Conjointly checks consumers' attitudes towards generative AI in marketing.
The rapid development of artificial intelligence (AI) holds promise to revolutionise various industries, and marketing is no exception. In recent years, a powerful branch of AI known as generative AI has emerged, which allows users to generate texts, images, videos, and even music. It allows businesses to streamline their content creation processes, and maybe deliver more compelling and personalised content to their audiences at scale.
As generative AI becomes more prevalent in marketing, questions arise regarding its impact on authenticity, trust, and overall consumer experience. In order to shed light on this topic, Conjointly ran a survey with 301 respondents representative of the USA general adult population between 5 and 7 June 2023. In this survey, respondents were asked to:
- Recall if they have recently encountered any marketing content generated by AI.
- Express their opinions on the types of marketing content suitable for generative AI.
- Share their attitudes towards AI-generated content on 5-point scale questions:
- Aesthetic impression of images
- Trustworthiness of images
- Confidence in identifying real vs. AI-generated images
- General attitude towards using generative AI for marketing content
- Attitude towards generative AI in delivering personalised marketing content
- Connection to a brand when it uses AI-generated marketing content
- Attitude towards revenue sharing with human creators whose works are used in AI training
- Choose up to three most prominent emotions when viewing human artworks vs. AI-generated images.
- Review a set of pictures and try to identify if each of them is an actual photograph or an AI-generated image.
- Provide open-ended responses to express their concerns/reservations and hopes/aspirations about using AI-generated content in marketing.
- Answer demographic questions, which were used for weighting and subgroup analysis.
Overall Results
Noticing generative AI in marketing
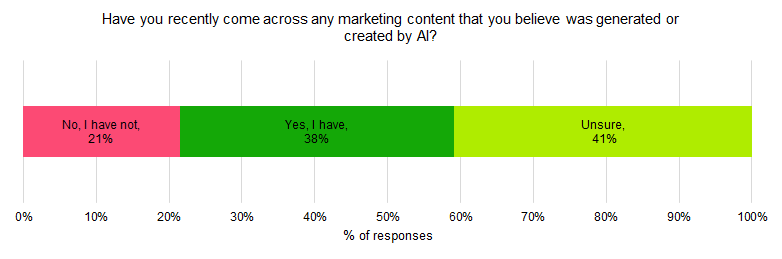
38% of respondents recalled having come across marketing content that they believed was generated by AI, while there were about 21% did not and 41% were unsure:
Younger respondents (and those who used ChatGPT) tended to encounter AI-generated marketing content more than others:
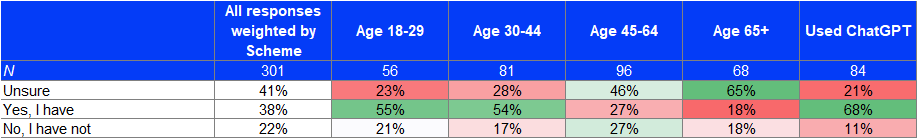
The colour coding represents the degree of deviation from the weighted all response, green = higher and red = lower.
Attitudes towards generative AI in marketing
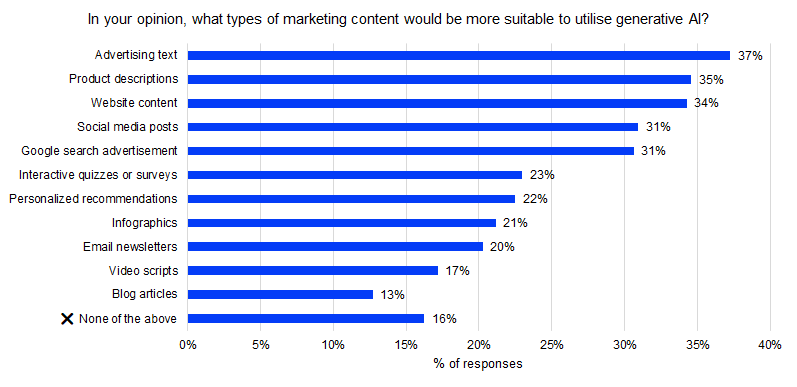
Many people (but not a majority) considered creating advertising text, product descriptions, and website content as suitable uses for generative AI:
The table below summarises respondents’ attitudes towards the use of generative AI in marketing:
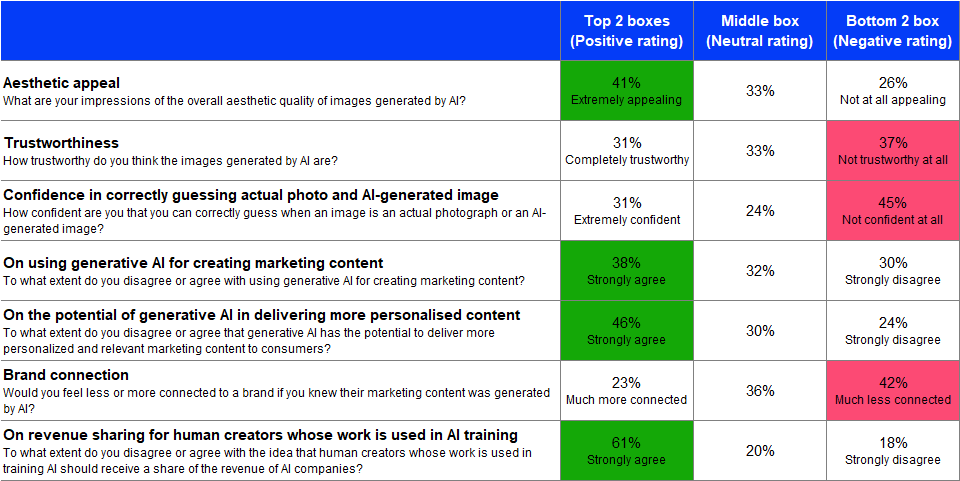
There were many respondents (but not a majority) who thought that the AI-generated images were appealing to them. Many respondents also agreed with using generative AI for creating marketing content, as well as its potential to deliver more personalised and relevant content.
