Recent Conjointly research reveals troubling difficulty in distinguishing AI-generated images from real photographs, alongside shifts in AI usage and perceptions.
Are there fewer AI-generated images nowadays? Or are they getting remarkably better that we simply can’t tell them apart from real photographs anymore?
Where’d they go? 😳 pic.twitter.com/7yUnLZwOxD
— Declaration of Memes (@LibertyCappy) October 11, 2024
In October 2024, Conjointly conducted a survey to assess how accurately consumers can distinguish between artificial intelligence (AI)-generated images and real photographs, along with how usage patterns and attitudes towards AI has changed. This study engaged 310 respondents representative of the USA general adult population, following up on a similar study from June 2023.
Our findings reveal notable gap between people’s perceived and actual ability in differentiating real photographs and AI-generated images. The proportion of respondents reporting as confident and extremely confident in distinguishing such images increased from 31% in June 2023 to 42% in October 2024. However, not a single respondent achieved 100% accuracy in identifying all images correctly. The percentage of respondents who could accurately identify at least 70% of the images dropped significantly from 25% to just 10% in the same period.
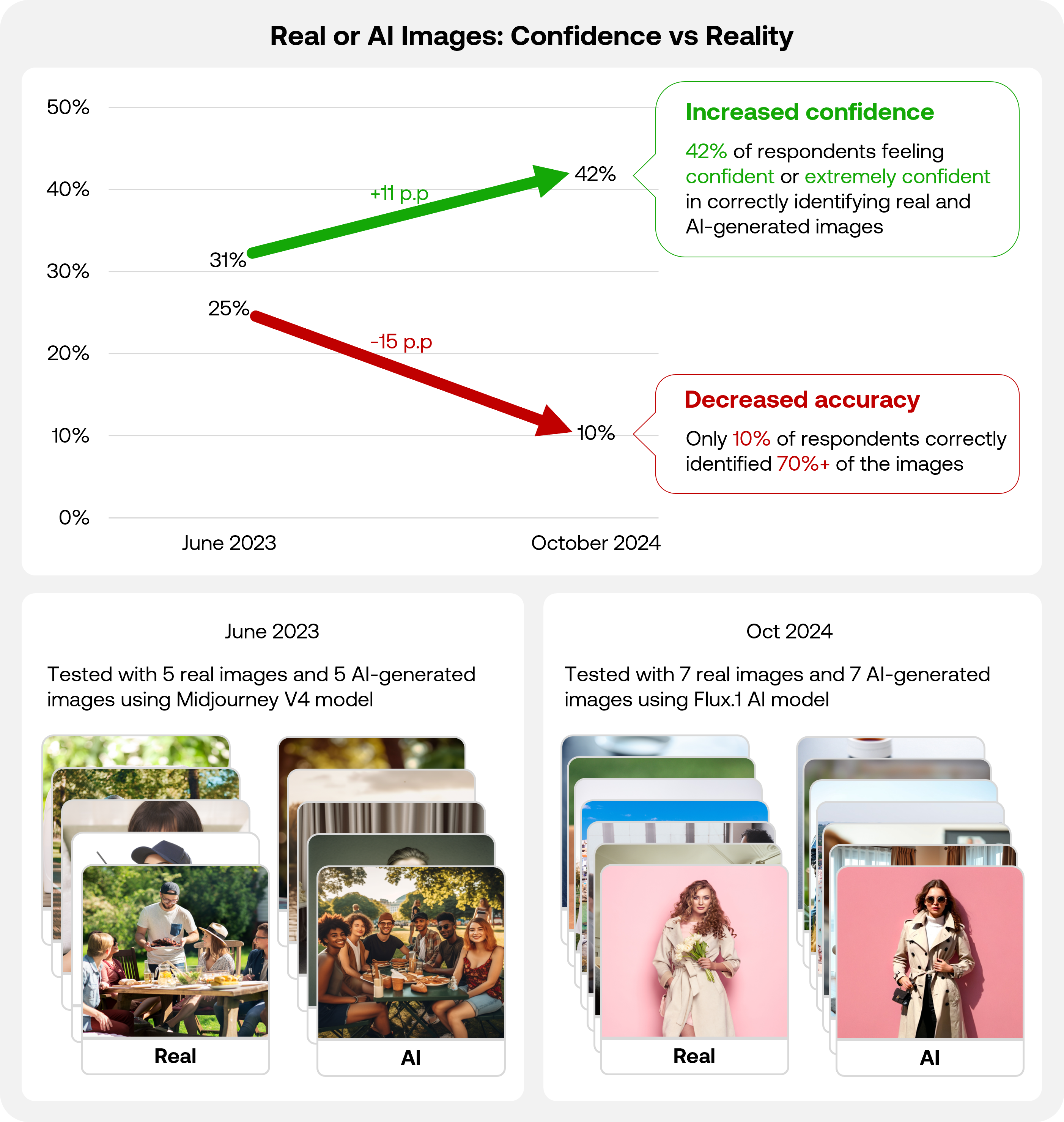
Diving deeper into the accuracy decline, the percentage of respondents who correctly identified real photographs significantly decreased from 57% to 51%, while those who correctly identified AI-generated images dropped even more sharply from 56% to 48%.
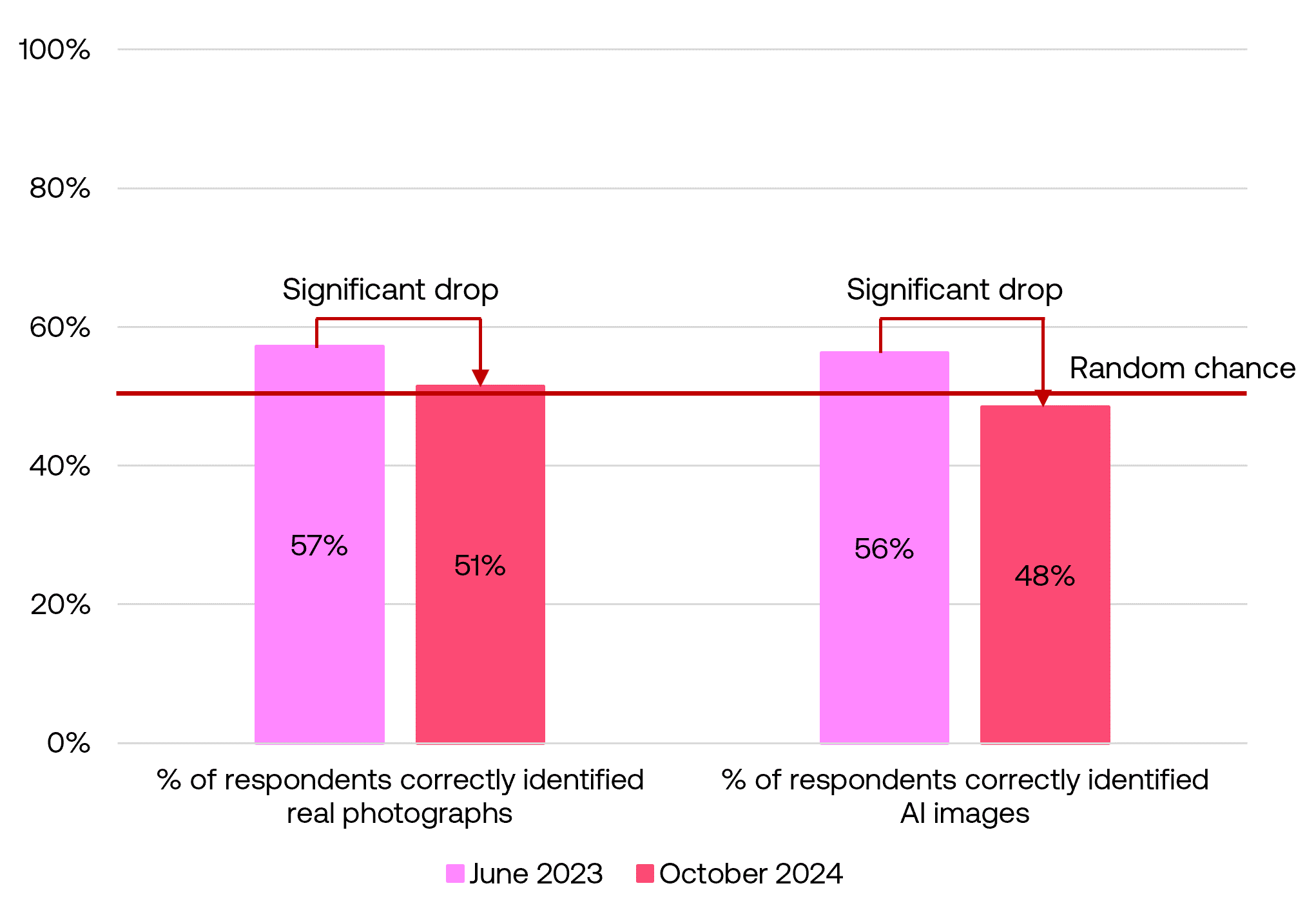
Identifying real photographs and AI-generated images
Respondents were shown seven real photographs and seven AI-generated images using the FLUX.1 model, and asked to identify each as either real or AI-generated. The overall accuracy rate sat at about chance level, with 51% of respondents correctly identifying real photos and 48% correctly identifying AI-generated images.
