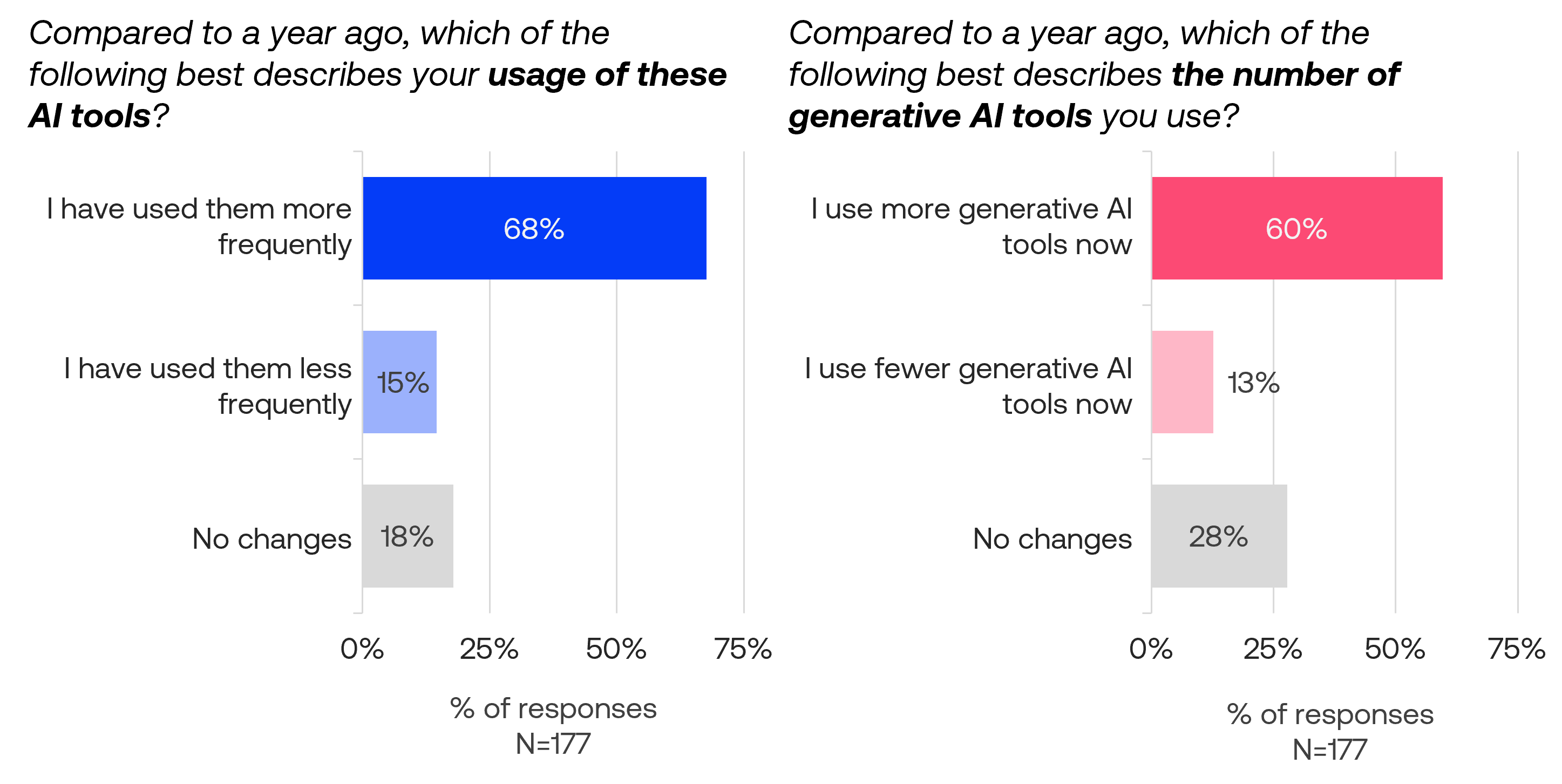
Active users increase frequency and number of AI tools used
Among active AI tool users, the majority reported increased engagement over the past year. 68% used AI tools more frequently compared to a year ago, while 60% expanded the number of generative AI tools in their toolkit. Conversely, only 15% reduced their usage frequency and 13% decreased the number of AI tools they use.