On the other hand, there were many respondents who thought AI-generated images were not trustworthy. Many respondents also showed low confidence in identifying AI-generated images from actual photographs, as well as felt less connected to a brand if it used AI-generated marketing content.
A majority of respondents agreed with the need for revenue sharing for human creators whose works are used in AI training.
Older people were less likely to consider AI-generated content appealing, trustworthy. They did not trust their ability to correctly identify AI-generated images.
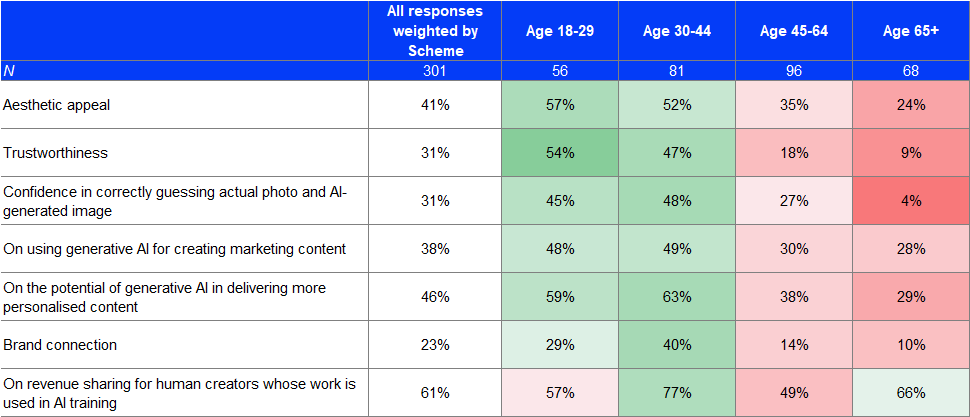
The colour coding represents the degree of deviation from the weighted all response, green = higher and red = lower.