Detailed results by image set
| Real photos | AI-generated images |
|---|---|
| Set 1: Sushi plate | |
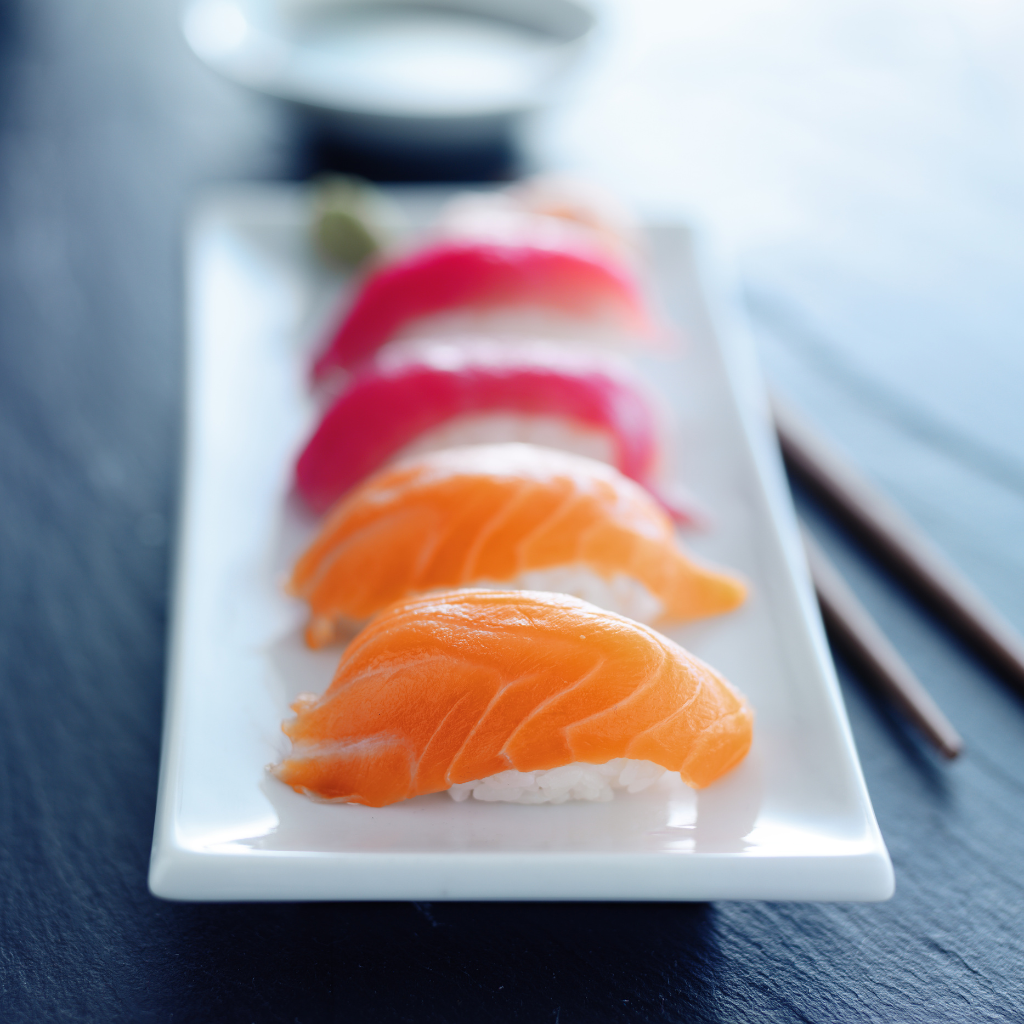 Real photo : 42% correctly identified |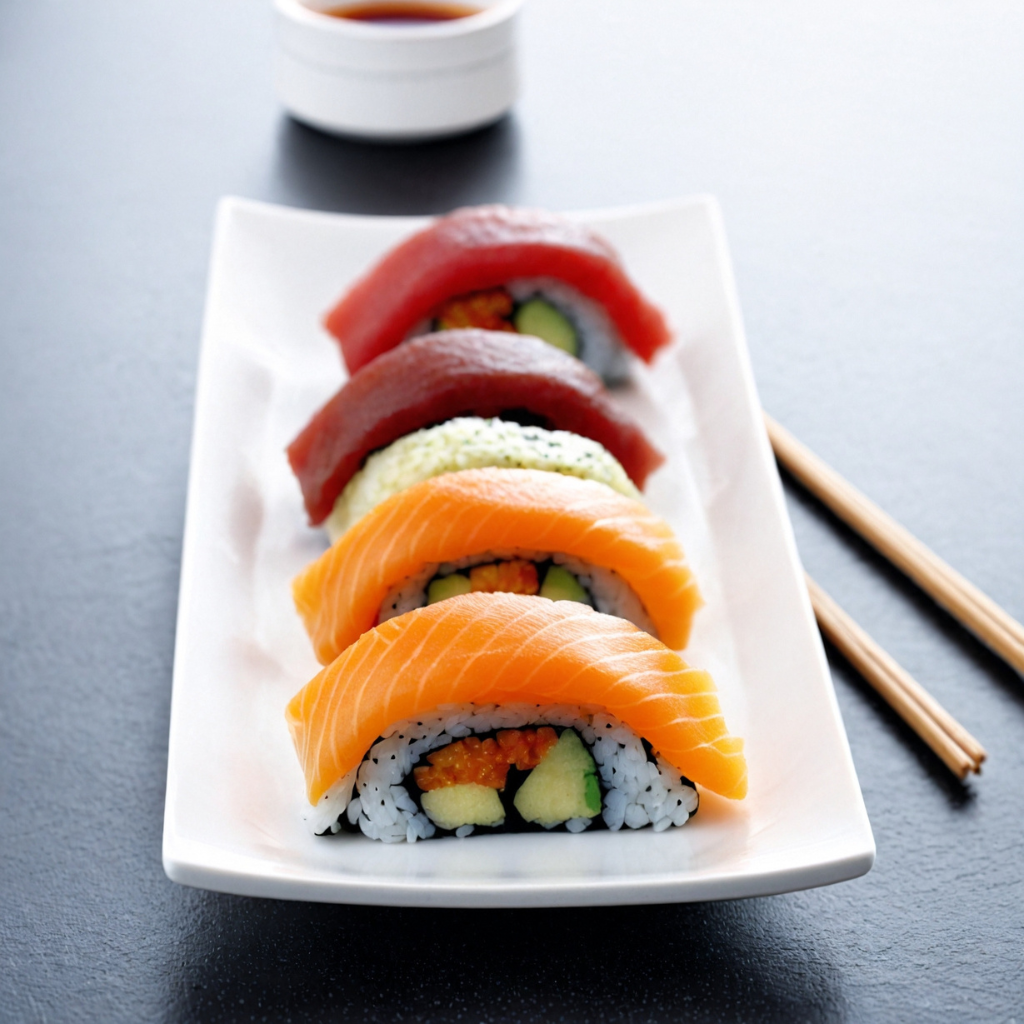  AI-generated image : 50% correctly identified |
| Set 2: Kitten in box | |
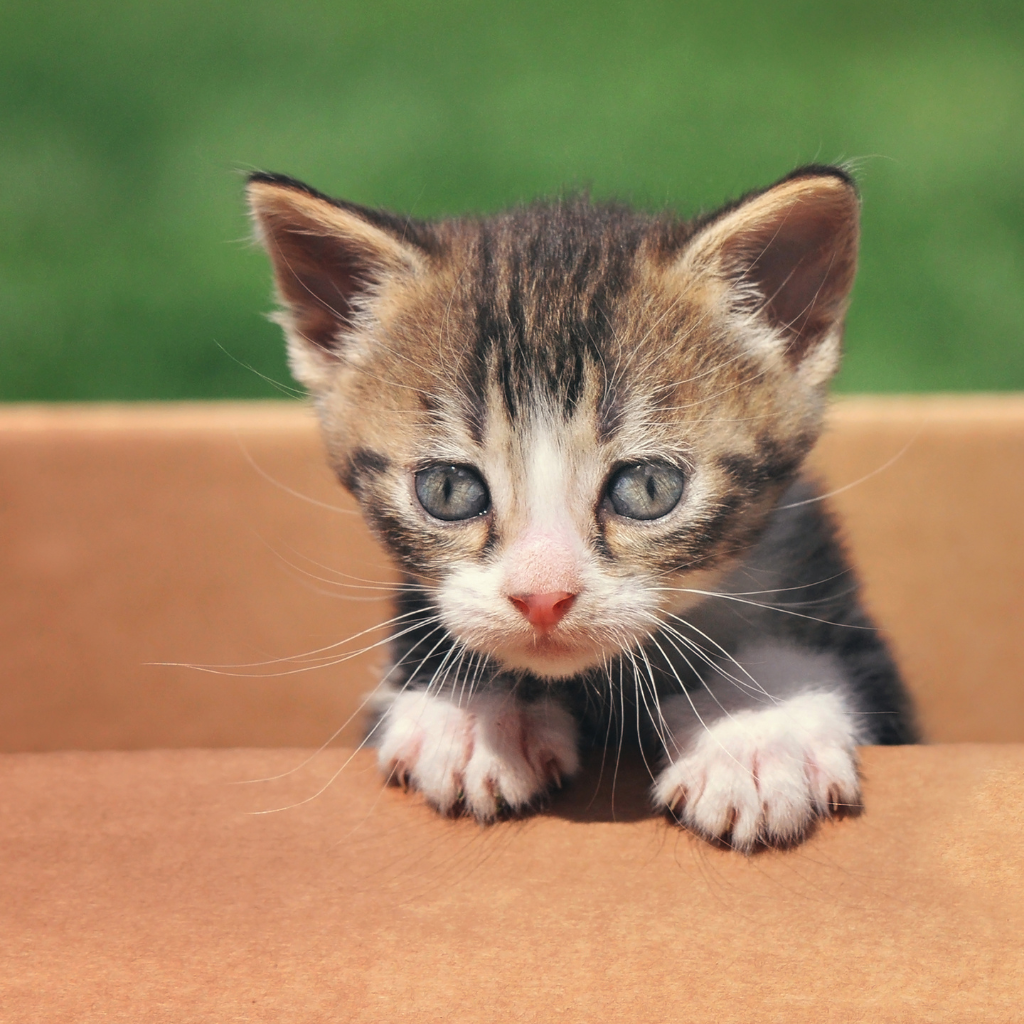 Real photo : 42% correctly identified |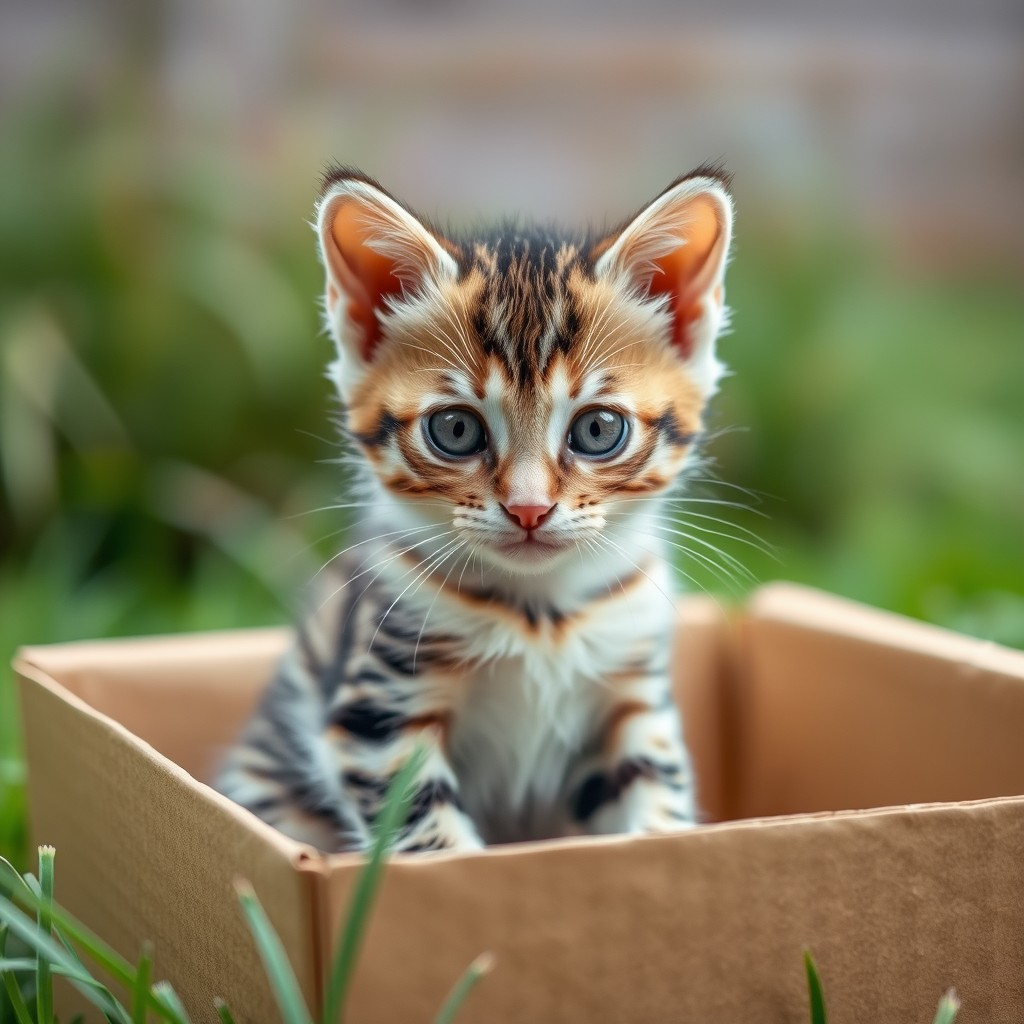  AI-generated image : 70% correctly identified |