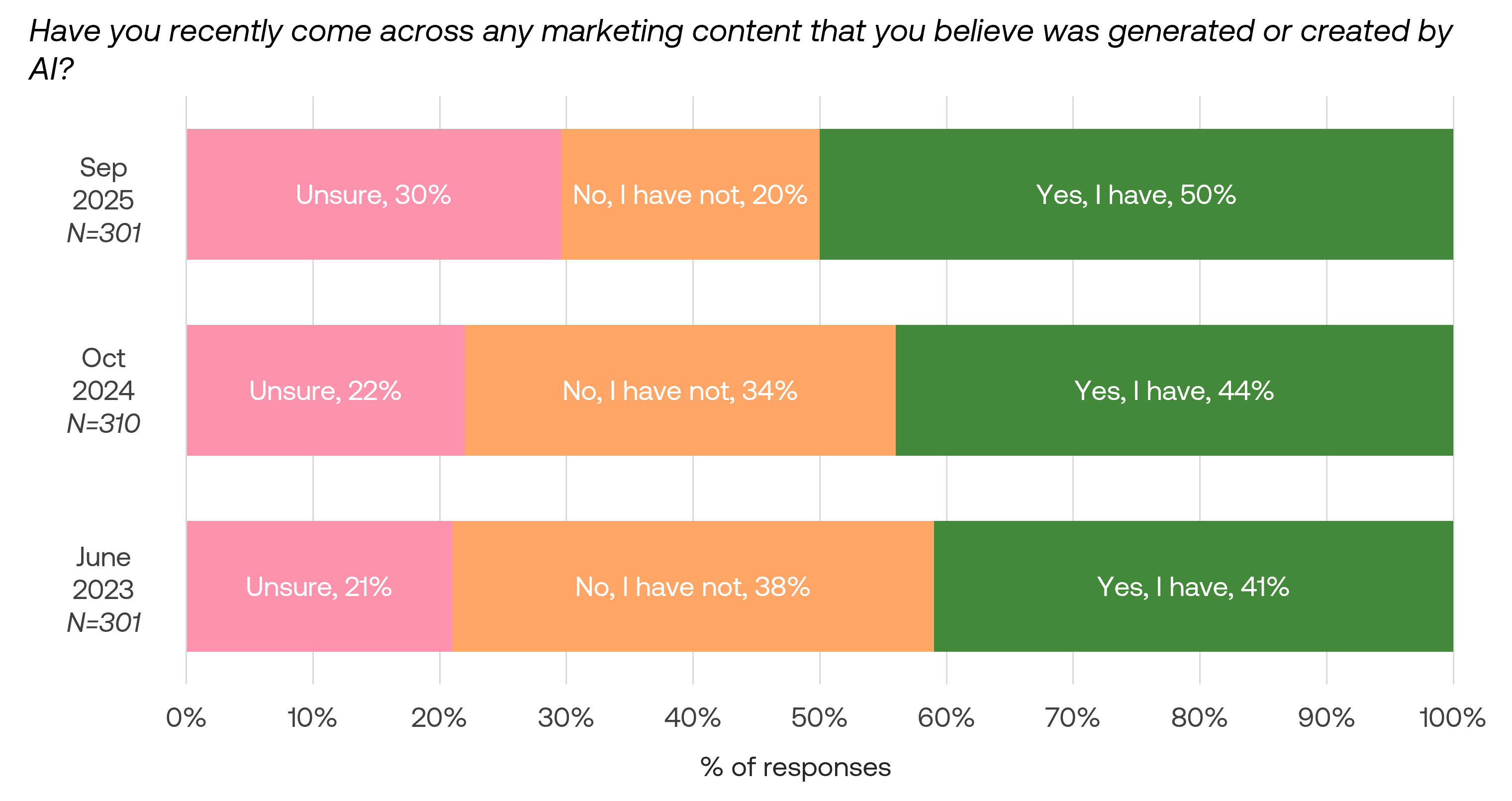
Half of consumers encounter AI-generated marketing content
50% of consumers reported recent encounters with AI-created marketing materials in September 2025, compared to 44% in October 2024 and 41% in June 2023. Interestingly, 30% of consumers reported uncertainty about whether marketing content was AI-generated, compared to 21% and 22% in previous surveys.