Emotions for human artworks v.s. AI-generated images
Human artworks tended to elicit more positive emotions such as “happy”, “joyful”, and “content”. AI-generated images tended to elicit the emotion of “surprised”, followed by “optimistic”, “confused”, and “worried”. This suggests that respondents tended to feel more apprehensive about AI-generated images.
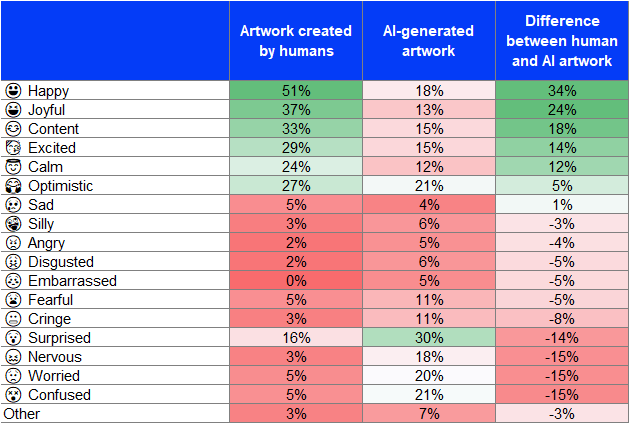
The colour coding represents the respondents’ distribution per column, green = higher % and red = lower %
Accuracy in identifying actual photographs vs. AI-generated images
We showed respondents five actual photographs and five images generated by Midjourney version 4. We asked them to guess if each was real or AI-generated. Overall, respondents