| Set 3: Adult group photo | |
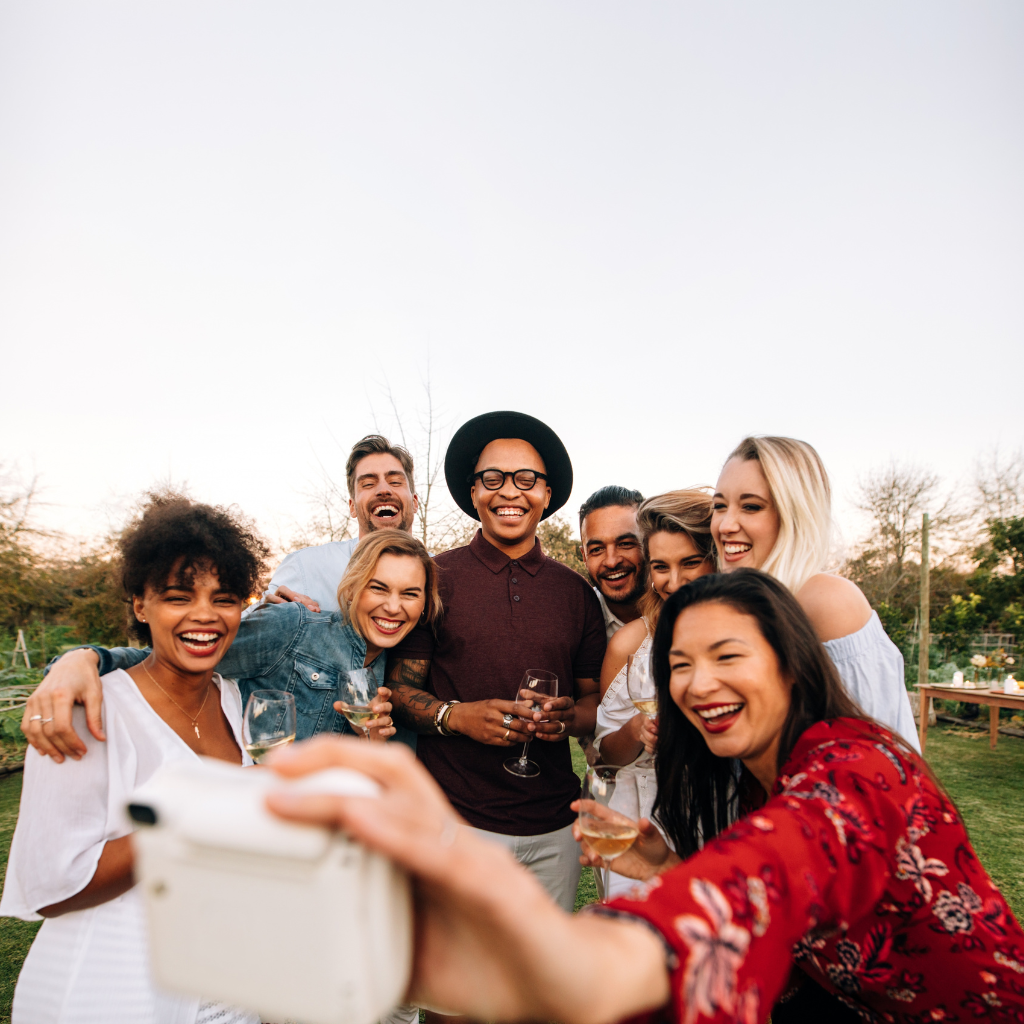 Real photo : 59% correctly identified |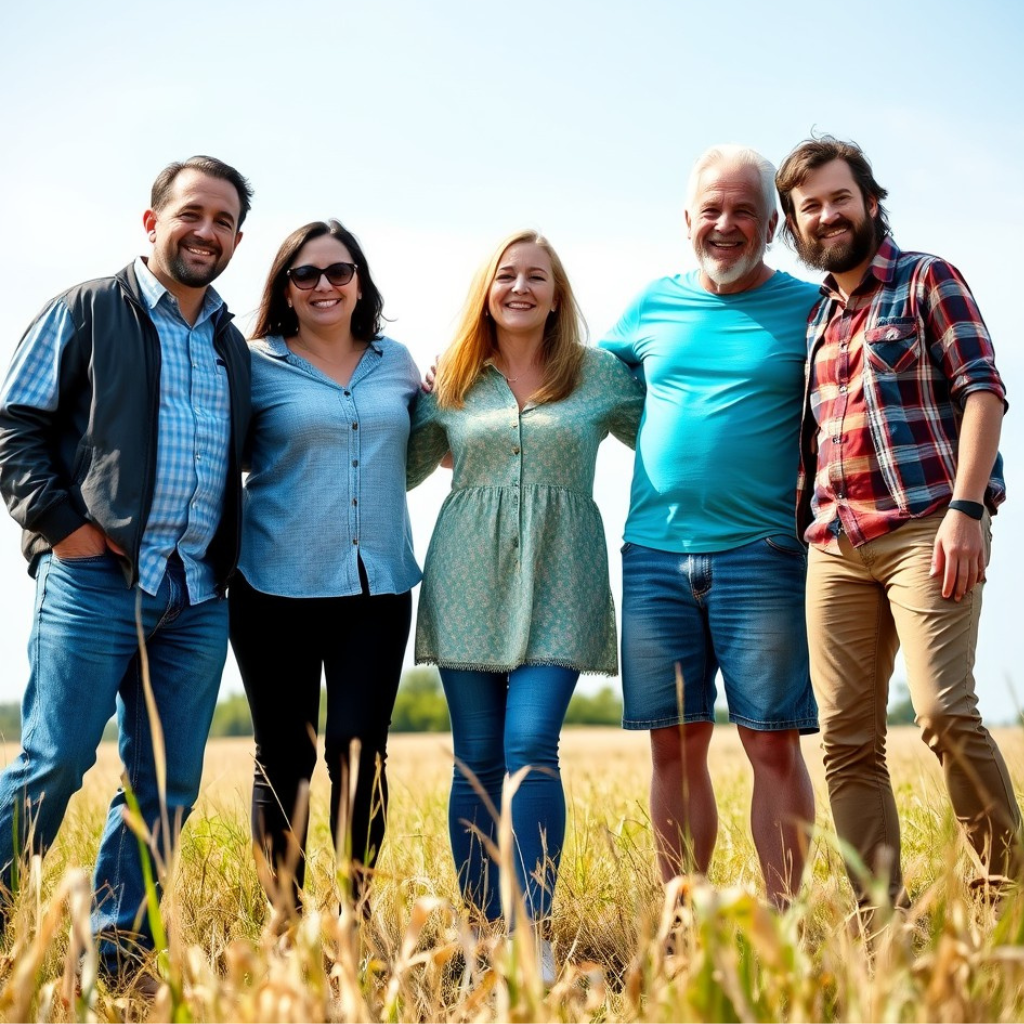  AI-generated image : 39% correctly identified |
| Set 4: Beachfront cityscape | |
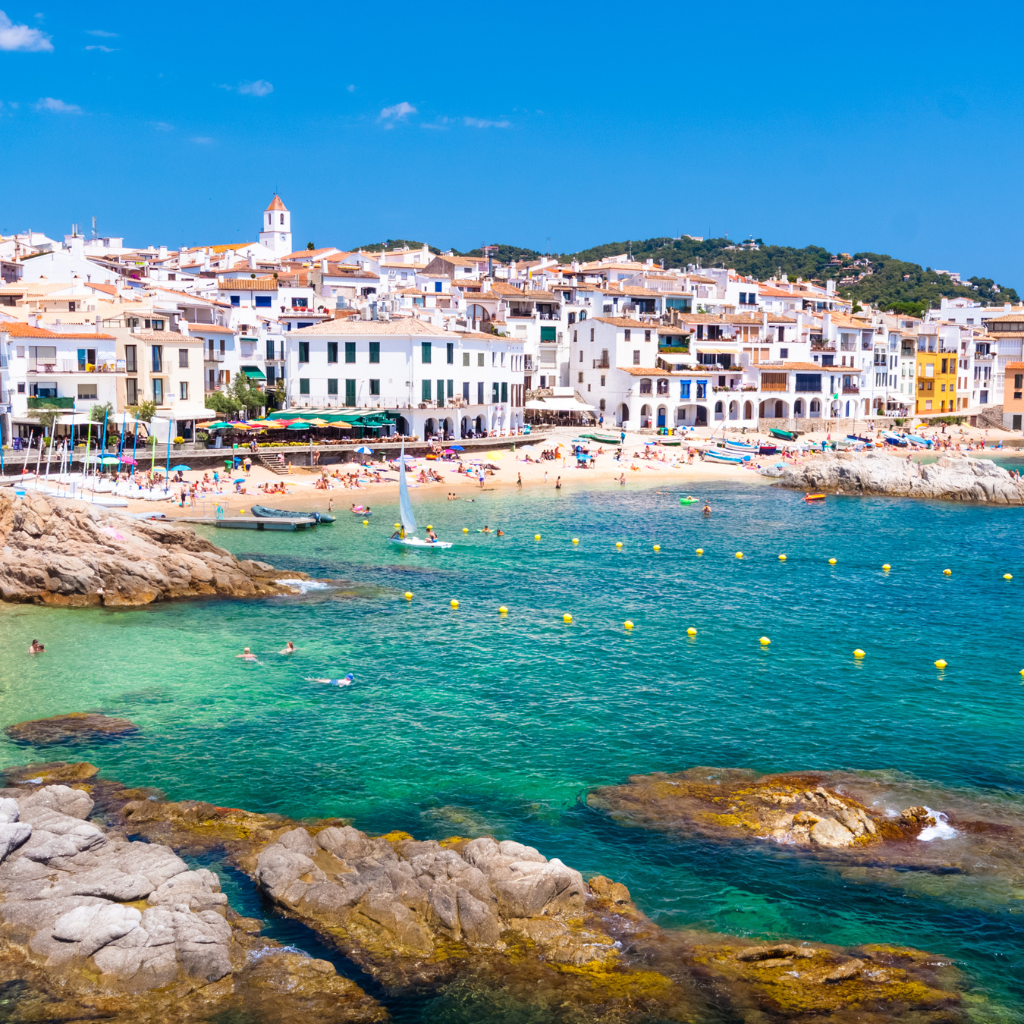 Real photo : 42% correctly identified |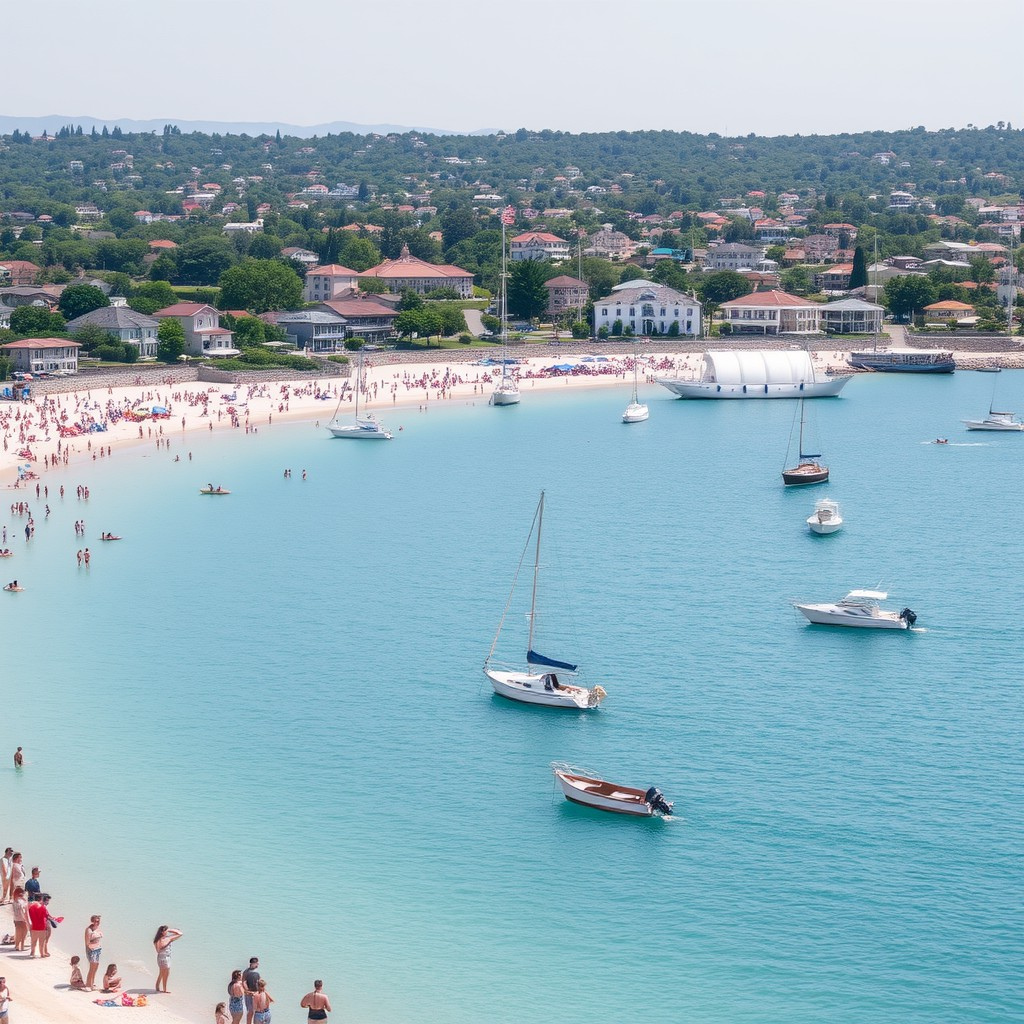  AI-generated image : 50% correctly identified |
| Set 5: Classroom scene | |