Changes in consumer perceptions of AI-generated content are mixed
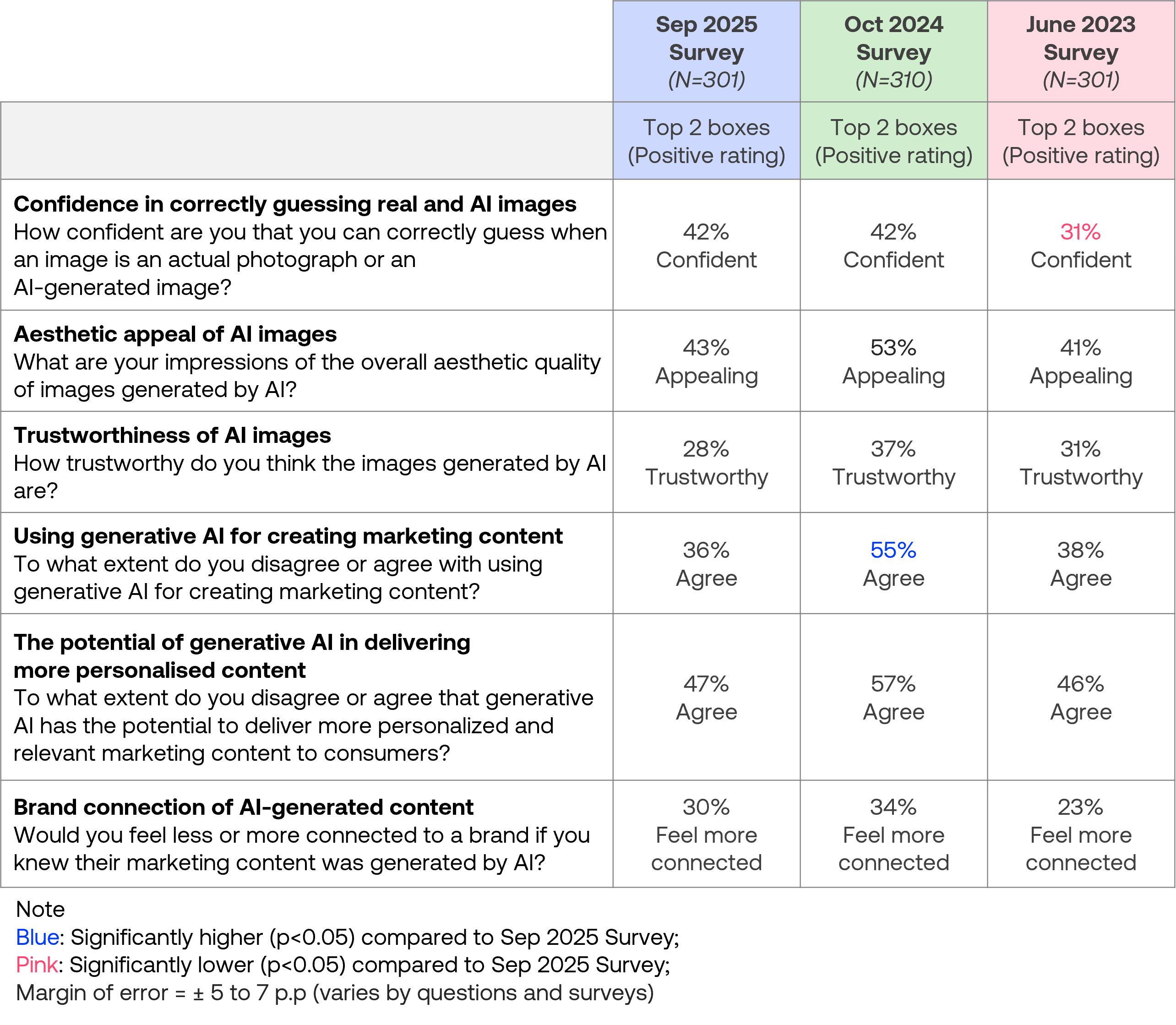
Consumer confidence in distinguishing between AI and real images remained stable at 42%, matching October 2024 levels.
Most consumer attitudes towards AI-generated content showed numerical declines compared to the October 2024 survey, though only agreement on using AI for marketing content declined significantly from 55% to 36%.
Other measures showed decreases that fell within the margin of error, including aesthetic appeal dropping from 53% to 43%, trustworthiness from 37% to 28%, and belief in AI’s potential for delivering personalised content from 57% to 47%.
Implications for brands and marketers
With consumer detection of real and AI-generated images performing at chance levels across all demographics and AI experience groups, the challenge of distinguishing AI content appears universal.
These findings suggest that transparency and disclosure remain important for brands, particularly given that consumers cannot reliably identify AI-generated content yet show mixed sentiment towards its use in marketing.
Simultaneously, brands may need to ensure their content maintains authentic qualities that resonate with consumers’ preferences, whether AI-generated or not.
Whether you’re navigating evolving consumer perceptions or need to test how your audience responds to product claims and marketing assets, Conjointly offers advanced research tools and expert support to help you gain actionable insights and stay ahead of these rapidly shifting dynamics. Schedule a free consultation today to discuss your project needs.