did not perform significantly better in identifying real photographs (57%) versus AI-generated images (56%), with both accuracies slightly surpassing the chance level (50%). But we made some interesting observations:
- More respondents would guess an actual photograph correctly when it shows a more natural human movement, which is reflected by more than 70% accuracy for Set 3 (toddler drinking milk) and Set 5 (Group of friends having picnic).
- Respondents would also guess an AI-generated image correctly when the image is more complicated which is prompted to have more flaws in detail, as shown in Set 5 (Group of friends having picnic).
| Image set | % of respondents guessing correctly a real photo | % of respondents guessing correctly an AI-generated image |
|---|---|---|
| Set 1: Laundry |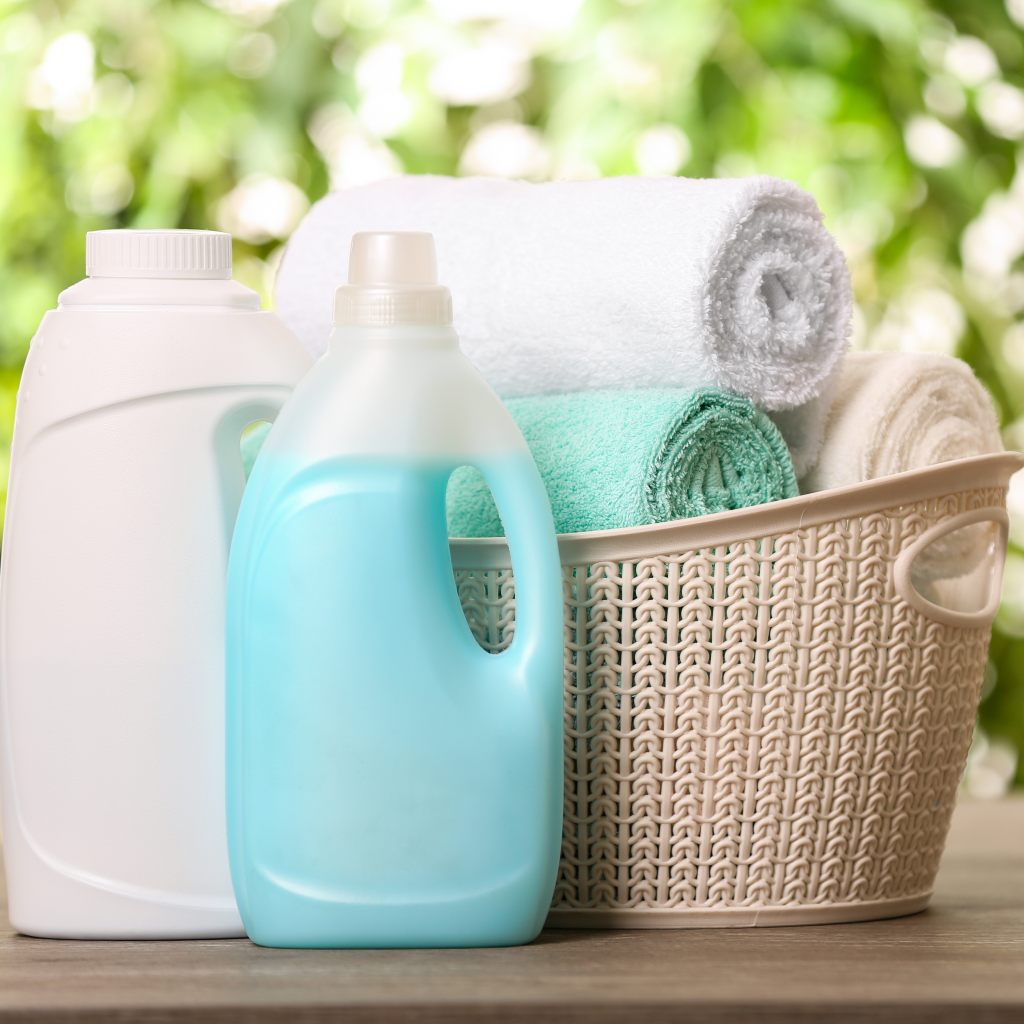  48% |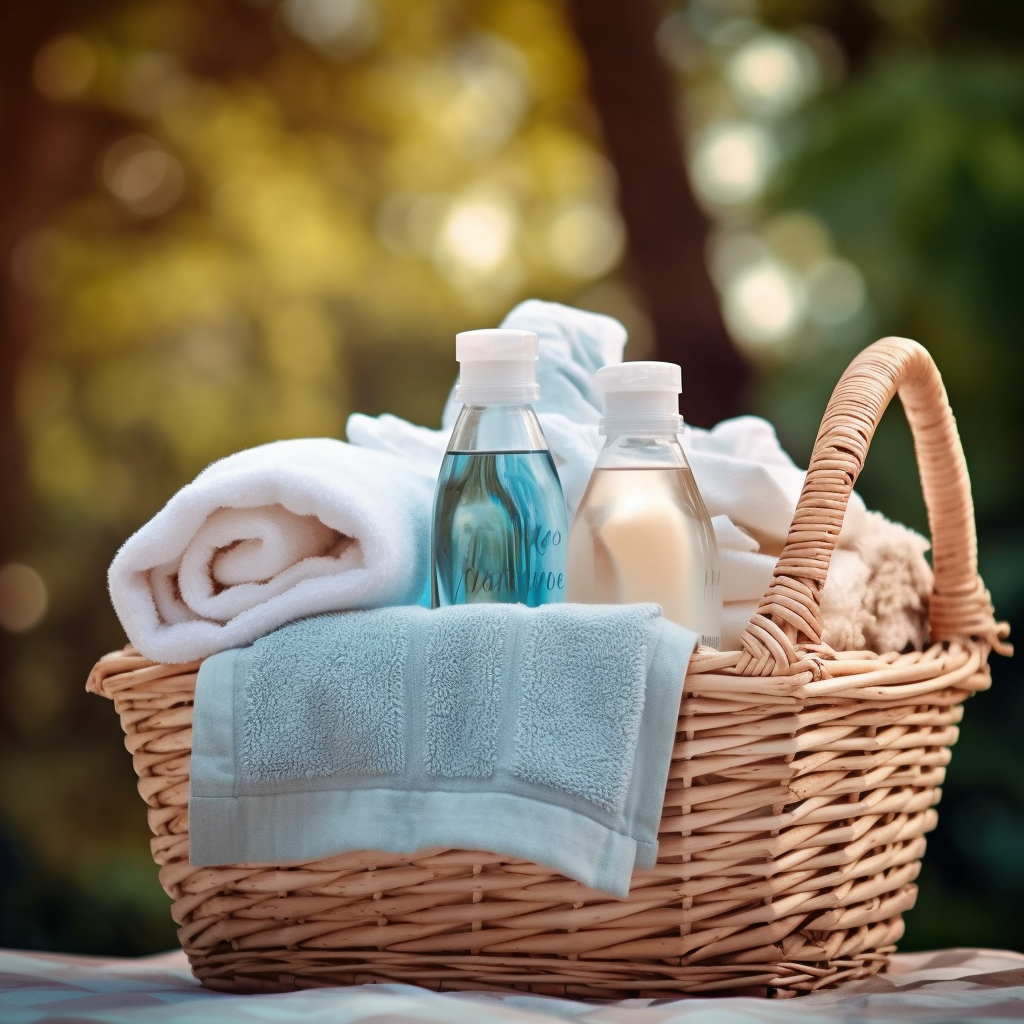  56% |
| Set 2: Elder people jogging |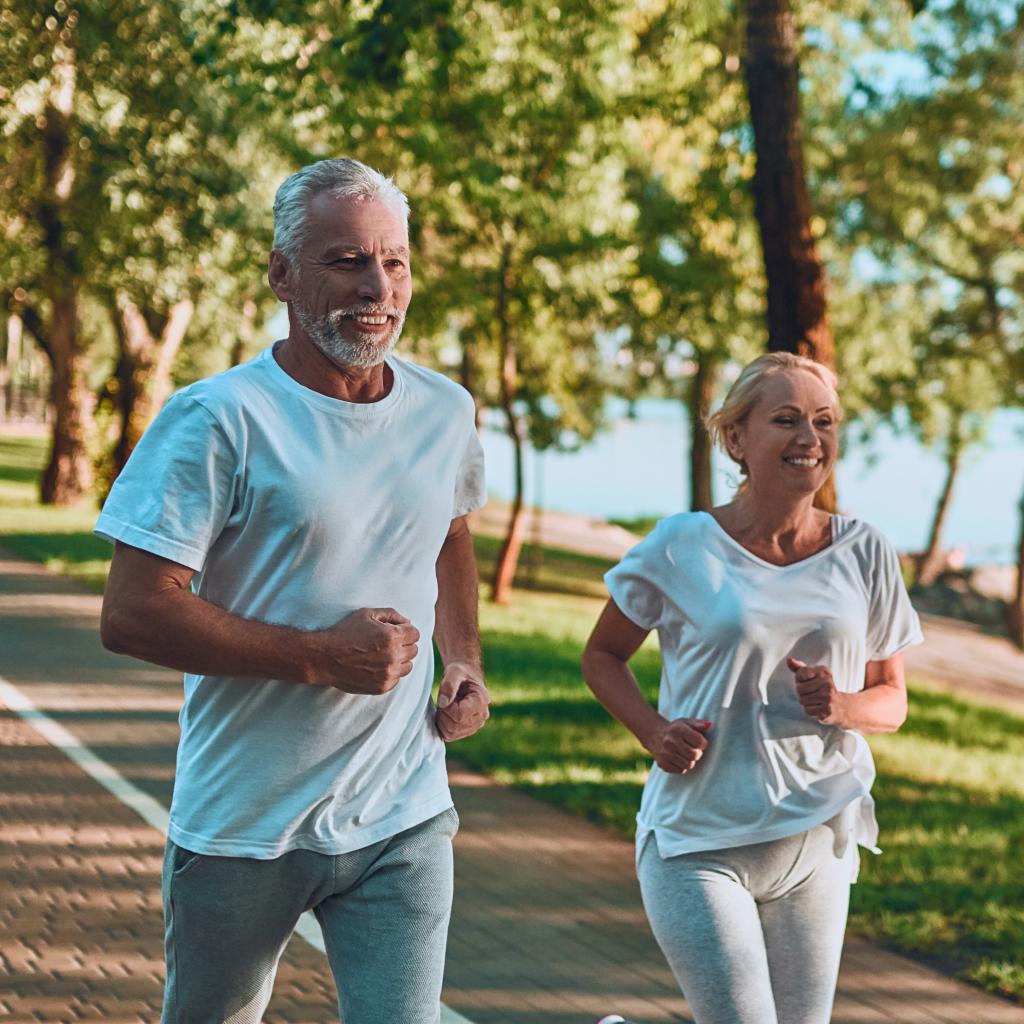  49% |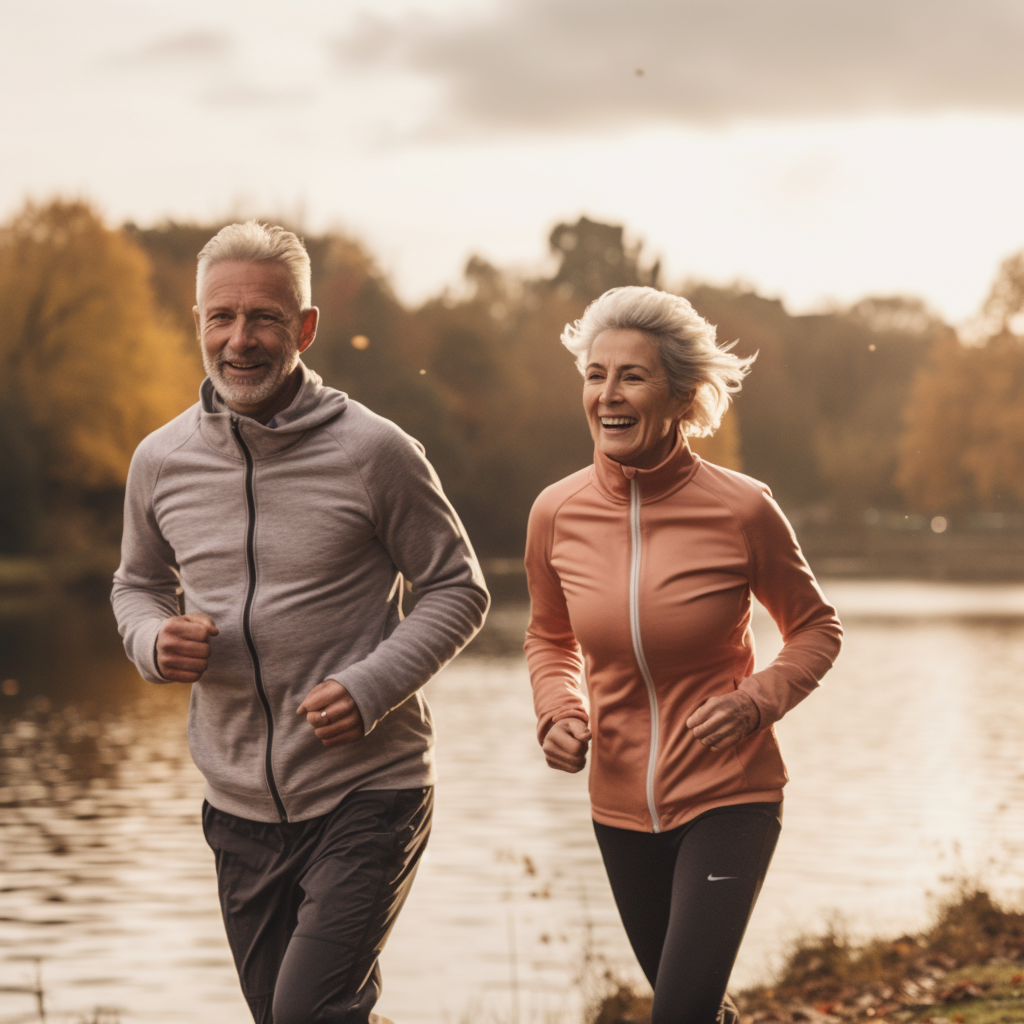  52% |
| Set 3: Toddler holding milk |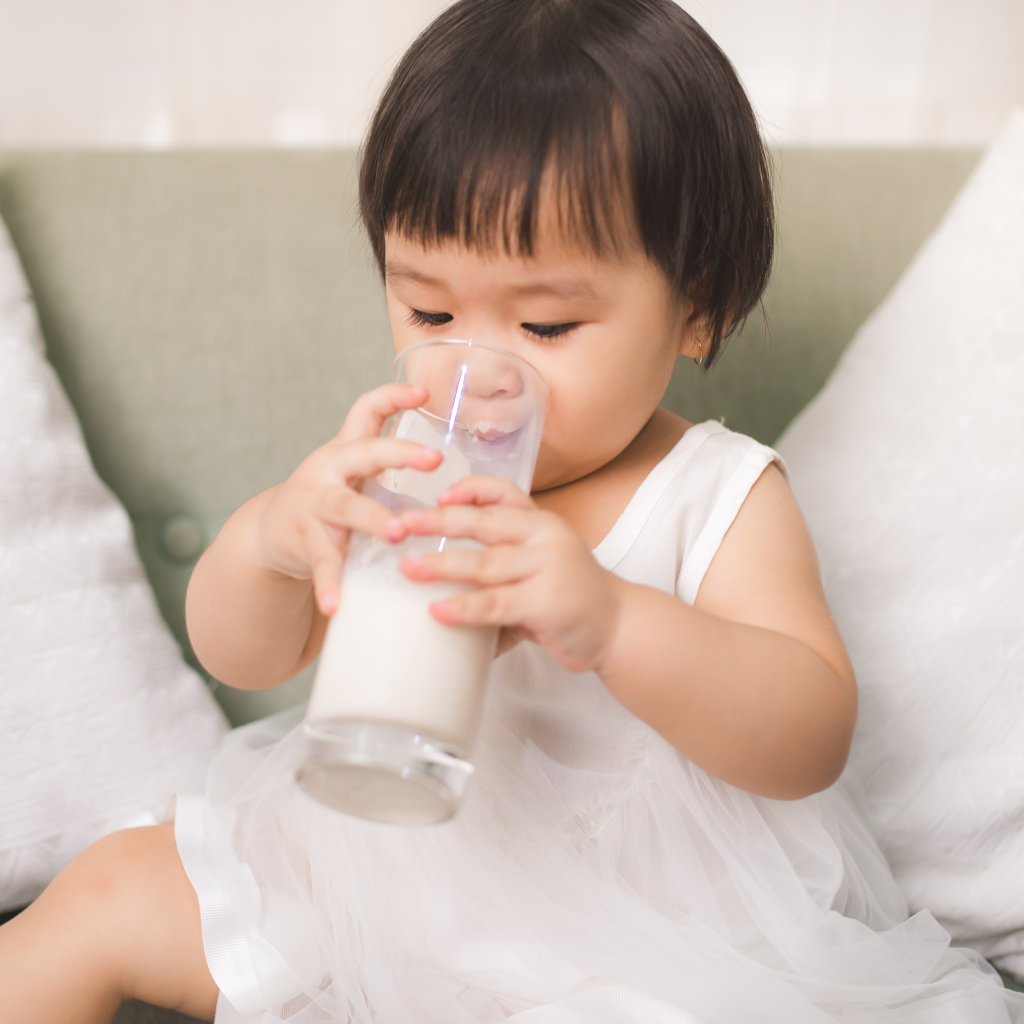  72% |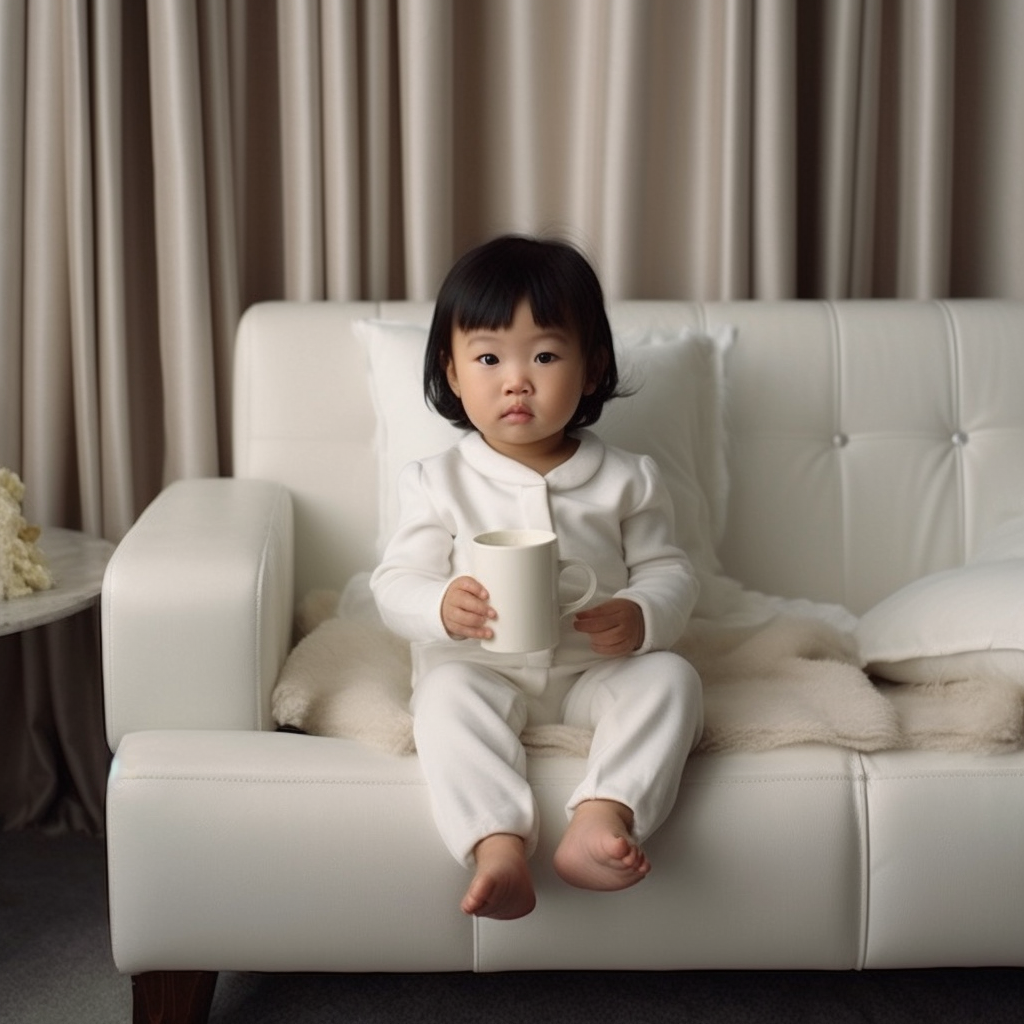  57% |
| Set 4: Female holding walkie-talkie |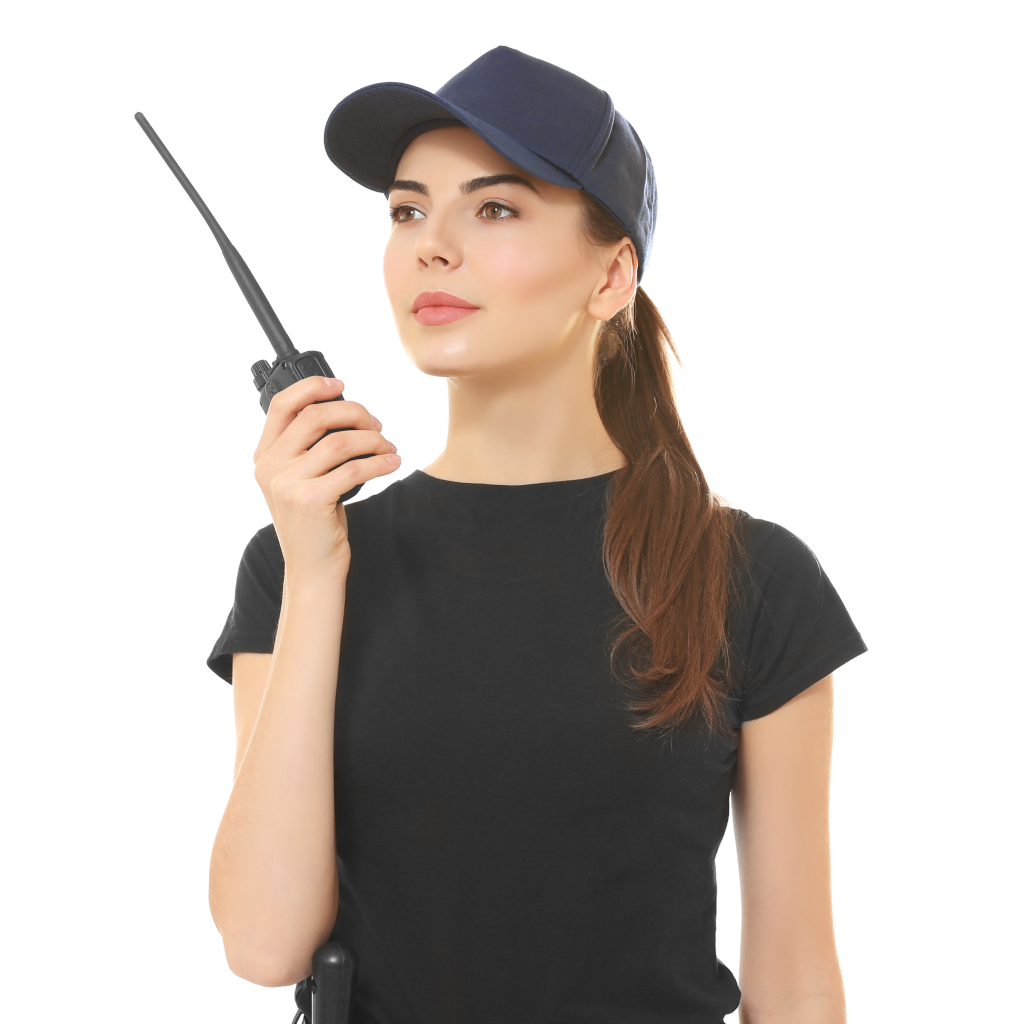  44% |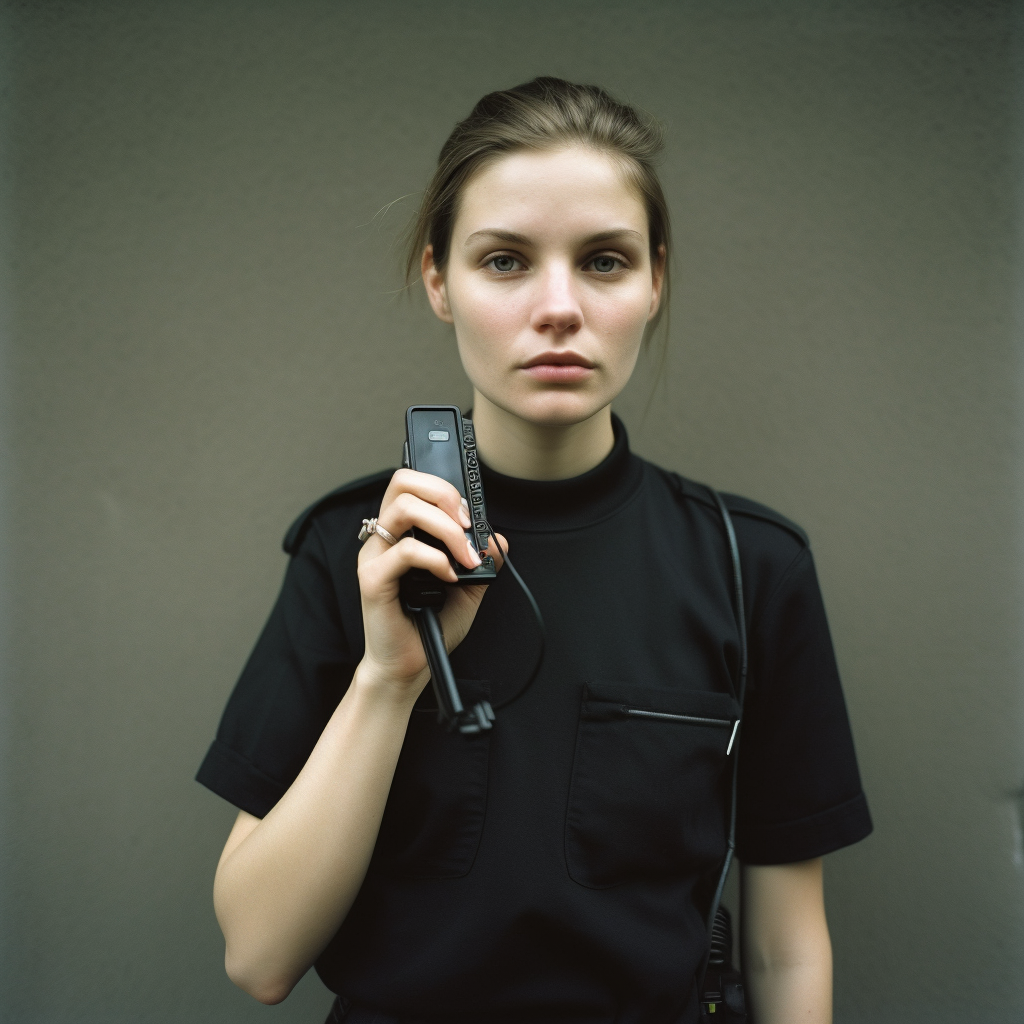  54% |
| Set 5: Group of friends having picnic |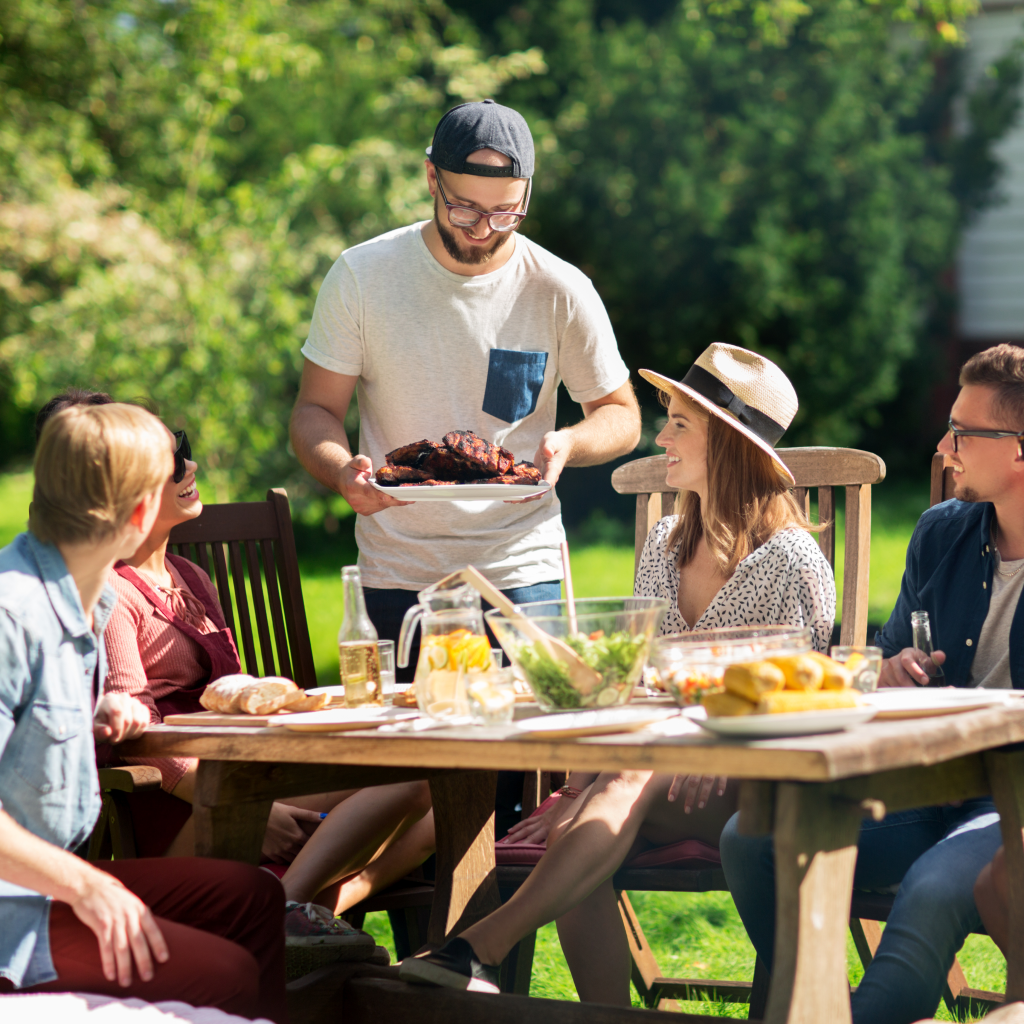  73% |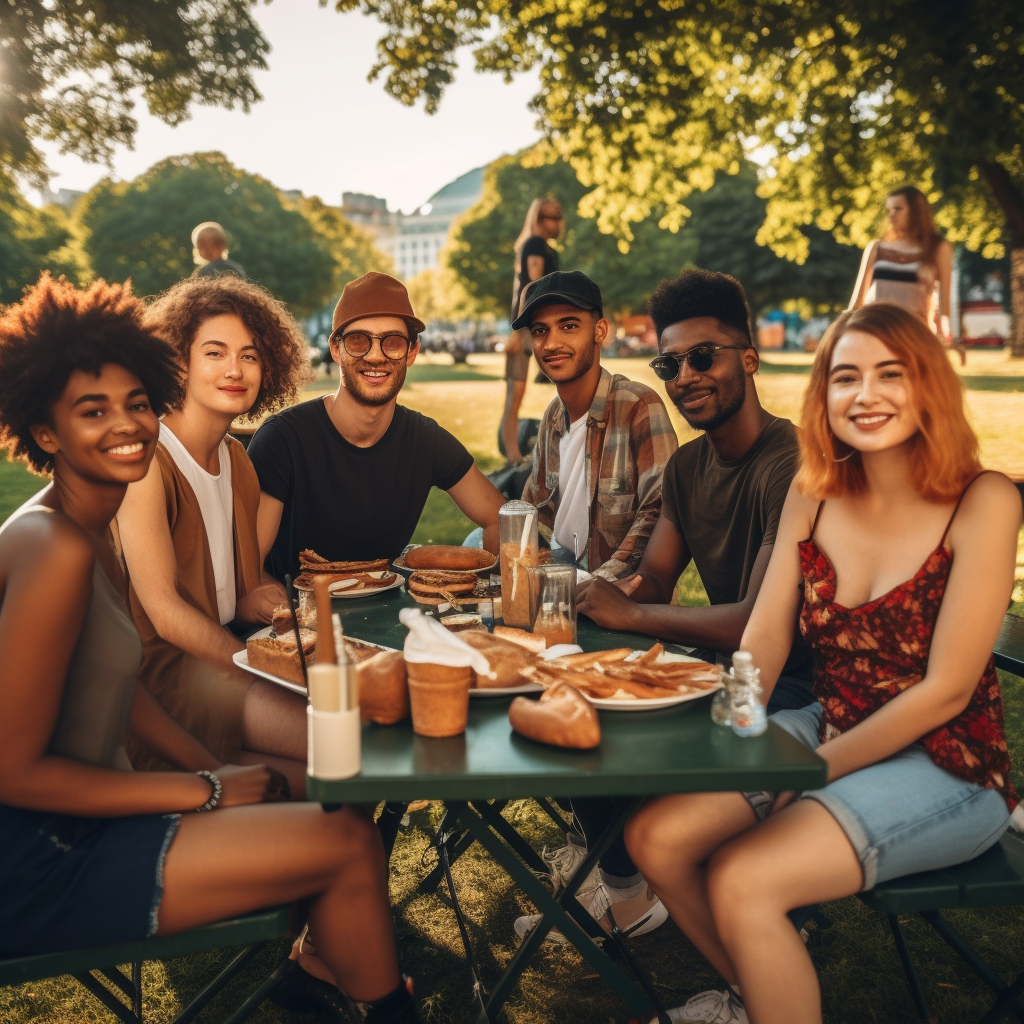  63% |
| Average | 57% | 56% |