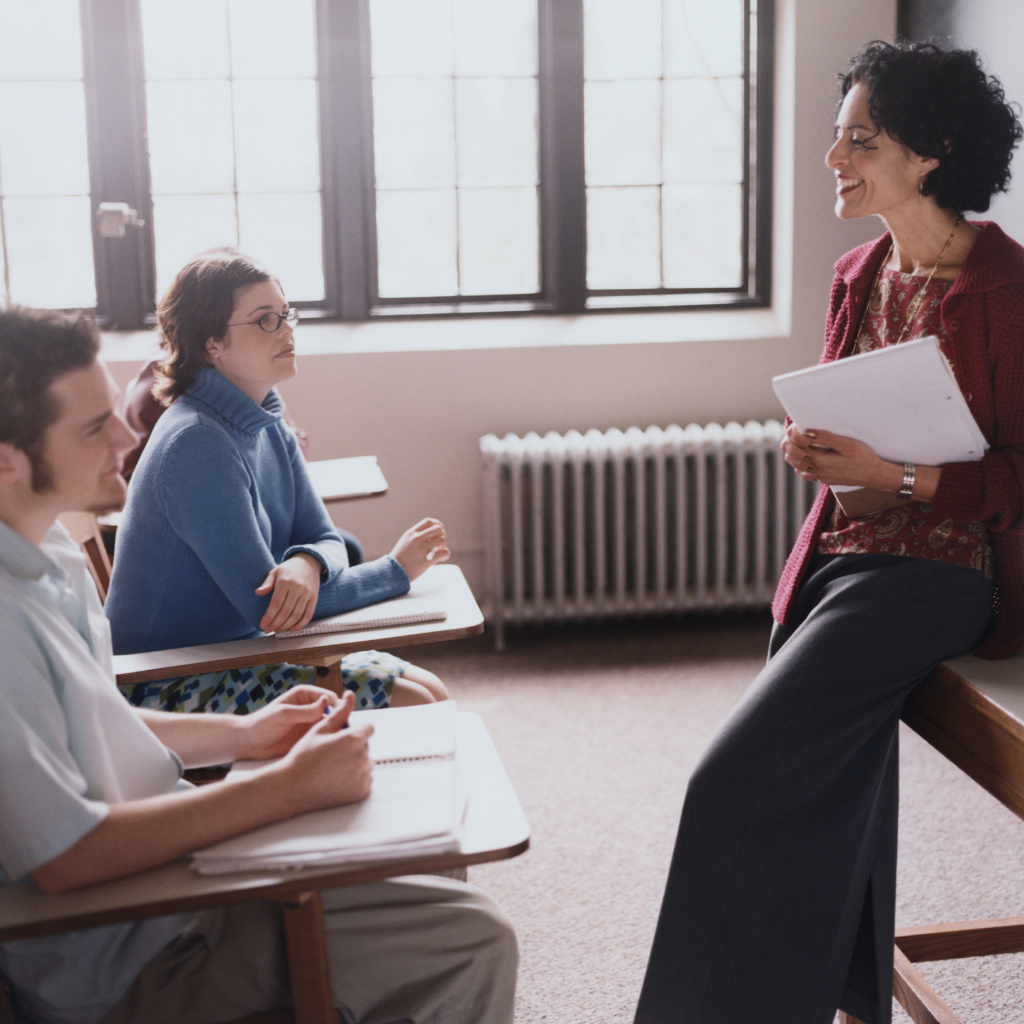 Real photo : 71% correctly identified |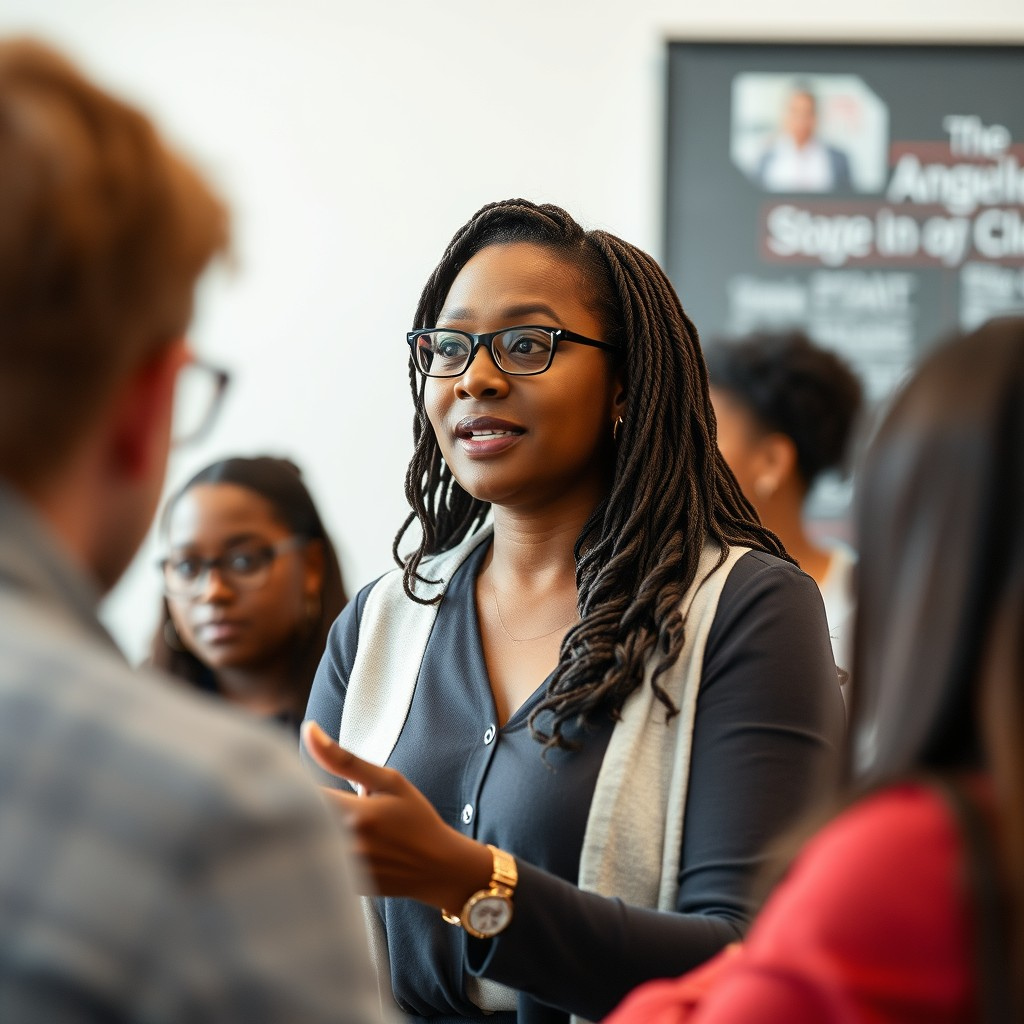  AI-generated image : 35% correctly identified |
| Set 6: Modern living room | |
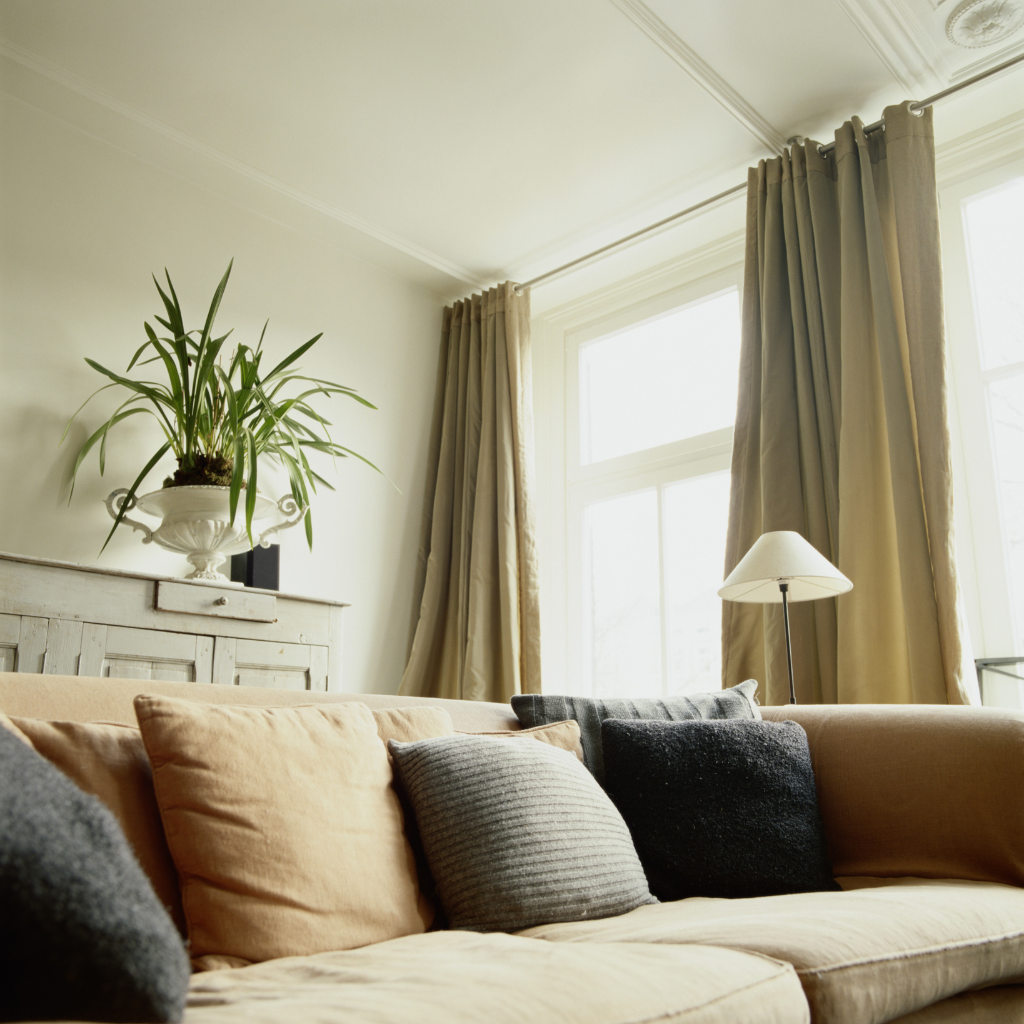 Real photo : 55% correctly identified |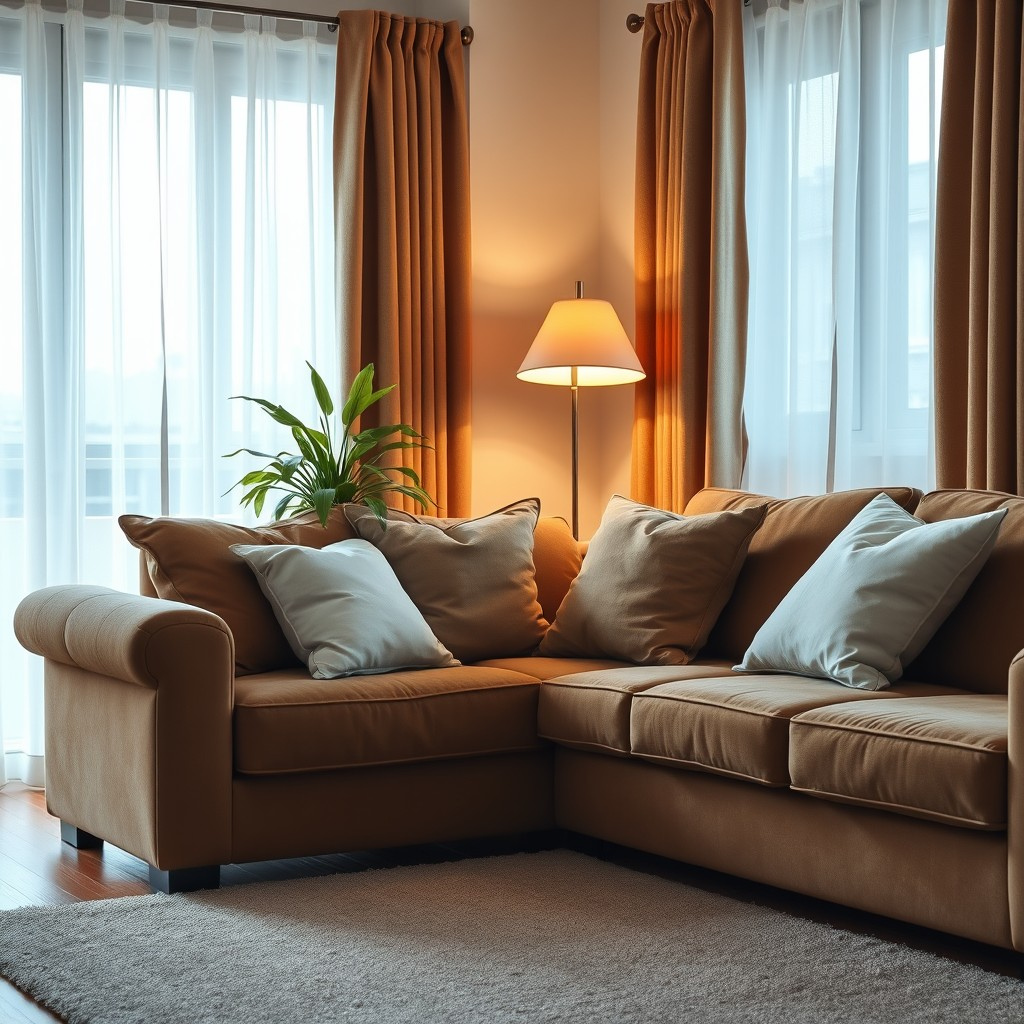  AI-generated image : 47% correctly identified |
| Set 7: Female model potrait | |