Younger respondents tended to do better in identifying the real photographs such as Set 2 (Elder people jogging) and Set 3 (Toddler holding milk). Older respondents showed a greater accuracy for Set 4 - AI (female holding walkie-talkie), likely due to the inaccurate depiction of the walkie-talkie in which they were more familiar with.
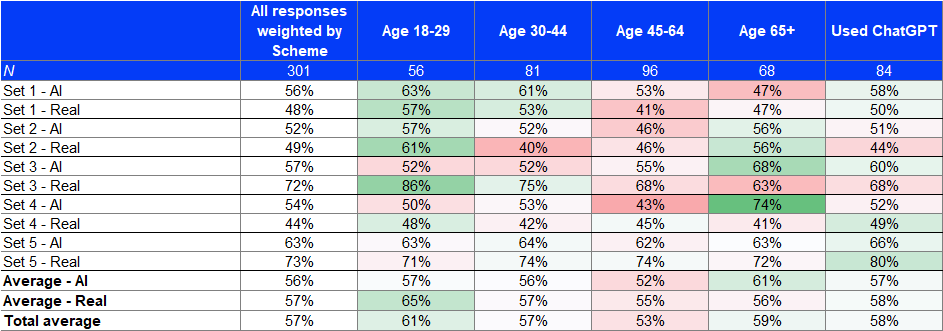
The colour coding represents the degree of deviation from the weighted all response, green = higher and red = lower.
Summary of open-ended responses
Do you have any concerns or reservations about using AI-generated content in marketing?
Respondents expressed that AI-generated content can offer convenience and be amusing, but there are also concerns over misuse and manipulation, plagiarism, job displacement, lack of innovation, privacy and security issues, and lack of human oversight and control.
Do you have any hopes or aspirations about using AI-generated content in marketing?
Respondents have varying levels of knowledge and experience with AI-generated content and its use in marketing, but have generally expressed a mix of hopes, aspirations and fears. Overall, respondents have expressed optimism towards the use of AI in marketing, citing factors such as efficiency, brand awareness, creativity, accessibility, accuracy and ethical considerations. There is also a general feeling of uncertainty and caution about the application of AI-generated content in marketing.
Key takeaways
- ~38% of USA consumers are aware of the usage of generative AI in marketing content. Many respondents believed that generative AI is suitable for advertising texts, product descriptions, and website content.
- Consumers express greater appreciation of human artwork and show apprehension towards AI-generated images.
- Consumers are not very good at identifying real vs. AI-generated images.
- Younger consumers and those who use ChatGPT have a greater tolerance for the usage of generative AI in marketing content. Younger consumers also perform better in identifying actual photos from AI-generated images.
- Consumers express their optimism regarding the efficiency and creativity of generative AI, but also have concerns about copyright, job loss, and potential for deception.