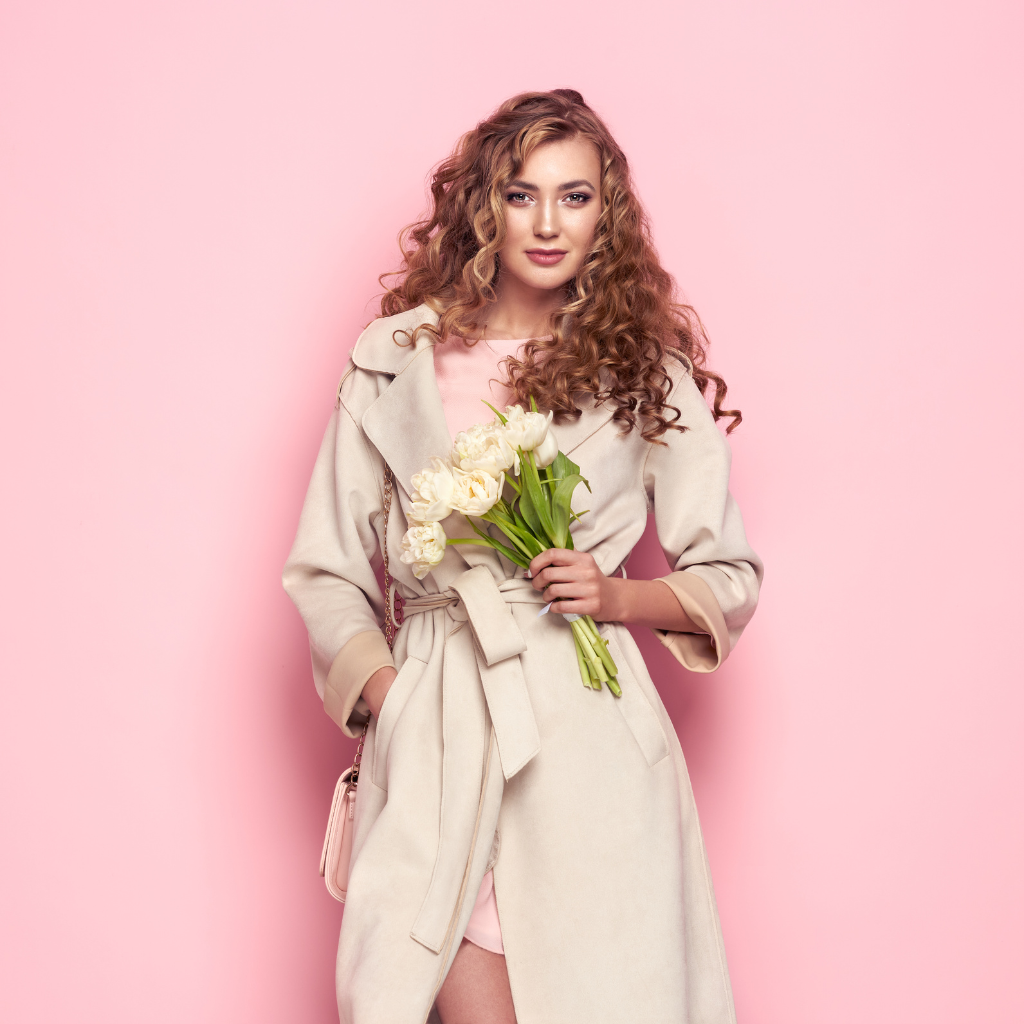 Real photo : 49% correctly identified |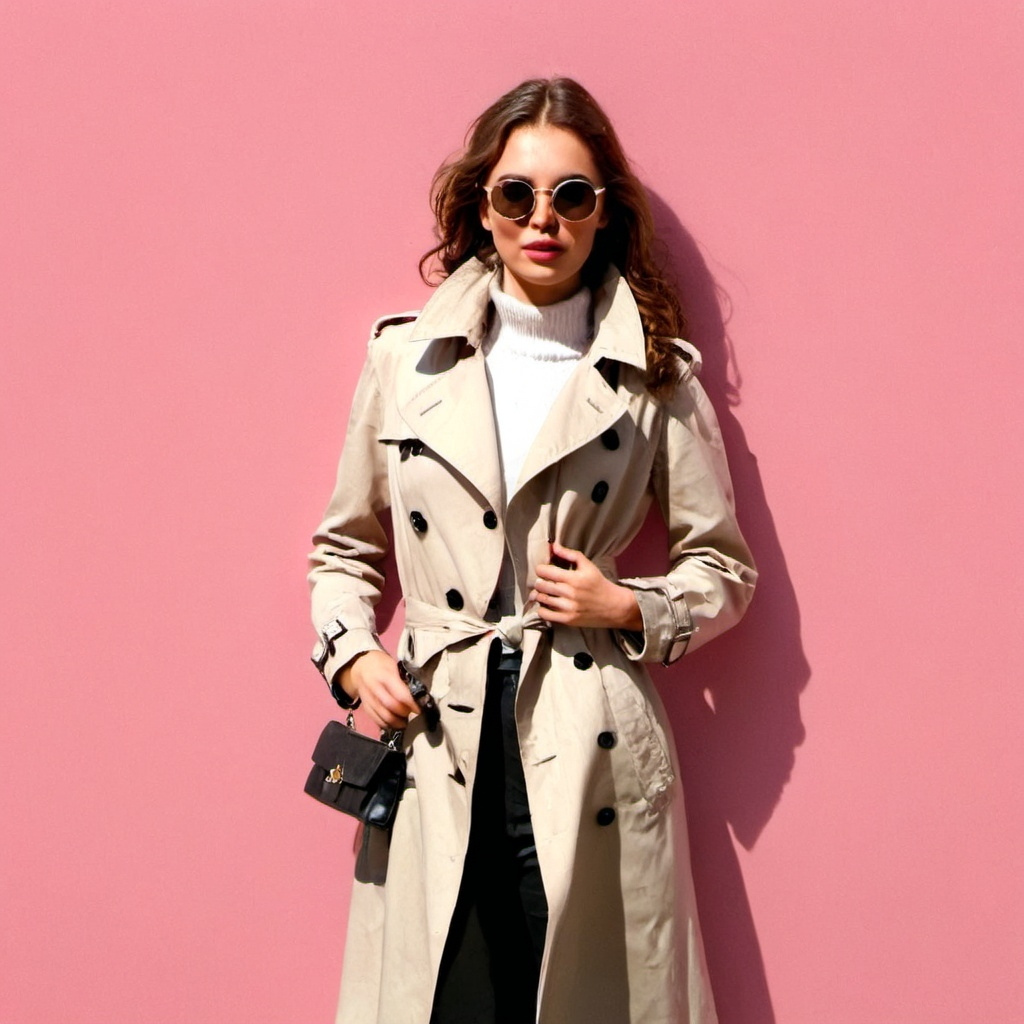  AI-generated image : 47% correctly identified |
| Average : 51% correctly identified Real photos | Average : 48% correctly identified AI-generated images |
Notably, identification accuracy fell for both real and AI images compared to the previous survey conducted in June 2023, with AI image detection saw a steeper decline, falling from 56% to 48%.
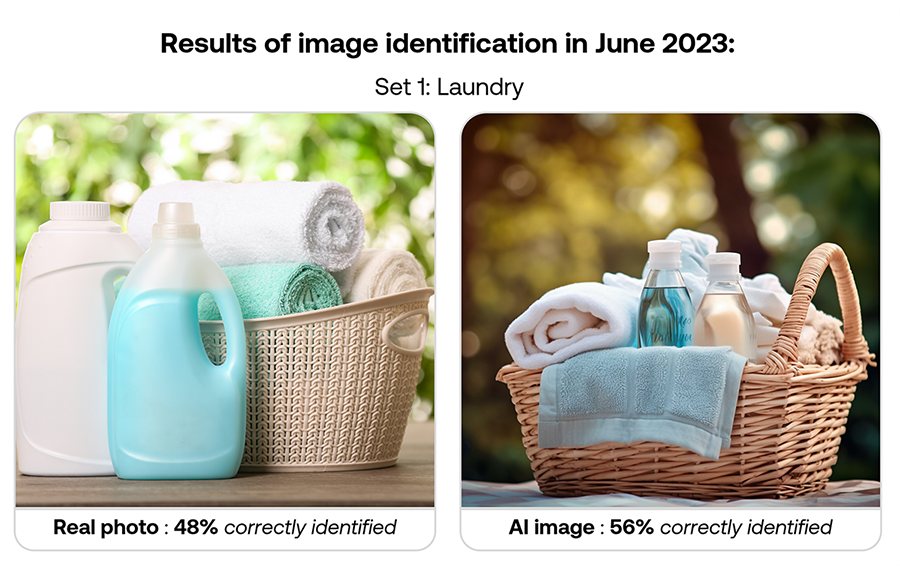
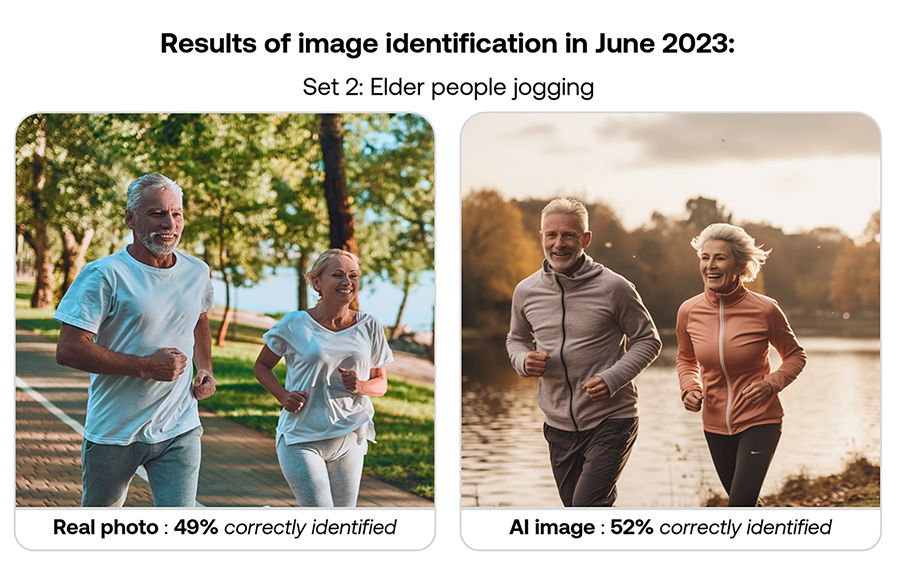
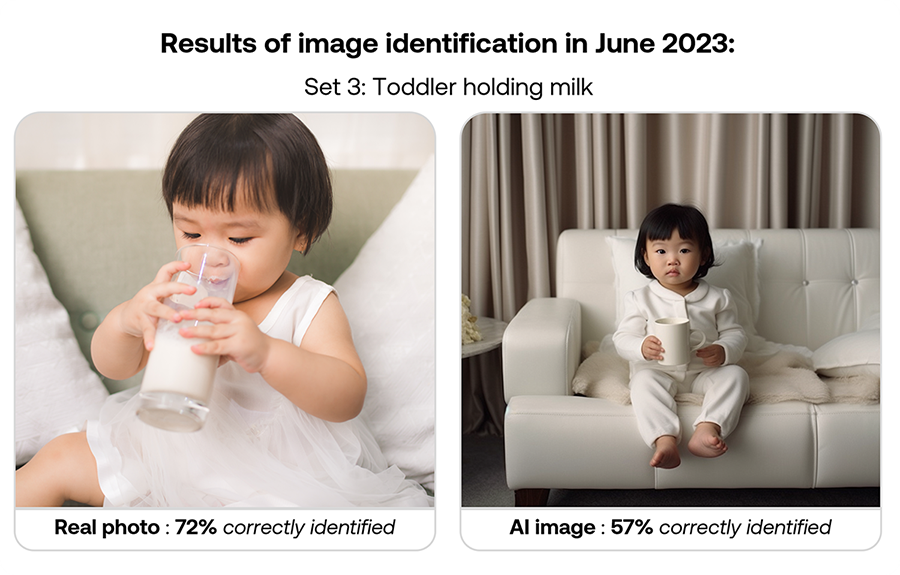
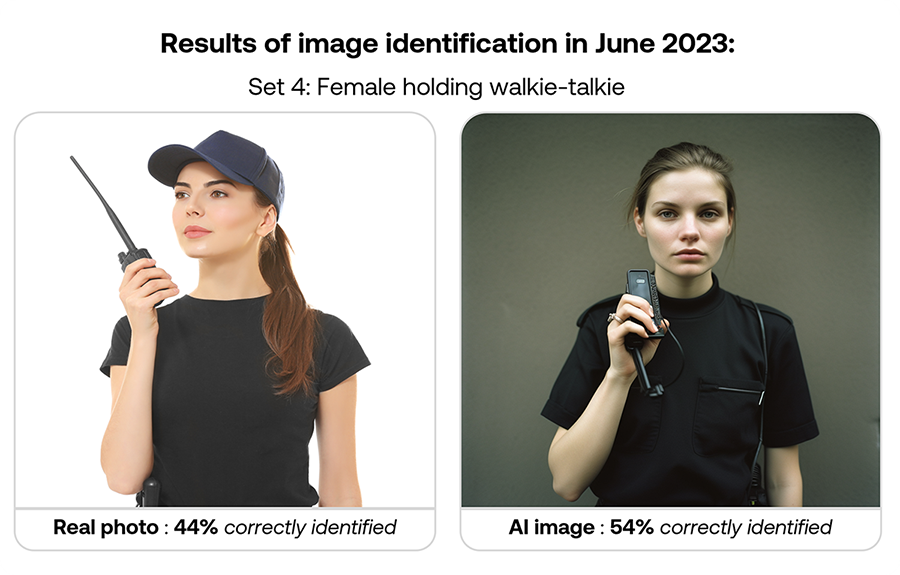
Here’s how participants performed in June 2023:
Image identification accuracy by age group
The youngest respondents (aged 18-29) demonstrated the highest overall performance in correctly identifying both AI and real images, with an average accuracy of 58% for AI and 55% for real images. This higher performance likely stems from their greater exposure to and familiarity with digital media and AI technologies.
The 45-64 age group showed notable accuracy with specific images, such as the AI images in set 1 sushi plate and set 4 beachfront cityscape, as well as the real image in set 5 classroom scene.
The 65+ age group achieved the lowest accuracy overall, particularly with AI-generated images, achieving only 39% average accuracy.
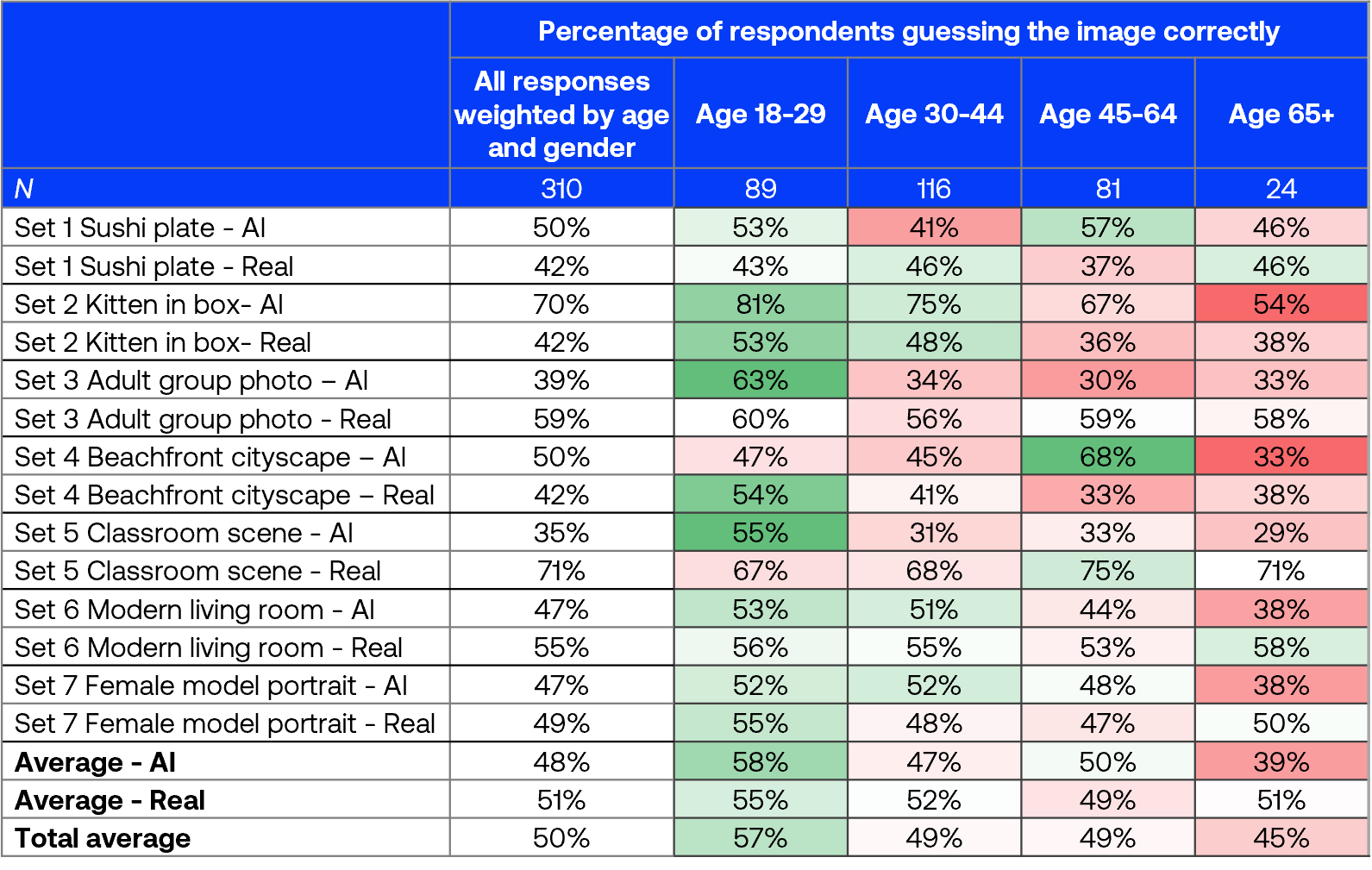
The colour coding represents the degree of deviation from the weighted all response, green = higher and red = lower.
AI tool usage and awareness
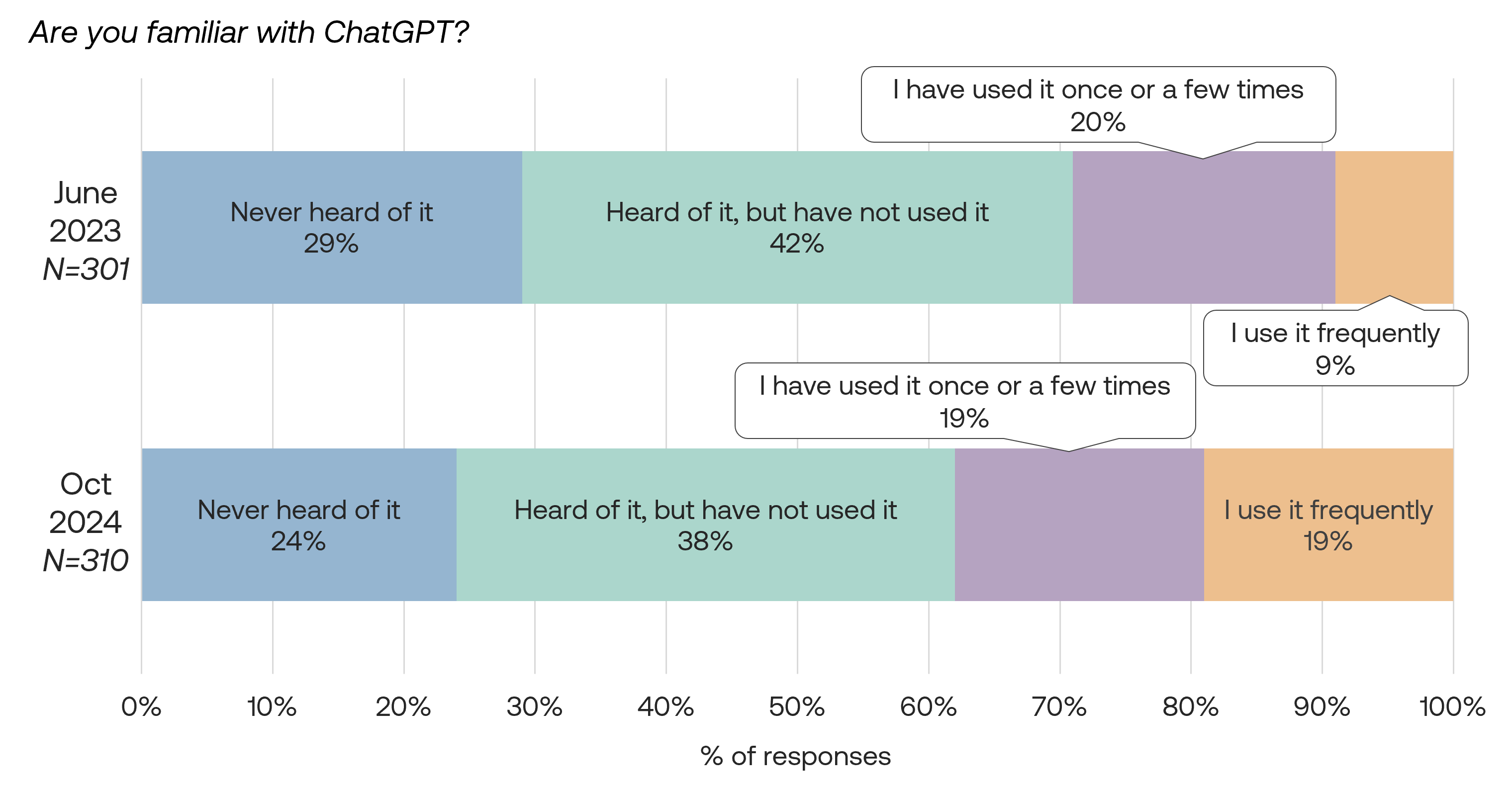
Awareness and adoption of ChatGPT
Compared to June 2023, this survey shows a doubling of frequent ChatGPT users from 9% to 19%, while those unaware decreased from 29% to 24% and those who are aware but haven’t used it declined from 42% to 38%.
Awareness and adoption of emerging AI tools
Looking into non ChatGPT tools, Google Gemini and Microsoft Copilot lead in awareness among AI tools, at 56% and 39% respectively, showing high visibility of AI-powered digital assistants integrated into major tech ecosystems. However, 26% of respondents remain unaware of any AI tools.
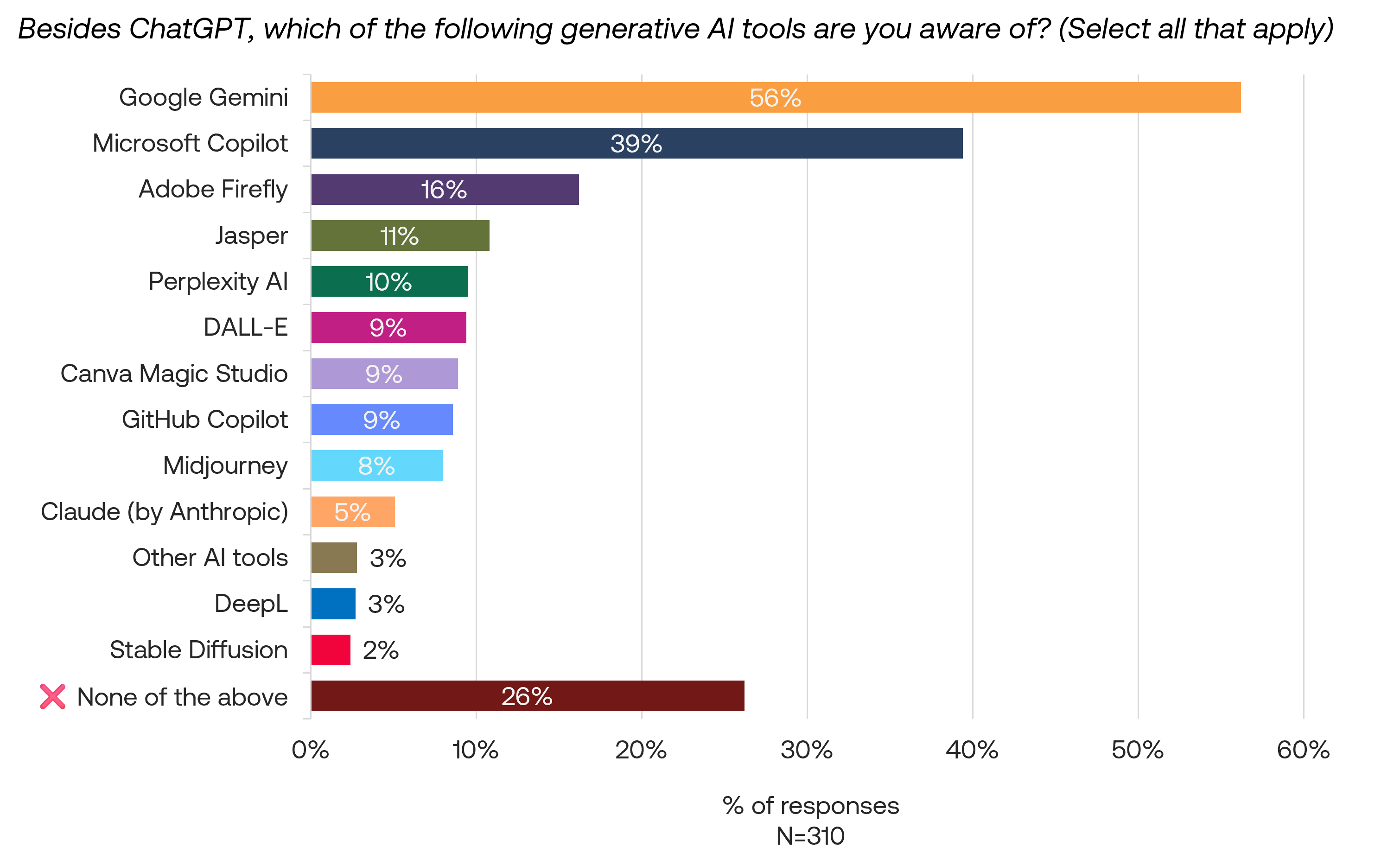
Among respondents aware of AI tools, Google Gemini leads in recent usage (41%), followed by ChatGPT (34%) and Microsoft Copilot (26%). 23% reported not using any listed tools.
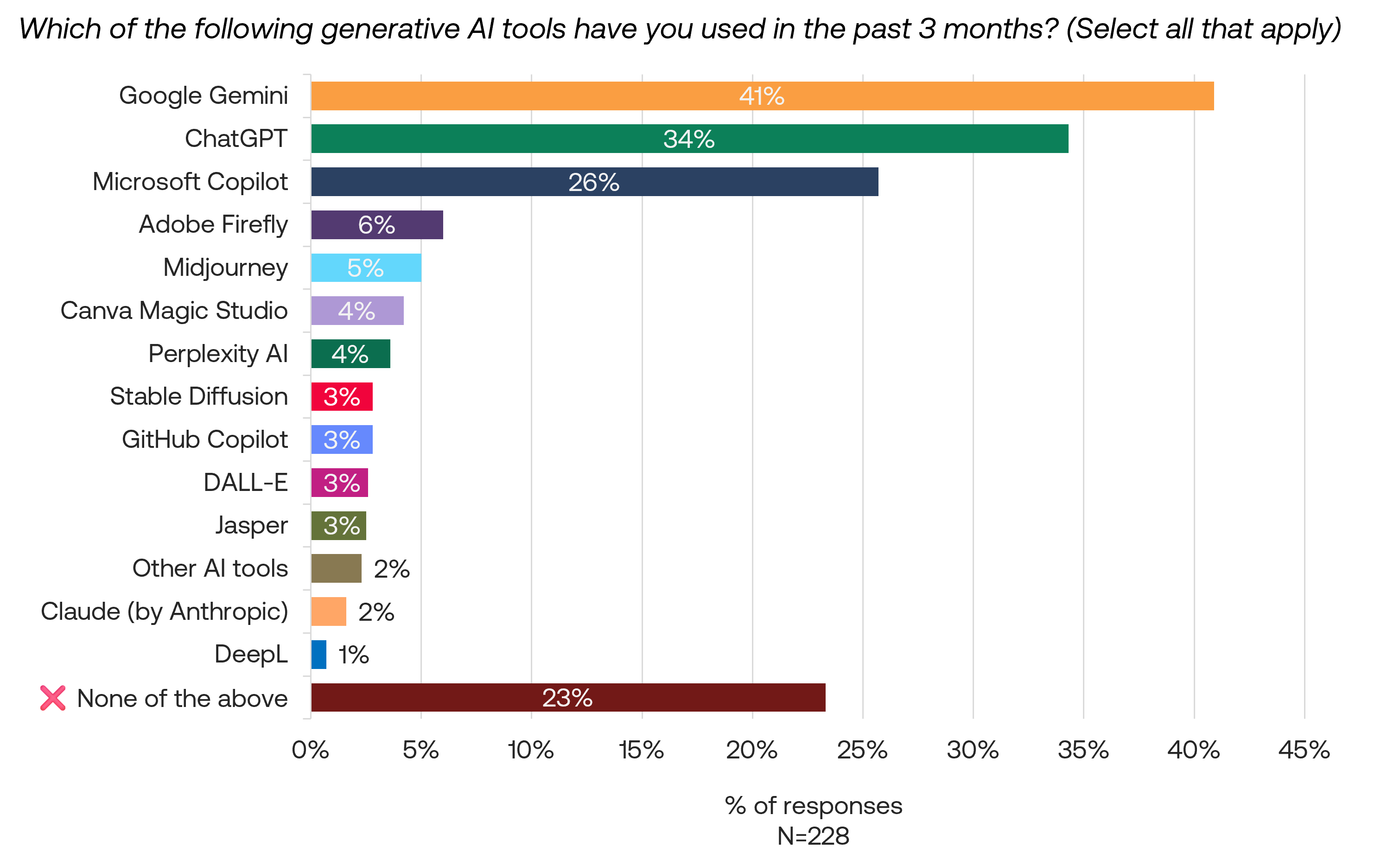
Changes in usage patterns among AI users
Among current users of ChatGPT and other AI tools, responses indicate a significant uptick over the past year. 63% report using AI tools more frequently, and 64% now use more AI tools. Only about 10% decreased their AI tool usage in both frequency and variety.
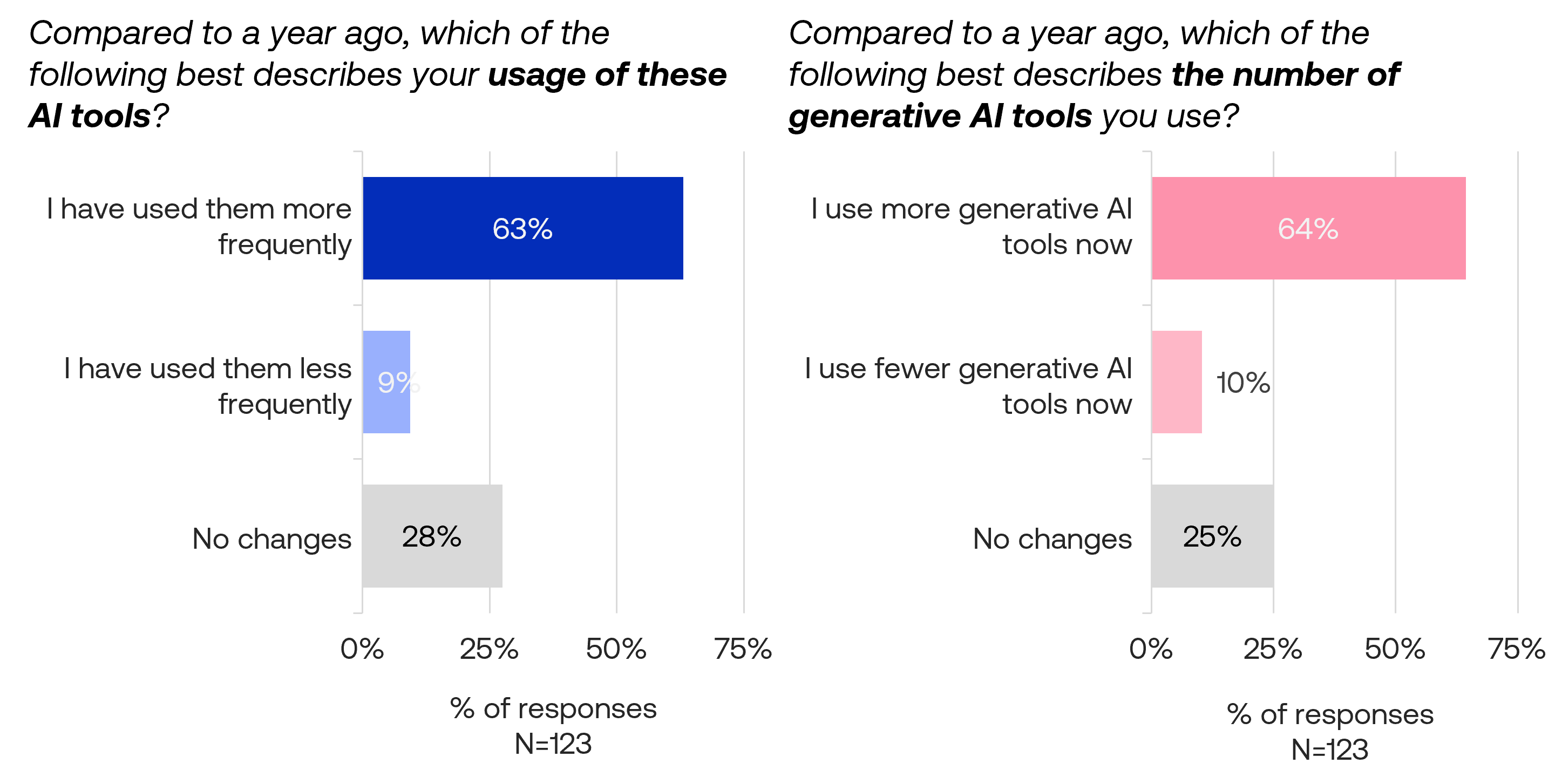
Noticing generative AI in marketing
44% of respondents reported recently encountering AI-generated marketing content, up from 38% in June 2023, while 22% hadn’t noticed such content and 34% were unsure.
Both younger respondents (aged 18-44) and AI tool users were more likely to report encountering AI-generated marketing content.
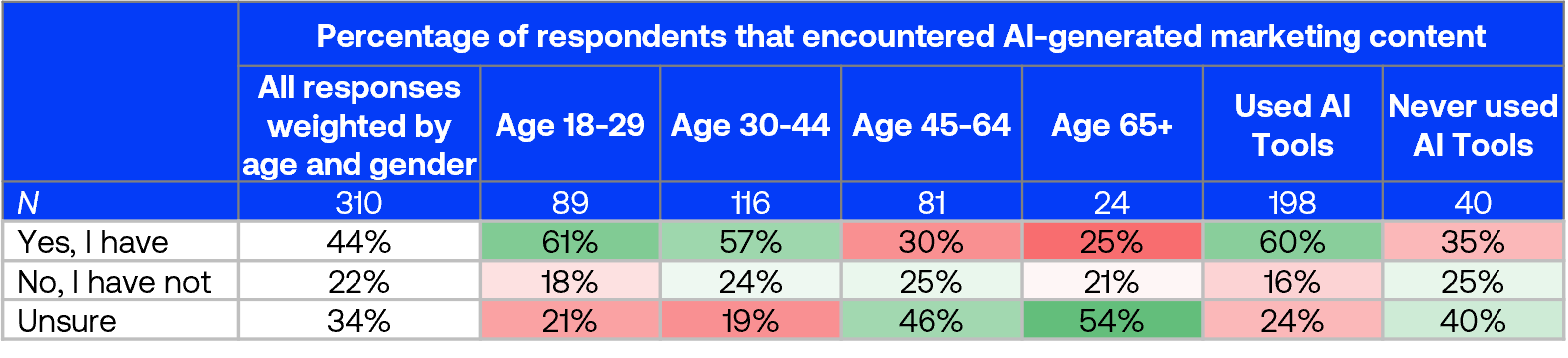
The colour coding represents the degree of deviation from the weighted all response, green = higher and red = lower.
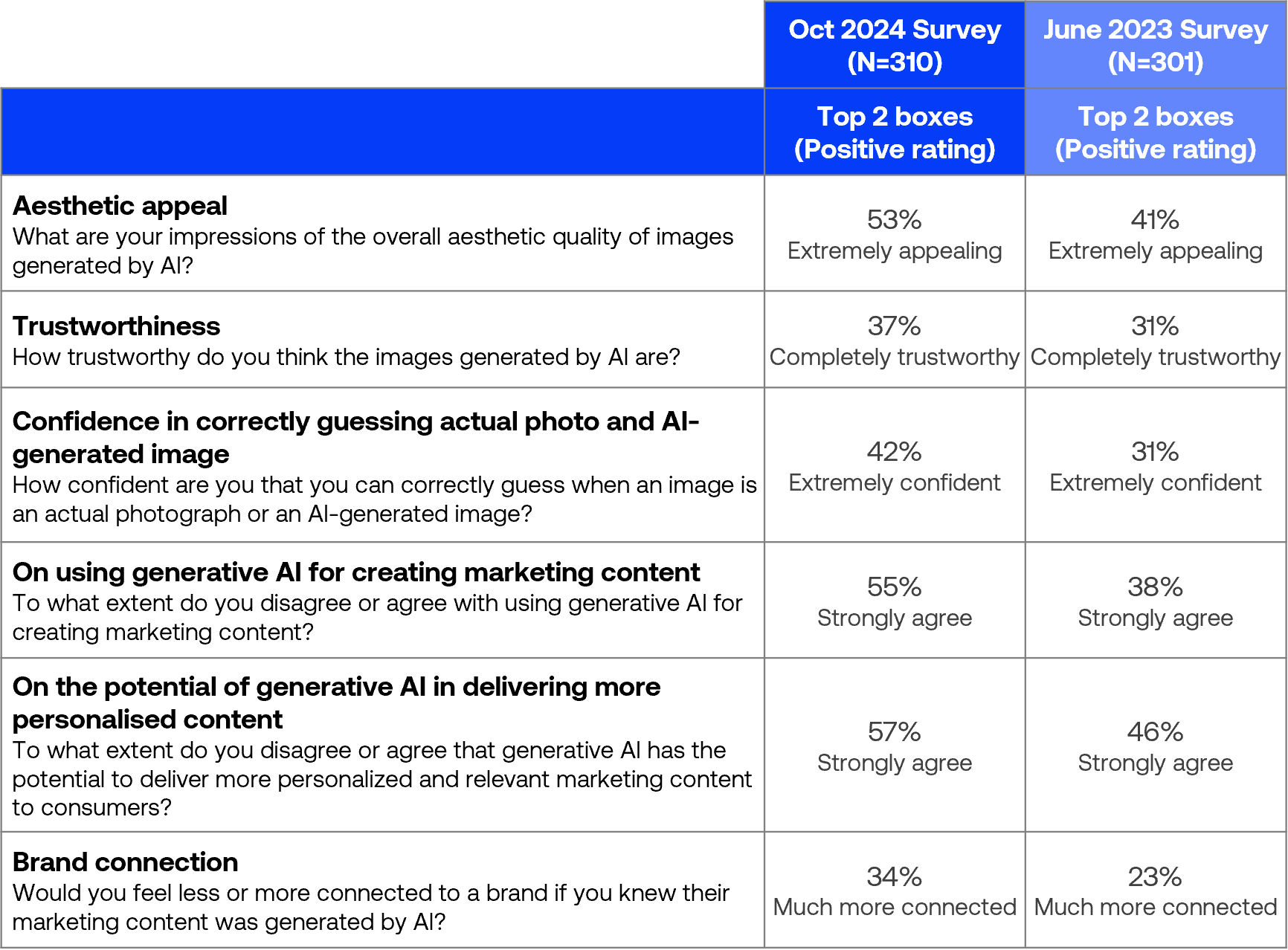
Attitude and preferences towards the use of generative AI in marketing
Consumer perception of AI-generated content improved across all measured aspects, with notable increases in aesthetic appeal (41% to 53%), confidence in identifying AI images (31% to 42%), and acceptance of AI in marketing (38% to 55%).
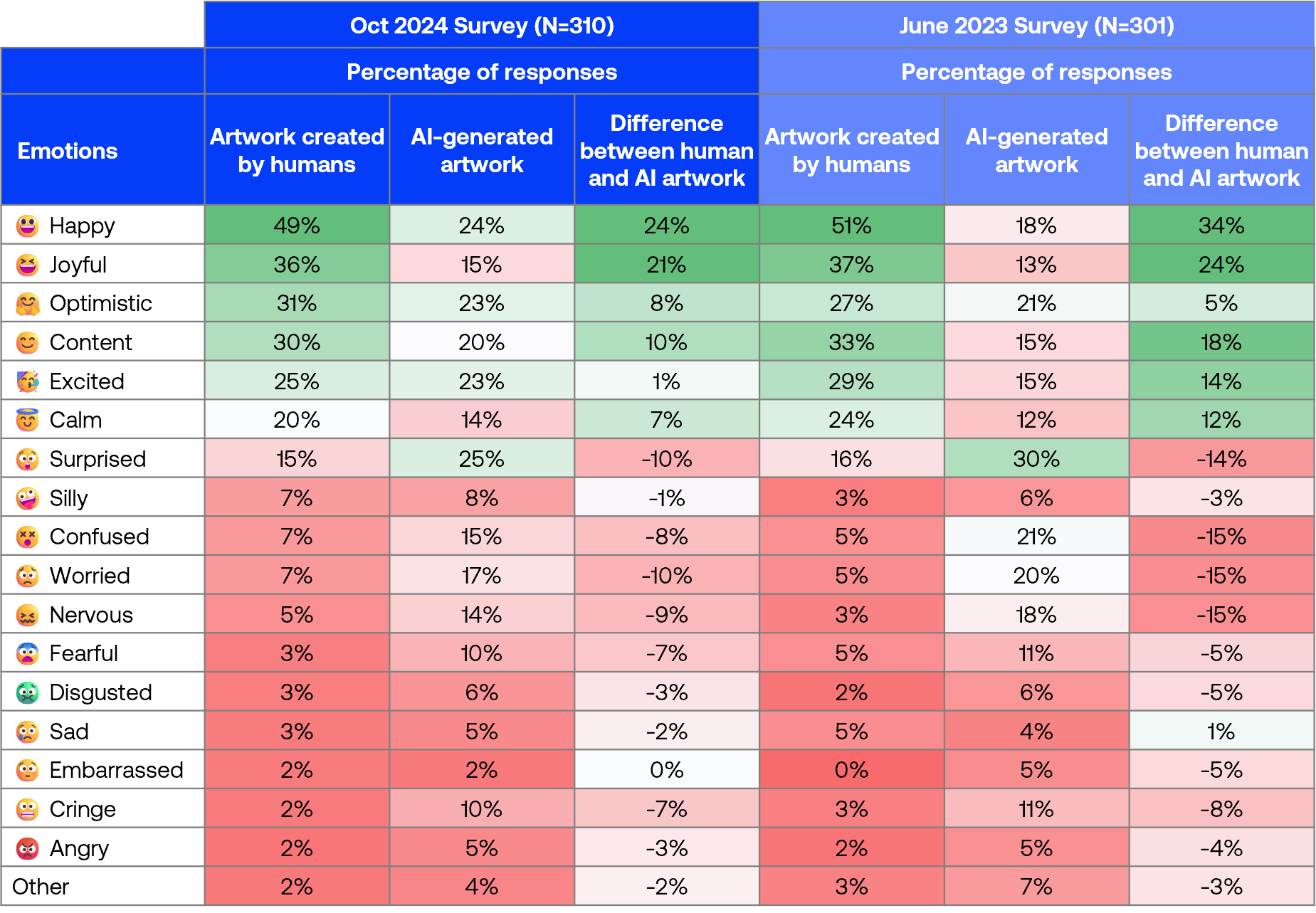
Emotions toward human artwork vs. AI-generated images
Overall, human artwork still elicits more positive emotions such as happy, joyful, and content. However, the differences in responses for human-created and AI-generated images have narrowed across most categories, with AI-generated images now evoking more positive emotions (e.g. happy increased from 18% to 24%) and fewer negative emotions (e.g. confused decreased from 21% to 15%).
Summaries of open-ended responses
What motivates you to use these generative AI tools?
Respondents primarily use generative AI for practical and creative purposes. Many are drawn by natural curiosity about the technology’s capabilities. The tools also serve as productivity aids for writing, research, and problem-solving tasks. Some respondents appreciate the creative applications, from image generation to content creation. The technology also appeals as a learning resource and for entertainment, with users noting its accessibility and ability to overcome creative blocks.
Do you have any concerns or reservations about using AI-generated content in marketing?
Trust and authenticity emerged as primary concerns. Respondents also raised points about potential job displacement and ethical considerations around privacy violations and accountability. Quality control and accuracy of AI-generated content remained key issues, particularly regarding cultural sensitivity. The increasing difficulty in distinguishing between AI and human-created content made some respondents uneasy.
Do you have any hopes or aspirations about using AI-generated content in marketing?
Respondents expressed mixed views about AI’s role in marketing’s future. Some anticipate enhanced creativity and personalization in content creation, along with improved efficiency in marketing operations. Others maintain reservations about maintaining authentic human connections and professional roles. A notable portion of respondents indicated they need more information before forming definitive opinions about AI’s marketing applications.
Key takeaways
- Consumers struggle to distinguish between real and AI-generated images, with accuracy of identifying AI images declining since our 2023 study.
- Age plays a role in AI image recognition. The 18-29 age group shows the highest accuracy, while older age groups demonstrate lower accuracy rates.
- AI tool adoption and awareness continues to grow, with Google Gemini leading both awareness and recent usage among AI tools.
- The use of AI-generated marketing content is becoming more noticeable, and the emotional gap between human and AI-created content is narrowing.
- Consumers express optimism about AI’s potential for enhanced creativity and productivity, but maintain concerns about trust, authenticity, job displacement, and the increasing difficulty in distinguishing AI from human-created content.